Abstract
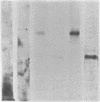
We report the amino acid composition, the NH2-terminal sequence, and the tryptic map by HPLC for murine L-cell colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1). CSF-1 purified by affinity chromatography was S-carboxymethylated under denaturing conditions and subjected to sequence microanalysis. CSF-1 contains four or five cysteine residues per subunit and approximately 30-40% carbohydrate by weight. Three contiguous cysteine residues were located in the NH2-terminal sequence. An additional two cysteine residues were located on the tryptic map. Previous studies as well as immunoblotting studies reported here suggest that sulfhydryl bridging plays a major role in maintaining the conformation of the protein. Carbohydrate was located on two tryptic fragments. The findings of a single NH2-terminal sequence in high yield and a relatively simple tryptic map (15 major peptides) suggest that CSF-1 contains two identical subunits. The NH2-terminal sequence of CSF-1 has only limited homology to insulin or insulin-like hormones but no homology with granulocyte/macrophage-CSF or interleukin 3.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boegel F., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Evaluation of radioimmunoassay and in vitro colony assay techniques for determination of colony-stimulating factor and inhibitory activity in murine serum and tissue. Blood. 1981 Dec;58(6):1141–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A. Nerve growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:191–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Metcalf D. The nature and action of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factors. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):947–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S. K., Stanley E. R. Structure-function studies of a colony stimulating factor (CSF-1). J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13679–13684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Schwartz R. M., Chen H. R., Hunt L. T., Barker W. C., Orcutt B. C. Data bank. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):8–8. doi: 10.1038/290008a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. C., Hapel A. J., Ymer S., Cohen D. R., Johnson R. M., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA for murine interleukin-3. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):233–237. doi: 10.1038/307233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Gough J., Metcalf D., Kelso A., Grail D., Nicola N. A., Burgess A. W., Dunn A. R. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a murine haematopoietic growth regulator, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):763–767. doi: 10.1038/309763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawke D., Yuan P. M., Shively J. E. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. II. Separation of amino acid phenylthiohydantoin derivatives by high-performance liquid chromatography on octadecylsilane supports. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):302–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Demple B., Chaires J. B. Analysis of the Escherichia coli ribosome-ribosomal subunit equilibrium using pressure-induced dissociation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck R. K., Metcalf D. Preparation and neutralization characteristics of an anti-CSF antibody. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Oct;86(2 Pt 1):247–252. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040860208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck R. K., Nagabhushanam N. G. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor. I. Response to acute granulocytopenia. Blood. 1971 Nov;38(5):559–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck R. K., Pigoli G., Waheed A., Boegel F. The role of colony-stimulating factor in granulopoiesis. J Supramol Struct. 1980;14(4):423–439. doi: 10.1002/jss.400140403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E. Sequence determinations of proteins and peptides at the nanomole and subnanomole level with a modified spinning cup sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):31–48. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Heard P. M. Factors regulating macrophage production and growth. Purification and some properties of the colony stimulating factor from medium conditioned by mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4305–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Sasagawa T., Resing K., Walsh K. A. A simple and rapid purification of commercial trypsin and chymotrypsin by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):408–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90465-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Purification and properties of L cell-derived colony-stimulating factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jul;94(1):180–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Purification of colony-stimulating factor by affinity chromatography. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):238–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Lee F., Rennick D., Hall C., Arai N., Mosmann T., Nabel G., Cantor H., Arai K. Isolation and characterization of a mouse cDNA clone that expresses mast-cell growth-factor activity in monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan P. M., Pande H., Clark B. R., Shively J. E. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. I. Preparation of samples by reverse-phase liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90350-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]