Abstract
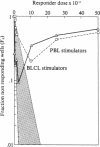
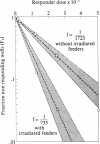
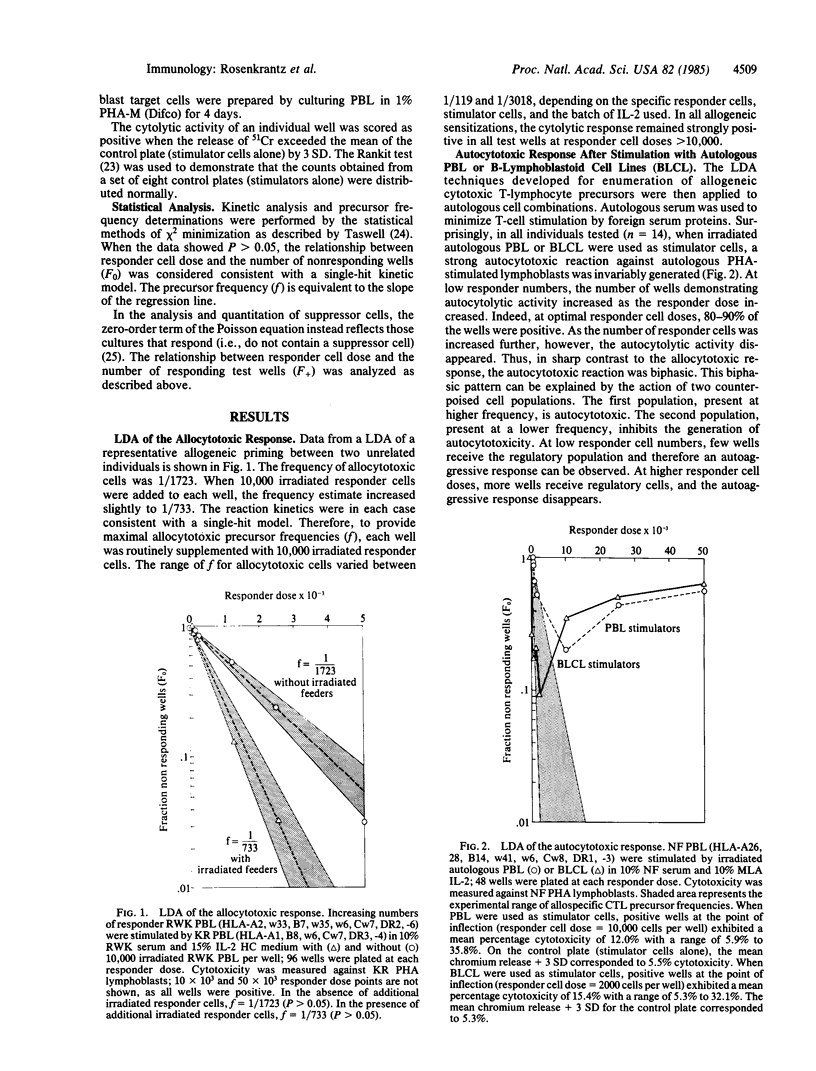
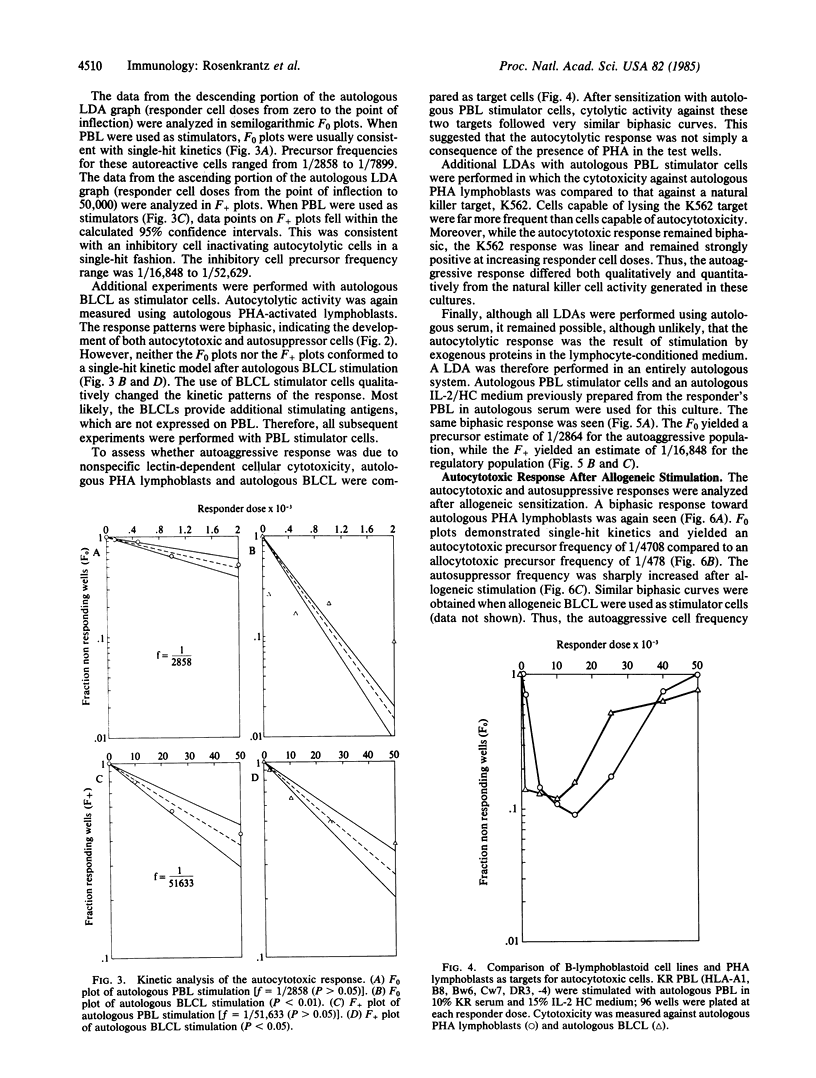
Using limiting dilution analysis, we have detected both the generation and suppression of autocytotoxic cells following autologous or allogeneic stimulation in vitro. Assay conditions were established in which the cytotoxic response toward an allogeneic sensitizing cell was consistent with a traditional single-hit kinetic model. Under identical conditions, cytolytic activity toward autologous phytohemaglutinin-activated lymphoblasts exhibited a distinct biphasic response. At low responder cell doses, a clear autocytotoxic response was observed. However, at higher responder cell numbers, this autocytotoxic reaction disappeared. This biphasic pattern of autocytotoxicity developed after stimulation with allogeneic or autologous peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes (PBL) or Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cells. This pattern of response is consistent with the counterpoised actions of two distinct cell populations, an autoaggressive population and a lower frequency autosuppressor population. Autocytotoxicity was not the result of mitogenic or xenogeneic antigenic stimulation, as it was observed after stimulation with autologous PBL in autologous serum and an autologous interleukin 2 preparation. Thus, cells capable of autocytotoxicity are present in peripheral blood but at a lower frequency than allocytotoxic T lymphocytes. Furthermore, autoaggressive cells are down-regulated by an autologous suppressor population. These findings suggest that immunologic self-tolerance is, at least in part, an actively maintained condition. Disturbances in this autoregulatory network may have relevance to the pathogenesis of some autoimmune diseases and graft-versus-host disease.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Denman A. M., Barnes R. D. Cooperating and controlling functions of thymus-derived lymphocytes in relation to autoimmunity. Lancet. 1971 Jul 17;2(7716):135–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman A., Katz D. H. Existence of T cells manifesting self-reactivity indistinguishable from alloreactivity. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1536–1543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corley R. B., Kindred B., Lefkovits I. Positive and negative allogeneic effects mediated by MLR-primed lymphocytes: quantitation by limiting dilution analysis. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1082–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Falk I., Melchers I., Simon M. M. Quantitative studies on T cell diversity. I. Determination of the precursor frequencies for two types of streptococcus A-specific helper cells in nonimmune, polyclonally activated splenic T cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):477–492. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOOD R. A., DALMASSO A. P., MARTINEZ C., ARCHER O. K., PIERCE J. C., PAPERMASTER B. W. The role of the thymus in development of immunologic capacity in rabbits and mice. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:773–796. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazier A., Tutschka P. J., Farmer E. R., Santos G. W. Graft-versus-host disease in cyclosporin A-treated rats after syngeneic and autologous bone marrow reconstitution. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):1–8. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Malmberg S. Response of human newborn lymphocytes to alloantigen: lack of evidence for suppression induction. Pediatr Res. 1984 May;18(5):414–419. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198405000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M. L., Goldstein A. L., Battisto J. R. Isogeneic lymphocyte interaction: recognition of self antigens by cells of the neonatal thymus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):613–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. THE NATURAL-SELECTION THEORY OF ANTIBODY FORMATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Nov 15;41(11):849–857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.11.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak R. W., Moody C. E., Staiano-Coico L., Weksler M. E. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. XII. Quantitative and qualitative differences between human autologous and allogeneic reactive T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1723–1727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattime E. C., Gillis S., Pecoraro G., Stutman O. Ia-dependent interleukin 2 production in syngeneic cellular interactions. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):480–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. F. Immunological function of the thymus. Lancet. 1961 Sep 30;2(7205):748–749. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90693-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Clonal analysis of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes: T4+ and T8+ effector T cells recognize products of different major histocompatibility complex regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4395–4399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelson E. M., Beatty P. G., Storb R., Hansen J. A. Immune responses in an untransfused patient with aplastic anemia: analysis of cytolytic and proliferative T cell clones. Hum Immunol. 1984 Jul;10(3):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Kaplan H. S. Generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes in the autologous mixed lymphocyte culture. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2165–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opelz G., Kiuchi M., Takasugi M., Terasaki P. I. Autologous stimulation of human lymphocyte subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1327–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman R., Rosen F. S. Identification of a subpopulation of lymphocytes in human peripheral blood cytotoxic to autologous fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1520–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin H., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Ruscetti F. W., Neubauer R. H., Brown R. L., Kawakami T. G. Spontaneous release of a factor with properties of T cell growth factor from a continuous line of primate tumor T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann J., Miller R. G. Generation of autoreactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes under limiting dilution conditions. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2128–2134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schendel D. J., Wank R., Dupont B. Standardization of the human in vitro cell-mediated lympholysis technique. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Feb;13(2):112–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb01146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonari K. Cytotoxic T cells generated in the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. I. Primary autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1111–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. P., Storb R., Thomas E. D., Su P. J., Mickelson E. M., Weiden P. L. Autoimmune and alloimmune phenomena in patients with aplastic anemia: cytotoxicity against autologous lymphocytes and lymphocytes from HLA identical siblings. Blood. 1980 Oct;56(4):683–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):701–702. doi: 10.1038/248701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]