Abstract
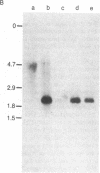
A search for uncharacterized genes of the S region of the murine H-2 major histocompatibility complex was undertaken; a series of cosmid clones previously aligned by overlap hybridizations were used as radiolabeled probes. Sequences hybridizing with liver poly(A)+ RNA were found within a cosmid covering a region 3' to the C4-Slp gene (the gene encoding the hemolytically inactive isoform of the fourth component of serum complement). Radiolabeled, short cDNA complementary to liver poly(A)+ RNA was used to establish the transcriptional polarity of the newly detected gene and to define fragments containing its 3' end. DNA sequence analyses and comparisons with porcine peptides established that the gene encodes the enzyme steroid 21-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.99.10), a cytochrome P-450 often referred to as P-450(C21), whose major site of expression is the adrenal gland. Two copies of the P-450(C21) gene, very similar yet distinguishable by restriction endonuclease analysis, were found individually associated with C4 and C4-Slp, genes that encode isoforms of mouse fourth component of complement. One of the P-450(C21) genes is coamplified with C4-Slp in H-2w7, a haplotype carrying a rare elongation of the S region. Comparisons with other members of the P-450 gene family show that the P-450(C21) genes encode peptides of extraordinary evolutionary conservation. The detection of a liver transcript of P-450(C21) raises the issue of the specific metabolic role of this enzyme in this organ and may have implications for the interpretation of human congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Bentley D. R., Porter R. R. A molecular map of the human major histocompatibility complex class III region linking complement genes C4, C2 and factor B. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):237–241. doi: 10.1038/307237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Porter R. R. Mapping of steroid 21-hydroxylase genes adjacent to complement component C4 genes in HLA, the major histocompatibility complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):521–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Woods D. E., Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R., Seidman J. G. Molecular map of the murine S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6947–6951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieter H. H., Muller-Eberhard U., Johnson E. F. Identification of rabbit microsomal cytochrome P-450 isozyme, form 1, as a hepatic progesterone 21-hydroxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):515–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91465-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman J. C., Jackson R., Desantola J. R., Shreffler D., Atkinson J. P. Development of a hemolytic assay for mouse C2 and determination of its genetic control. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):344–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniu M., Armes L. G., Tanaka M., Yasunobu K. T., Shastry B. S., Wagner G. C., Gunsalus I. C. The primary structure of the monoxygenase cytochrome P450CAM. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):889–894. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi K., Narayanan K. S., Adams H. R., Busch H. Utilization of the citric acid procedure and zonal ultracentrifugation for mass isolation of nuclear RNA from Walker 256 carcinosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1966 Jul;26(7):1582–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiwatashi A., Ichikawa Y. Purification and reconstitution of the steroid 21-hydroxylase system (cytochrome P-450-linked mixed function oxidase system) of bovine adrenocortical microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 23;664(1):33–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. O., Shiverick K. T. Cytochrome P-450-dependent oxidation of progesterone, testosterone, and ecdysone in the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Aug 15;233(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90595-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. The murine Ah locus. Comparison of the complete cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 cDNA nucleotide and amino acid sequences. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10705–10713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F., Klein D. H-2 haplotypes, genes, and antigens: second listing. I. Non-H-2 loci on chromosome 17. Immunogenetics. 1982;16(4):285–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00372302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Strauss M., Tosi M., Steinmetz M., Klein J., Meo T. Multiple duplications of complement C4 gene correlate with H-2-controlled testosterone-independent expression of its sex-limited isoform, C4-Slp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1746–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami Y., Sogawa K., Suwa Y., Muramatsu M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Gene structure of a phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3958–3962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Okada Y., Sogawa K., Hirose T., Inayama S., Omura T. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for mRNA of mitochondrial cytochrome P-450(SCC) of bovine adrenal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4647–4651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Negishi M. Multiple forms of cytochrome P-450 and the importance of molecular biology and evolution. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 15;31(14):2311–2317. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90523-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Dupont B., Pollack M. S., Levine L. S., New M. I. Complement C4 allotypes in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: further evidence for different allelic variants at the 21-hydroxylase locus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):312–322. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolucci E. S., Shreffler D. C. H-2-linked murine factor B phenotypes. Immunogenetics. 1983;17(1):67–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00364290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson E. B., Lamm L. U. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of Chromosome 6. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):47–70. doi: 10.1159/000132004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Gotoh O., Kawajiri K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Distinct organization of methylcholanthrene- and phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 genes in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Malissen M., Hood L., Orn A., Maki R. A., Dastoornikoo G. R., Stephan D., Gibb E., Romaniuk R. Tracts of high or low sequence divergence in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2995–3003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Lévi-Strauss M., Duponchel C., Meo T. Sequence heterogeneity of murine complementary DNA clones related to the C4 and C4-Slp isoforms of the fourth complement component. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):389–394. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Chaplin D. D., Weis J. H., Dupont B., New M. I., Seidman J. G. Two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes are located in the murine S region. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):465–467. doi: 10.1038/312465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a bovine adrenal cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1986–1990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabusaki Y., Shimizu M., Murakami H., Nakamura K., Oeda K., Ohkawa H. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA coding for 3-methylcholanthrene-induced rat liver cytochrome P-450MC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2929–2938. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan P. M., Nakajin S., Haniu M., Shinoda M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Steroid 21-hydroxylase (cytochrome P-450) from porcine adrenocortical microsomes: microsequence analysis of cysteine-containing peptides. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):143–149. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]