Abstract
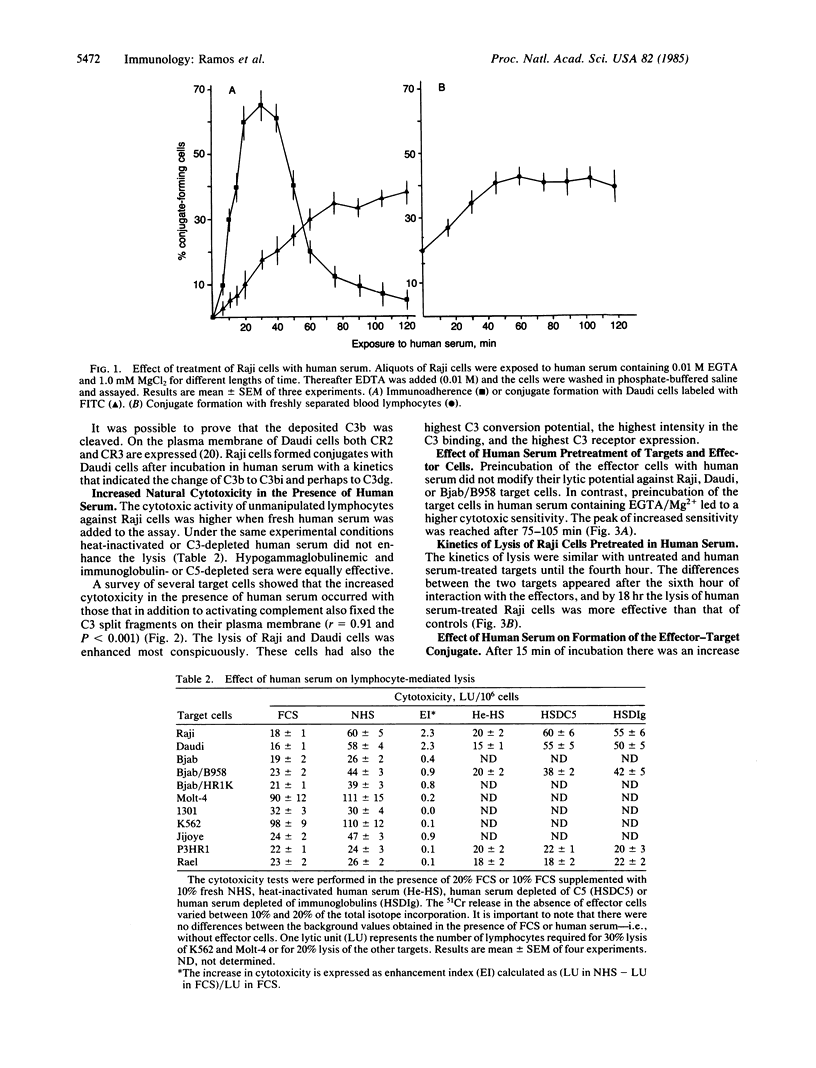
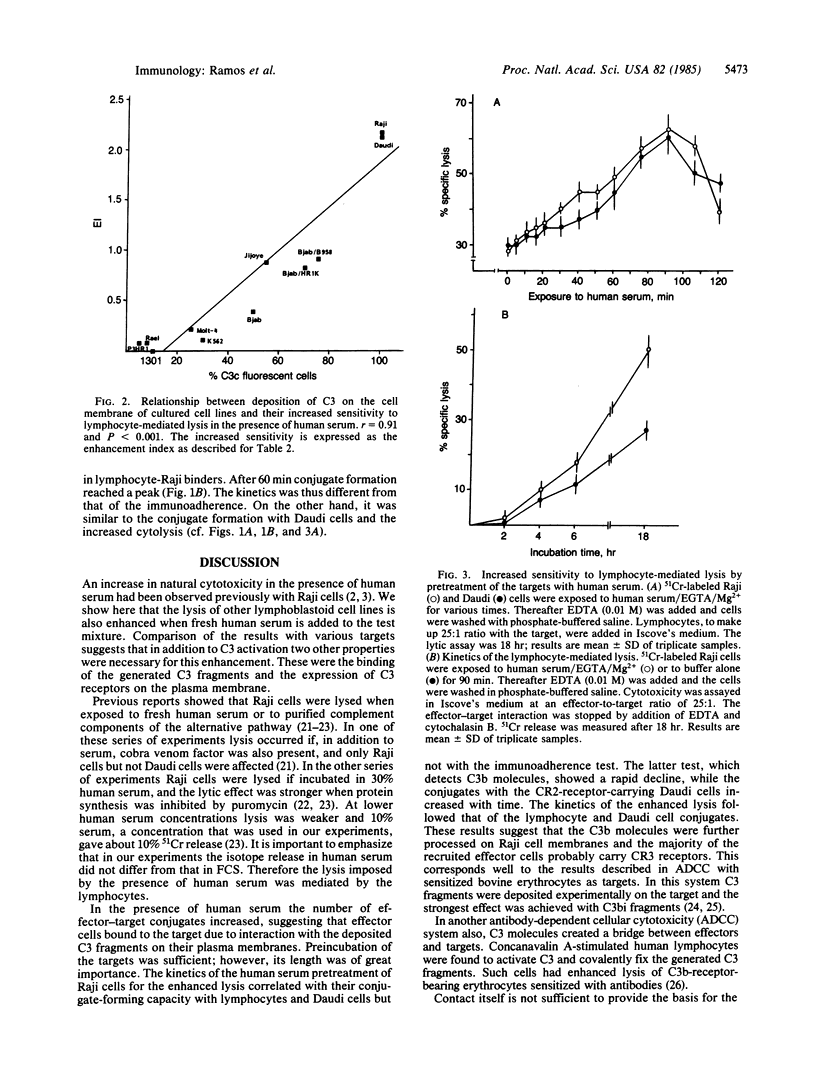
Lymphocyte-mediated lysis of cells of the Raji, Daudi, Jijoye, and Bjab lines was elevated when fresh human serum was added to the assay. A higher proportion of effector-target conjugates was observed in the presence of human serum. In similar experiments lysis of 1301, Rael, and P3HR-1 cells was unaltered. All cell lines activated the alternative pathway of complement but they varied in the expression of receptors for complement component 3 (C3) and in the ability to fix the C3 cleavage products on their membrane. The enhancement of lysis in the presence of human serum occurred only with those cells that bound C3. This characteristic was correlated to the expression of C3 receptors. Analysis of the nature of the deposited C3 was performed with Raji cells. Raji cells exposed to human serum bound C3b as indicated by the immunoadherence test. The C3b was further processed to C3bi, because the immunoadherence declined with time and conjugate formation increased with Daudi cells, which carry the C3 receptors CR2 and CR3. This suggests that in the lytic assay lymphocytes with C3bi receptors are recruited in the presence of human serum. We assume that the bridge of C3 molecules between targets and effectors increases the avidity of their interaction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. J., Lint T. F., Mortensen R. F., Gewurz H. C567-initiated cytolysis of lymphoid cells: description of the phenomenon and studies on its control by C567 inhibitors. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):198–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzko D. B., Lachmann P. J., McConnell I. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from patients with Burkitt's lymphoma and infectious mononucleosis. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 1;22(1):98–109. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Sim R. B. Substances that can trigger activation of the alternative pathway of complement have anti-melanoma activity in mice. Int J Cancer. 1984 May 15;33(5):683–687. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdei A., Benczur M., Fábry Z., Dierich M. P., Gergely J. C3 cleaved by membrane proteases binds to C3b acceptors expressed on concanavalin A-stimulated human lymphocytes and enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Aug;20(2):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. The human C3b receptor. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1983;6(2-3):159–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00205871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Wong W. W. Complement ligand-receptor interactions that mediate biological responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:243–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R., Barel M., Krikorian L., Charriaut C. Analysis of gp 140, a C3b-binding membrane component present on Raji cells: a comparison with factor H. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jun;14(6):542–548. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Nadler L., Nussenzweig V. Identification of the membrane receptor for the complement fragment C3d by means of a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1021–1033. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Hughes-Jones N. C. Initiation of complement activation. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):143–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01893018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell I., Klein G., Lint T. F., Lachmann P. J. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by human B cell lymphoma lines is associated with Epstein-Barr virus transformation of the cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jul;8(7):453–458. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka K. Complement and tumor immunology. Adv Cancer Res. 1971;14:231–293. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocera A., Montesoro E., Balbo P., Ferrarini M., Leprini A., Zicca A., Grossi C. E. Complement receptor distinguishes between two subsets of large granular lymphocytes with different natural killer activity and cytochemical and ultrastructural features. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Oct;18(4):345–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb01806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Baba T. Rosette formation of human erythrocytes on cultured cells of tumour origin and activation of complement by cell membrane. Nature. 1974 Apr 5;248(448):521–522. doi: 10.1038/248521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Nishioka K. Complement receptors on cell membranes. I. Evidence for two complement receptors. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1444–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C3b deposition during activation of the alternative complement pathway and the effect of deposition on the activating surface. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1930–1935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Perlmann P., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Interaction of target cell-bound C3bi and C3d with human lymphocyte receptors. Enhancement of antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1592–1603. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos O. F., Masucci M. G., Klein E. Activation of cytotoxic activity of human blood lymphocytes by tumor-promoting compounds. Cancer Res. 1984 May;44(5):1857–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. D. Analysis of the different types of leukocyte membrane complement receptors and their interaction with the complement system. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(3-4):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Pangburn M. K., Medicus R. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Raji cell injury and subsequent lysis by the purified cytolytic alternative pathway of human complement. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Mar;15(3):384–396. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Bokisch V. A., Dixon F. J. Receptor for soluble C3 and C3b on human lymphoblastoid (RAJI) cells. Properties and biologocal significance. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):696–711. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Perrin L. H. Binding of components of the properdin system to cultured human lymphoblastoid cells and B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Feb 1;143(2):271–289. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Rao P. E., Van Voorhis W. C., Craigmyle L. S., Iida K., Talle M. A., Westberg E. F., Goldstein G., Silverstein S. C. Identification of the C3bi receptor of human monocytes and macrophages by using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wåhlin B., Perlmann H., Perlmann P., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C3 receptors on human lymphocyte subsets and recruitment of ADCC effector cells by C3 fragments. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2831–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yefenof E., Klein E., Yron I. Contribution of activated C3 to lymphocyte-mediated target lysis: complement-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Mol Immunol. 1984 Dec;21(12):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yefenof E., Klein G., Kvarnung K. Relationships between complement activation, complement binding, and EBV absorption by human hematopoietic cell lines. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jun 15;31(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yefenof E., Yron I., Klein E. Complement-dependent cellular cytotoxicity due to alternative pathway C3 activation by the target cell membrane. Cell Immunol. 1984 Sep;87(2):698–702. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


