Abstract
During mitosis, global translation is suppressed, while synthesis of proteins with vital mitotic roles must go on. Prior evidence suggests that the mitotic translation shift involves control of initiation. Yet, no signals specifically targeting translation initiation factors during mitosis have been identified. We used phosphoproteomics to investigate the central translation initiation scaffold and “ribosome adaptor,” eukaryotic initiation factor 4G1 (eIF4G1) in interphase or nocodazole-arrested mitotic cells. This approach and kinase inhibition assays, in vitro phosphorylation with recombinant kinase, and kinase depletion-reconstitution experiments revealed that Ser1232 in eIF4G1 is phosphorylated by cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1):cyclin B during mitosis. Ser1232 is located in an unstructured region of the C-terminal portion of eIF4G1 that coordinates assembly of the eIF4G/-4A/-4B helicase complex and binding of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal-integrating kinase, Mnk. Intense phosphorylation of Ser1232 in mitosis strongly enhanced the interactions of eIF4A with HEAT domain 2 of eIF4G and decreased association of eIF4G/-4A with RNA. Our findings implicate phosphorylation of eIF4G1(Ser1232) by Cdk1:cyclin B and its inhibitory effects on eIF4A helicase activity in the mitotic translation initiation shift.
INTRODUCTION
In metazoans, canonical translation initiation is mediated by eukaryotic initiation factor 4F (eIF4F), a heterotrimeric complex consisting of eIF4E/-4G/-4A, which forms at the 5′ 7-methylguanidine (m7G) cap of mRNAs. The cap-binding protein eIF4E engages the central scaffold eIF4G, which forms a helicase complex with eIF4A and its cofactor eIF4B, required for unwinding and scanning of complex, structured 5′ untranslated regions (UTRs) (1). eIF4G recruits ribosomes to mRNAs via eIF3, a 13-subunit complex associated with the 40S ribosomal subunit. In addition, eIF4G establishes contact with the 3′ poly(A) tail [via the poly(A) binding protein (PABP)]. eIF4G and its many ribonucleoprotein (RNP) partners engage in dynamic interactions during translation initiation that are highly responsive to adaptive changes of the intracellular milieu. Primary effectors of this are phosphorylation sites clustered in two flexible regions of eIF4G: adjacent to the PABP binding site and in the “interdomain linker” (IDL) separating the structured huntingtin, elongation factor 3, A subunit of protein phosphatase 2A, and target of rapamycin (HEAT) (2) domains 1 and 2 (Fig. 1A). Phorbol ester activation of Pkc/Raf/Erk signaling results in phosphorylation of IDL residues Ser1186 (by Pkc-α [3]) and Ser1232 (by Erk1/2 [4]) in eIF4G. These events control interactions of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal-integrating kinase 1 (Mnk1) (3) and the eIF4A/-4B helicase complex (4) with the C-terminal HEAT2/-3 of eIF4G. Mitogenic stimuli, through posttranslational changes in the eIF4G IDL, may rearrange the mRNP to promote unwinding of complex 5′ UTRs (4). Its central position as a scaffold and translation effector at the crossroads of major signal transduction pathways make eIF4G a prime candidate for an involvement in complex posttranscriptional gene regulatory programs, e.g., during the cell cycle.
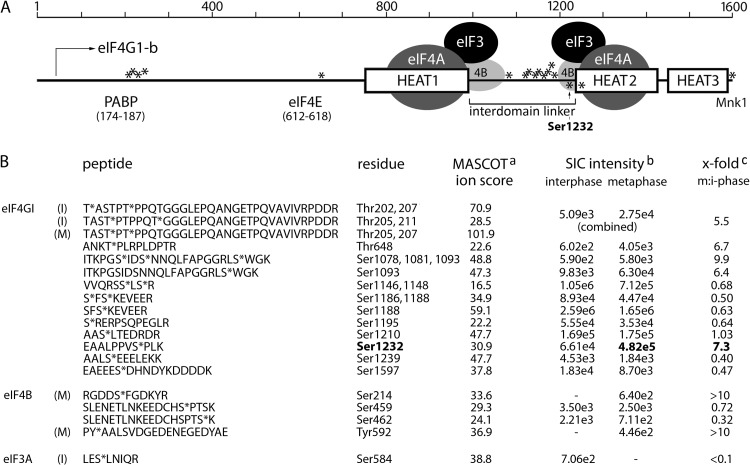
FIG 1.
eIF4G phosphorylation in interphase and mitosis. (A) Schematic view of eIF4G HEAT1-3 domains, the IDL, and areas of interaction with binding partners PABP, eIF4E, and Mnk. Previously proposed interactions within HEAT1- or HEAT2/-4A/-4B translation initiation helicase complexes (4), phosphosites identified in our screen (*), and Ser1232 are indicated. (B) Amino acid sequence of peptides identified by LC-MS/MS after TiO2 enrichment of phosphopeptides from trypsin-digested Flag-eIF4G. Phosphorylated residues are indicated (*). aMASCOT ion score: matches of MS/MS fragment ion masses of the investigated peptides are always based on probability (P) (23). This score is presented as −10 log10 (P), where P is the absolute probability of the observed match being a random event (scores of >20 are acceptable). bSIC, selected ion chromatogram of 2+ precursor ion (10-ppm window). The intensity values were calculated at peak apex. cThe fold changes in SIC intensities between metaphase and interphase are indicated.
Translation control is required for proper transition through the cell cycle. It is robust during interphase but declines drastically in mitosis (5, 6), possibly due to a block of an initiation event(s) (7). The mitotic translation shift likely occurs in response to the surge in phosphorylation associated with mitotic entry. Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1), after association with cyclin B, is the primary regulatory node that directs mitotic progression by phosphorylation of a large number of substrates. Various mechanisms were proposed to account for the mitotic translation shift, for instance, 14-3-3σ binding to eIF4B (8) or mitotic phosphorylation of eEF1D (decreasing tRNA delivery to elongating ribosomes [9]). It was posited that dephosphorylation of the eIF4E-binding proteins (4E-BPs) disrupts eIF4F formation and diminishes protein synthesis in mitosis (10). mTOR (mTORC1; in a complex with raptor [11, 12]) controls cap-dependent translation initiation through its downstream substrates, the 4E-BPs. The 4E-BPs, competitive inhibitors of eIF4G-4E binding when in a hypophosphorylated state (13), counter eIF4F formation and prevent 40S subunit recruitment to the m7G cap. Recent studies, however, show that mTORC1 is active in mitosis (14–16) and that its substrates involved in translation control, e.g., 4E-BPs (16) and ribosomal protein S6 kinase (17), remain phosphorylated in mitosis.
Mitosis implies not only repressed cap-dependent protein synthesis but also enhanced synthesis of selected proteins involved in the mitotic process. The translation of such proteins, e.g., Cdk11/p58 (essential for centrosome maturation and bipolar spindle formation [18]) may be specifically induced in mitosis (19), e.g., by alternative, cap-independent initiation bypassing the mitotic initiation block at the cap (20). Despite many studies of the phenomenon, the molecular mechanisms responsible for the mitotic translation shift remain enigmatic. In this work, we used quantitative phosphoproteomic, kinase inhibitor, coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP), and kinase depletion/in vitro phosphorylation approaches to unravel functional changes to eIF4G occurring during mitosis. Our work revealed that Cdk1:cyclin B1 phosphorylates eIF4G(Ser1232) in mitosis and rearranges protein interactions within the eIF4G C terminus in a manner consistent with inhibition of 5′ UTR scanning and unwinding.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell lines, cell synchronization, kinase inhibitors, and translation inhibitors.
HEK293 and HeLa cells were grown in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM), 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and nonessential amino acids (Invitrogen). Doxycycline (DOX)-inducible HEK293 cells expressing myc-eIF4G1(41-1600)-Flag and myc-eIF4G1(682-1600)-Flag were described previously (21). Cell synchronization for fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) and proteomic analyses was achieved by double thymidine block (Th block) and/or nocodazole (NOC) treatment. Briefly, cells were synchronized at the G1/S boundary by incubation with 5 mM Th (12 h), followed by 12 h of incubation in growth medium prior to the addition of 5 mM Th (12 h). Then, cells were released from Th block in growth medium containing 100 nM NOC (12 to 14 h). To release cells from NOC-induced mitotic arrest, the cells were washed and 10% FBS-containing medium was added for various intervals. To isolate mitotic cells by shake-off, HeLa cells were grown to ∼60 to 80% confluence, mitotic cells were recovered by tapping on the flask 30 to 40 times, and adherent cells were detached with trypsin. For other experiments, HEK293 cells were synchronized with 4 mM Th (9 h) followed by 200 nM NOC (16 h) or by release into 10% FBS-containing medium followed by 2 μM NOC (1 to 3 h). Inhibitors of MEK1 (UO126; Cell Signaling), Cdk1 (aminopurvalanol A; EMD), or tyrosine kinases (PD166285), the PKA activator forskolin, NOC, puromycin.2HCl (PMY), anisomycin (AMY) (all Tocris) and thymidine (EMD) were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and used at the concentrations shown below.
LC-MS/MS.
Proteomic analyses were carried out at the Duke University Proteomics Core Facility. Samples delivered in 50 mM NH4HCO3, pH 8.0, were supplemented with 0.1% Rapigest SF surfactant (Waters Corp.) and reduced with 5 mM dithiothreitol (DTT) (30 min) at 70°C, and free sulfhydryls were alkylated with 10 mM iodoacetamide (45 min). For proteolytic digestion, 500 ng sequencing-grade trypsin (Promega) was added to the resin at 37°C (18 h). Peptides were subjected to phosphopeptide enrichment using a 200-μl TiO2 tip (Protea Bio), eluted in 50 μl 20% acetonitrile and 5% aqueous ammonia, pH 10.5, and acidified to pH 2.5 with formic acid prior to drying. The samples were resuspended in 10 μl 2% acetonitrile, 0.1% formic acid, and 10 mM citric acid and subjected to chromatographic separation on a Waters NanoAquity ultraperformance liquid chromatograph (UPLC) equipped with a 1.7-μm BEH130 C18 75-μm (internal diameter [ID] by 250-mm reversed-phase column. The analytical column was connected to a fused silica PicoTip emitter (New Objective) and coupled to an LTQ-Orbitrap XL mass spectrometer through an electrospray interface. For qualitative identifications, raw liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) data files were processed in a Mascot distiller and submitted to independent Mascot database searches (Matrix Science) against Swiss-Prot (human taxonomy) containing forward and reverse entries of each protein. Search tolerances for LTQ-Orbitrap XL data were 10 ppm for precursor ions and 0.8 Da for product ions using trypsin specificity with up to two missed cleavages. All searched spectra were imported into Scaffold (Proteome Software), and protein confidence thresholds were set using a Bayesian statistical algorithm based on the Peptide/ProteinProphet algorithms, which yielded a peptide/protein false-discovery rate of 1.0% (22). Phosphorylation site localization was assessed by exporting peak lists to ascore.med.harvard.edu (23). Phosphopeptide abundances across metaphase and interphase samples were obtained by generating selected ion chromatograms (20-ppm window around most abundant charge state of precursor ions with seven-point Boxcar smoothing) from raw LC-MS data. MS responses at peak apex were used for quantitating abundance.
Cell lysis and FACS.
For synchronization assays, cells were trypsinized and washed twice in 4°C PBS. A portion of cells was removed for FACS analysis, and the rest was lysed by adding an equal cell-packed volume of lysis buffer (10 mM HEPES [pH 7.4], 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.5% NP-40, 2 mM DTT, protease inhibitors without EDTA [Roche], phosphatase inhibitors [Pierce]) on ice (10 min). In all other assays, cells were scraped in 4°C PBS, washed with PBS, and lysed as described above. For FACS, cells were washed twice with PBS and fixed with 90% methanol. Then cells were washed once with PBS, incubated with 0.25% Tween in PBS (10 min), washed with PBTB (PBS, 0.1% Tween, 0.5% bovine serum albumin [BSA]), and stained with anti-p-H3(Ser10) Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated antibody (1:200) in PBTB with 1% normal goat serum. After 1 h of incubation, cells were washed with PBTB prior to staining with 10 μl 7-amino-actinomycin D (AAD) (Becton, Dickinson) in 100 μl PBS containing 200 μg/ml RNase A (Qiagen). DNA histograms of histone H3-phosphorylation were acquired using a FACS CANTO flow cytometer (Becton, Dickinson) and analyzed using Flow Jo software (Tree Star).
In vitro kinase assay.
HEK293 cells arrested in mitosis by sequential double Th/NOC block were scraped in ice-cold PBS and Dounce homogenized in kinase buffer (20 mM HEPES-KOH [pH 7.4], 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT) with protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Cell lysates were aliquoted, snap-frozen, and stored at −80°C. Ten micrograms lysate was incubated with 2 μg recombinant purified glutathione S-transferase (GST)–eIF4G1(682-1600) (24) or GST-Rb (amino acids [aa] 773 to 928; Sigma) in the presence of 250 μM ATP with or without Cdk1 inhibitor at 30°C. Reactions were stopped with 4°C wash buffer, and GST-tagged proteins were isolated using glutathione-Sepharose as described previously (24). In vitro phosphorylation with recombinant (His-tagged) Cdk1:(GST-tagged) cyclin B1 (Millipore) was carried out by following the manufacturer's protocol.
IP, pulldown, and immunoblotting.
Immunoprecipitation (IP), GST pulldown, and immunoblotting were performed as described previously (3, 21). Cyclin B1-depletion of mitotic HEK293 cell lysates was performed with protein G-Sepharose (GE Healthcare) coupled with anti-cyclin B1 antibody (or mock depletion with rabbit IgG). Cdk1 was depleted with p13sucl-Sepharose (Millipore); protein G-Sepharose was used for mock depletion. Antibodies against eIF4G1, -4A, -4B, Mnk1, DDX3X, PDCD4, histone H3, Rb, Plk1, rpS6, p-eIF4G1(Ser1148), p-H3(Ser10), p-H3(Ser10)-Alexa Fluor 647, Erk1/2, p-Erk1/2(Thr202/204), p-Rb(Ser807/811), GST, Cdk1, rabbit IgG isotype control (Cell Signaling Technologies), c-myc, PABP (Sigma), p-eIF4G1(Ser1232), p-Plk1(Thr210), eIF1AX (Novus Biologicals), cyclin B1, puromycin (Millipore), and DRBP76 (BD Biosciences) were used.
RNA binding assay.
Lysates (10 mg total protein) from HEK293 cell lines expressing eIF4G1(682-1600) fragments synchronized with Th block (16 h, 4 mM) or NOC (16 h, 200 nM) were preincubated with 100 μl protein A-Sepharose (Pharmacia Biotech) for 1.5 h at 4°C. Supernatants were treated with recombinant RNase inhibitor (Invitrogen) and Halt protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Scientific) for 15 min and incubated with synthetic, 5′-biotinylated RNA (0.5 pM; 5′-bio-r(GAACACCAUGGCGACGUAGCUUUUUUUUUUGCUACGUCGC)-3′; IDT) for 15 min at 4°C. RNA pulldown was performed for 1.5 h at 4°C with 150 μl streptavidin-agarose beads (GE Healthcare) preblocked with 1% BSA in lysis buffer for 1.5 h. Beads with bound RNA-protein complexes were washed four times with 0.5 ml buffer containing an RNase inhibitor. Washed beads were treated with 75 μl loading buffer and heated 15 min at 95°C to dissociate all bound proteins. Samples were subjected to immunoblotting with the antibodies indicated below. Quantitative binding was measured by chemiluminescence with the Odyssey imaging system (Li-Cor Biothechology) using Image Studio software.
eIF4G1 knockdown/knock-in cell lines.
A plasmid expressing engineered microRNA targeting the 3′ UTR of eIF4G1 (miR-4G; nucleotides [nt] 5183 to 5205; GenBank number AY082886) was generated as described previously (25). Briefly, the miR-30 cassette fragment was PCR-amplified from a pCMV-miR-30 plasmid generously provided by B. Cullen (Duke University) using primer pair 5′-CTTAAGTGACCAGCCTACAGTCGGAAACCATC-3′/5′-GGGCCCCACAACTTGTAGTGCTCTTTCAAAG-3′, digested with NotI-ApaI, and inserted into the corresponding sites of the pcDNA5/FRT/TO backbone (Invitrogen). The resulting pcDNA5/FRT/TO miR-30 plasmid was digested with MluI-ApaI, and the fragment containing the cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter, tetracycline operator, and miR-30 cassette was subcloned into pcDNA3.1, generating pcDNA 3.1/TO/miR-30. To replace the miR-30 sequence with miR-4G, two oligonucleotides (5′-GCCTCGAGATCTGCGATGTGATGTGCCTGAACTAATAAGTGAAGCCACAGATG-3′/5′-GCCTCGAGGATCCGCAGTGTGATGTGTCTGAACTAATAACATCTGTGGCTTCAC-3′) were annealed, PCR extended, digested with XhoI, and inserted into the XhoI-digested pcDNA 3.1/TO/miR30. The resulting pcDNA3.1/TO/miR-4G plasmid was linearized with ScaI and transfected into HEK293 Flip-In T-REX cells with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen). G418-selected colonies were screened for eIF4G1 depletion upon doxycycline (DOX) induction. For eIF4G1 reconstitution, tagged myc-eIF4G1-Flag constructs subcloned into pcDNA5/FRT/TO were cotransfected into DOX-inducible eIF4G1-knockdown cells with the Flip-In recombinase. Cells were reconstituted with eIF4G1-b, either wild type (wt) or Ser1232Ala, as described previously (3). Hygromycin B selection yielded isogenic cell lines with effective DOX-inducible knockdown/knock-in of eIF4G1 or eIF4G1(Ser1232Ala).
RESULTS
Phosphoproteomic analyses of eIF4G1 in mitosis.
High-throughput phosphoproteomics revealed multiple potential phosphosites in eIF4G1 (26, 27). Some of these have been empirically confirmed, linked to specific kinases, and implicated in the organization of protein-protein interactions within the eIF4G scaffold (3, 4). However, how signaling networks converging on eIF4G participate in complex gene regulatory programs, e.g., the cell cycle, remains obscure. To elucidate a role for eIF4G1 phosphorylation in mitotic translation, we performed MS identification of in vivo-phosphorylated eIF4G1 [referred to as “eIF4G” from here on for endogenous eIF4G1 and as “eIF4G(amino acid numbers)” for truncated versions] in inter- and metaphase. Since IP of endogenous eIF4G is inefficient, we expressed N-terminally (myc) and C-terminally (Flag)-tagged eIF4G-b (aa 41 to 1600 of full-length eIF4G [Fig. 1A]) in a previously described DOX-inducible cell line (HEK293eIF4G) (21). DOX-induced cells were arrested in G1/S transition with double Th block (interphase sample). Release from the double Th block and mitotic arrest with NOC yielded the metaphase sample. Lysates from both samples were used in Flag-IP to purify eIF4G, equal quantities of which were subjected to LC-MS/MS.
First, we investigated if steady-state eIF4G protein-protein interactions change between interphase and mitosis (Table 1). To retain the formation of translation initiation complexes, the sample lysates were not treated with RNase. eIF4G binding was specific, rather than to Flag-Sepharose, since Flag-IP from uninduced cells yielded substantially reduced amounts only of the most abundant binding partners, likely due to cryptic expression of some Flag-eIF4G in the uninduced state (Table 1). The minimum detection level was set at 2 peptides/protein (except for eIF4B [Table 1]), and the quantitative value (amount of assigned spectra normalized to the molecular mass of the protein) for each condition is shown (Table 1). For each protein, the value from positive IP in mitosis (M) was divided by the respective value in interphase (I). Under the conditions of our assay, eIF4G binding to eIF4E was unchanged in mitosis, but binding to eIF4A1 and 2 was slightly enhanced (Table 1). Our biochemical and mechanistic studies of mitotic signaling to eIF4G corroborate this observation (see Fig. 8 and 9). Increased mitotic eIF4G binding also was observed with GRP78 (Hspa5; a chaperone not previously known to bind eIF4G), DDX3 (a DEAD box helicase known to interact with eIF4G [28]), and eIF1A (which is part of the 43S preinitiation complex) (Table 1). Among proteins with reduced eIF4G association in mitosis, PDCD4 stands out. At 20% of interphase levels, reduced eIF4G binding possibly is the result of the previously described mitotic degradation of PDCD4 (16). We validated changing binding of DDX3, eIF1A, and PDCD4 in synchronized cells arrested in mitosis by coimmunoprecipitation with eIF4G (see Fig. 7 below).
TABLE 1.
Proteomic analysis of eIF4G immunoprecipitates in interphase and mitosisa
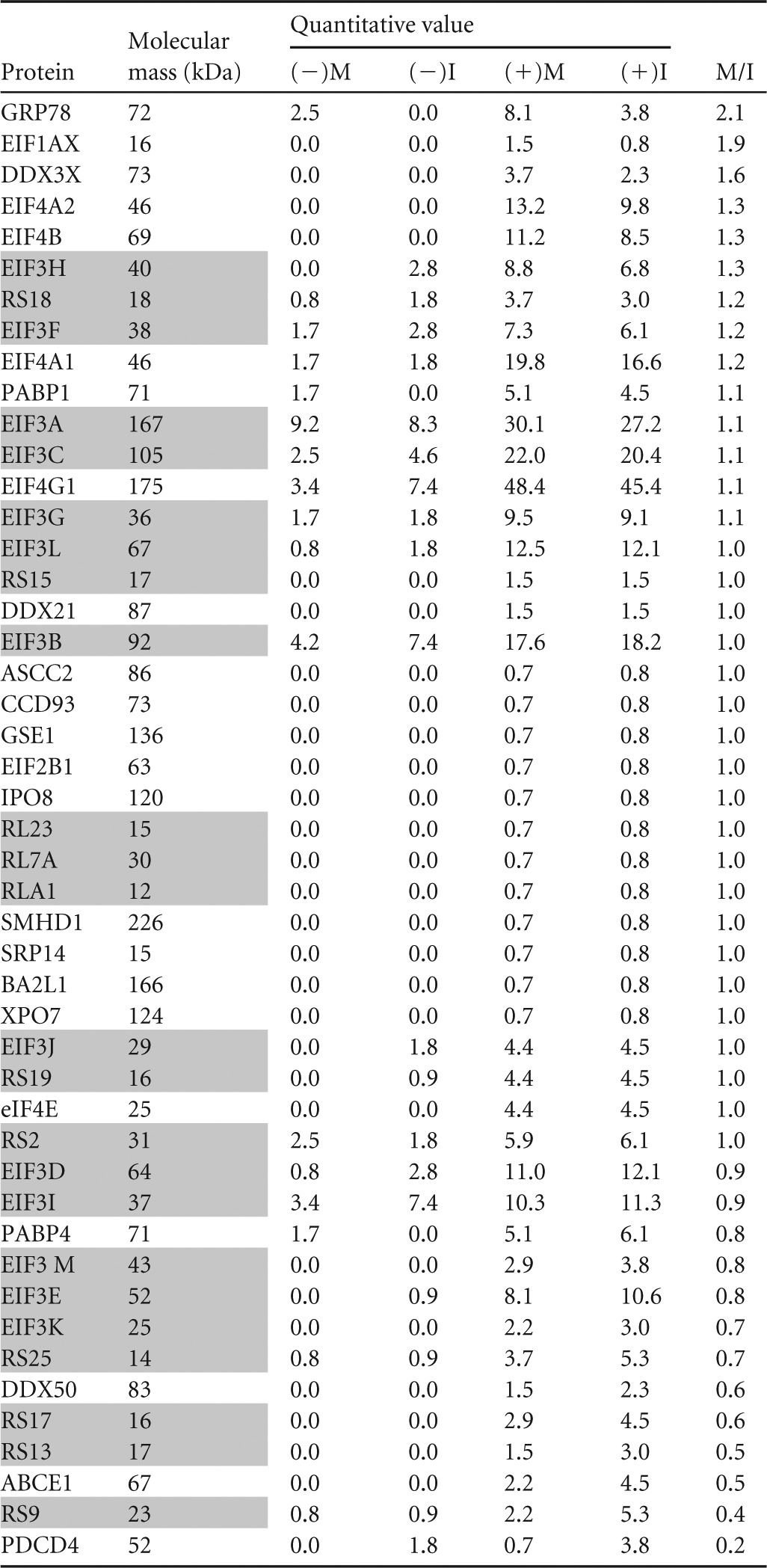
I, interphase; M, mitosis; (−), uninduced negative control; (+), DOX-induced sample. Ribosomal and eIF3 proteins are shaded.
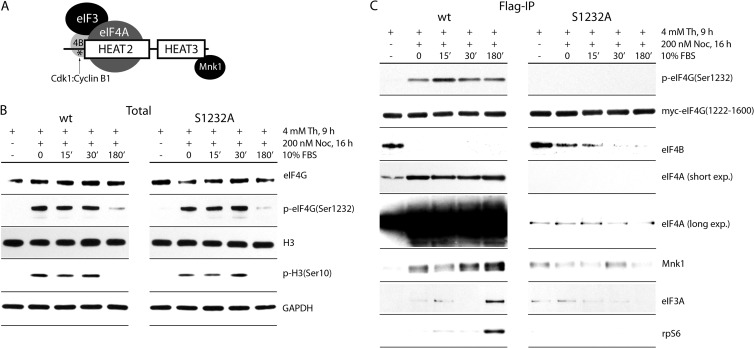
FIG 8.
Regulation of eIF4A and Mnk1 interactions by mitotic phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) by Cdk1:cyclin B1. (A) Schematic representation of the eIF4G(1222-1600) fragment. Structural HEAT2 and -3 domains, the distal portion (aa 1222 to 1235) of the IDL, the position of p-Ser1232 (*), and the interactions with eIF3A/-4A/-4B and Mnk1 are shown. Dynamics of endogenous eIF4G(Ser1232) and H3(Ser10) phosphorylation (B) and eIF4G(1222-1600) interactions (C) during cell cycle progression are also shown. HEK293 cells transfected with wt or Ser1232Ala mutant myc-eIF4G(1220-1600)-Flag fragments were synchronized by Th block (4 mM, 9 h) at the G1/S boundary, followed by NOC (200 nM, 16 h) arrest in mitosis. Cells were released from NOC block into growth medium for 15 to 180 min. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting (B) or Flag-IP followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Endogenous eIF4G (B) was detected with an antibody against an N-terminal epitope; myc-eIF4G(1222-1600) was detected with anti-myc antibody (C). The assay was repeated three times, and a representative series is shown.
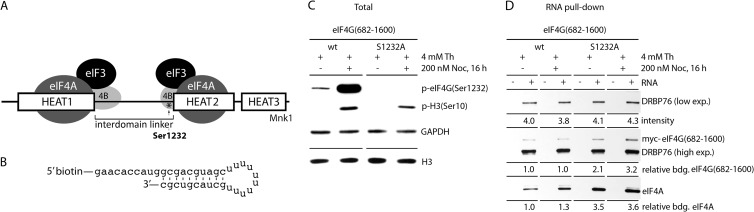
FIG 9.
A nonphosphorylatable Ser1232Ala substitution in eIF4G stimulates the RNA-binding properties of the eIF4G/-4A helicase complex in mitosis. (A) Schematic representation of the eIF4G(682-1600) fragment used. The structured HEAT1 to -3 domains, the interdomain linker, the position of Ser1232(*), and interactions with initiation factors eIF3A/-4A/-4B and protein kinase Mnk1 are shown. (B) Sequence of a 5′-biotinylated stem-loop RNA probe used as an eIF4A binding substrate. Mitotic phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) histone H3(Ser10) (C) and RNA-binding assay results (D) for Ser1232 and S1232A eIF4G/eIF4A complexes are shown. HEK293 cells, expressing wt or Ser1232Ala mutant myc-eIF4G(682-1600)-Flag fragments, were DOX induced and synchronized by Th (16 h, 4 mM) block or arrested in mitosis with Th (9 h, 4 mM) and then with NOC (16 h, 200 nM). The cells were lysed and subjected to immunoblotting (C), or to biotinylated-RNA pulldown with streptavidin-agarose beads and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (D). Relative binding of eIF4G/eIF4A complexes with RNA was determined by quantitative chemiluminescence measurements as described in Materials and Methods. The experiment was repeated three times, and a representative assay is shown. The quantitative data represent an average value of binding; standard deviation did not exceed 15% for any of the values.
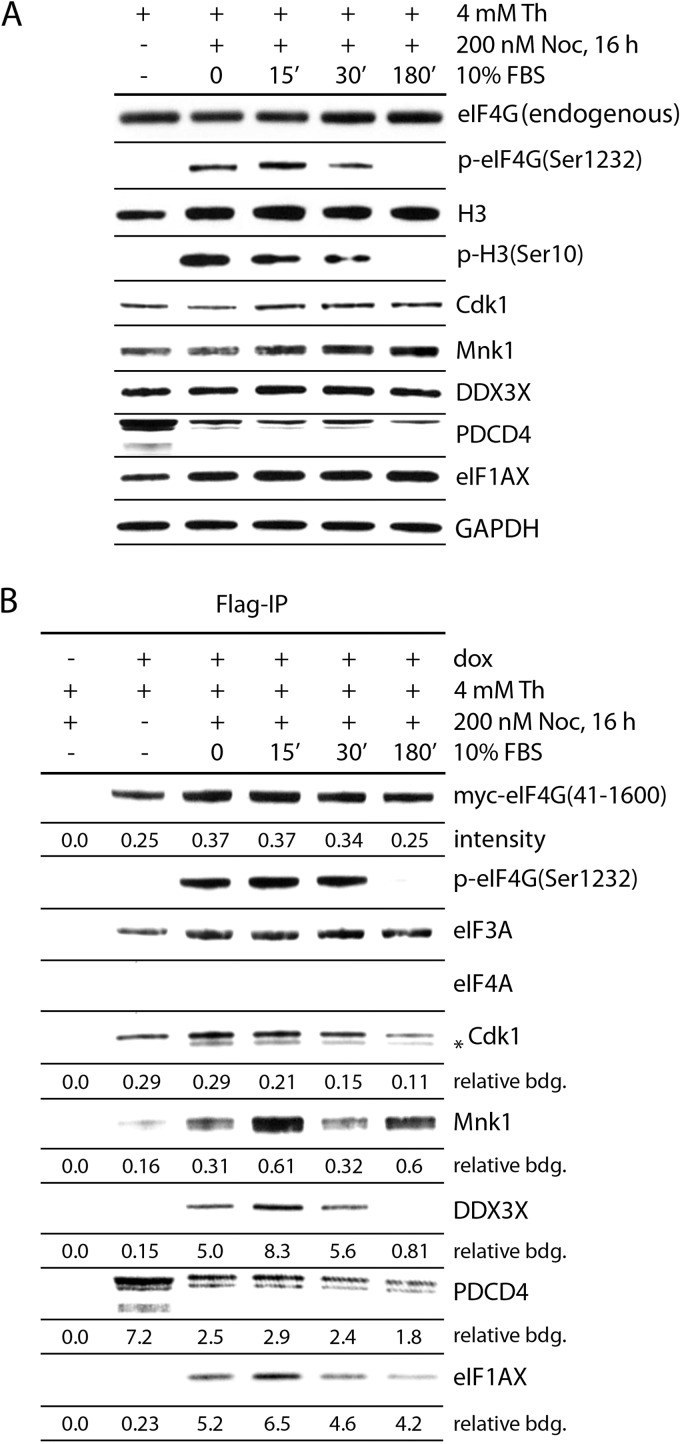
FIG 7.
Dynamics of eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation and binding with initiation factors/kinases during mitotic entry and exit. HEK293eIF4G cells were either mock (−) or DOX induced (+) and synchronized by Th block (4 mM, 9 h) or arrested in mitosis with NOC (200 nM, 16 h). The cells were released from NOC block with growth medium and processed at the indicated time points. The cells were lysed and subjected to immunoblotting (A) or myc-eIF4G-Flag precipitation with anti-Flag-agarose (B) and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Endogenous eIF4G and exogenous eIF4G(41-1600) (A) were detected with an antibody against an N-terminal epitope; myc-eIF4G(41-1600) (B) was detected with anti-myc antibody. The asterisk indicates a band detected with anti-Cdk1 antibody, presumably Cdk1 dephosphorylated on the Thr14 and Tyr15 sites, representing the mitotically active form of the kinase. The amounts of immunoprecipitated proteins were determined by quantitative chemiluminescence measurements (see Materials and Methods). “Relative binding” is the value of the corresponding protein divided by value for myc-eIF4G(41-1600). The quantitative data represent an average value of binding from three independent experiments. Standard deviation in all cases was less than or equal to 20%.
Mitotic phosphorylation of eIF4G.
Phosphopeptide abundance across M and I samples was obtained by generating selected ion chromatograms (20-ppm window around the most abundant charge state of the precursor ion, with seven-point Boxcar smoothing) from raw LC-MS data. Once the corresponding peaks were identified, the peak height of manually selected ion chromatograms was used to calculate peptide abundance. Using this approach we detected 17 sites in eIF4G that were potentially phosphorylated in interphase and metaphase (with varying probability/identification certainty [Fig. 1B]) (23). These sites mainly cluster in two regions: near the N terminus (Thr202/5/7/11) and in the distal IDL separating HEAT1 and 2 domains (29) (Fig. 1B). All sites were previously identified in high-throughput mass spectrometry studies (30). Four of the peptides contained sites whose phosphorylation was significantly enhanced in mitosis: Thr205/7 (5.4-fold), Thr648 (6.7-fold), Ser1078/81/93 (9.9-fold), and Ser1232 (7.3-fold) (Fig. 1B). We focused our studies on Ser1232 for several reasons: (i) Ser1232 had the highest signal intensity and the second-strongest mitotic increase of all phosphorylation sites identified (Fig. 1B). (ii) Ser1232 was identified by phosphopeptide mapping as a major serum-responsive phosphosite on eIF4G before (31). It is more likely to be functionally significant, since a higher percentage of eIF4G moieties would be affected by this phosphorylation. (iii) Only two phosphospecific eIF4G antibodies are commercially available (against Ser1148 and Ser1232; phosphorylation of Ser1148 is not increased in mitosis) [Fig. 2D. (iv) Ser1232 is located at the border of the flexible IDL and the structured HEAT2 domain (Fig. 1B), an area that coordinates binding to eIF4B and eIF3 (4). (v) A functional consequence of Ser1232 phosphorylation (dissociation of eIF4B from eIF4G HEAT2) is known (4). In addition to eIF4G, our screen also revealed cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation sites in its binding partners eIF4B and eIF3A (Fig. 1B). The significance of this finding is discussed below (see Fig. 8).
FIG 2.
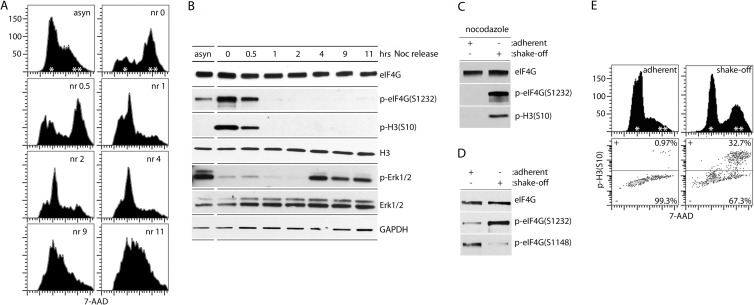
eIF4G(Ser1232) is phosphorylated specifically in mitosis. (A and B) HEK293 cells were synchronized by double Th block and incubated for 12 h with NOC (mitotic arrest), released from NOC (nr), and processed at the indicated intervals. Asynchronous cells (asyn) were used as controls. Cells were fixed and stained with 7-AAD for FACS analysis of DNA content (A) or lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting as shown (B). (C to E) Mechanical shake-off of either NOC-treated (C) or untreated (D and E) HeLa cells was performed to separate mitotic cells from adherent cells in interphase. Cells were lysed for immunoblot analysis (C and D) or fixed and stained with 7-AAD and p-H3(Ser10) Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated antibody for FACS analysis (E). All assays were performed for a minimum of three times, and representative series are shown.
eIF4G is phosphorylated at Ser1232 in mitosis.
To confirm our phosphoproteomic data, we used antibodies to p-eIF4G(Ser1232) to investigate eIF4G phosphorylation during cell cycle progression (Fig. 2A and B). HEK293 cells were arrested in mitosis with double Th block followed by NOC treatment (Fig. 2A). Flow cytometry of 7-AAD-stained cells revealed that most cells were arrested in the G2/mitosis (M) phase (Fig. 2A, nr 0). After release from NOC block, the synchronized cells completed mitosis, reentered the G1 phase, and further progressed through the cell cycle (Fig. 2A, nr 0.5 to nr 11). P-Ser1232 peaked in prophase/prometaphase (Fig. 2B, nr 0), slightly diminished in mitosis (nr 0.5) and diminished upon G1 entry (nr 1)/throughout the G1/S-phase (nr 2 to nr 11) in a pattern that tracked the mitotic marker phospho-histone 3 [p-H3(Ser10)] (32).
To exclude the possibility of Ser1232 phosphorylation due to NOC toxicity, we mechanically separated adherent (interphase) from detachable (mitotic) HeLa cells with the classic shake-off method. First, cell cultures that were incubated in the presence of NOC for the same interval were subjected to shake-off (Fig. 2C). Adherent (interphase) cells lacked p-eIF4G(Ser1232), whereas the detachable, mitotic fraction exhibited abundant signal [Fig. 2C; p-H3(Ser10) confirmed the mitotic state of the shake-off fraction]. Second, shake-off in the absence of NOC (Fig. 2D) produced a cell pool enriched for mitotic cells [∼1/3 of shake-off cells stained positive for p-H3(Ser10) (Fig. 2E)]. This population exhibited enhanced Ser1232 phosphorylation compared to the interphase sample, while phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1148) trended in the opposite direction (Fig. 2D). Thus, eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation occurs specifically and spontaneously during mitosis.
eIF4G(Ser1232) is a substrate of Cdk1:cyclin B1 in vivo.
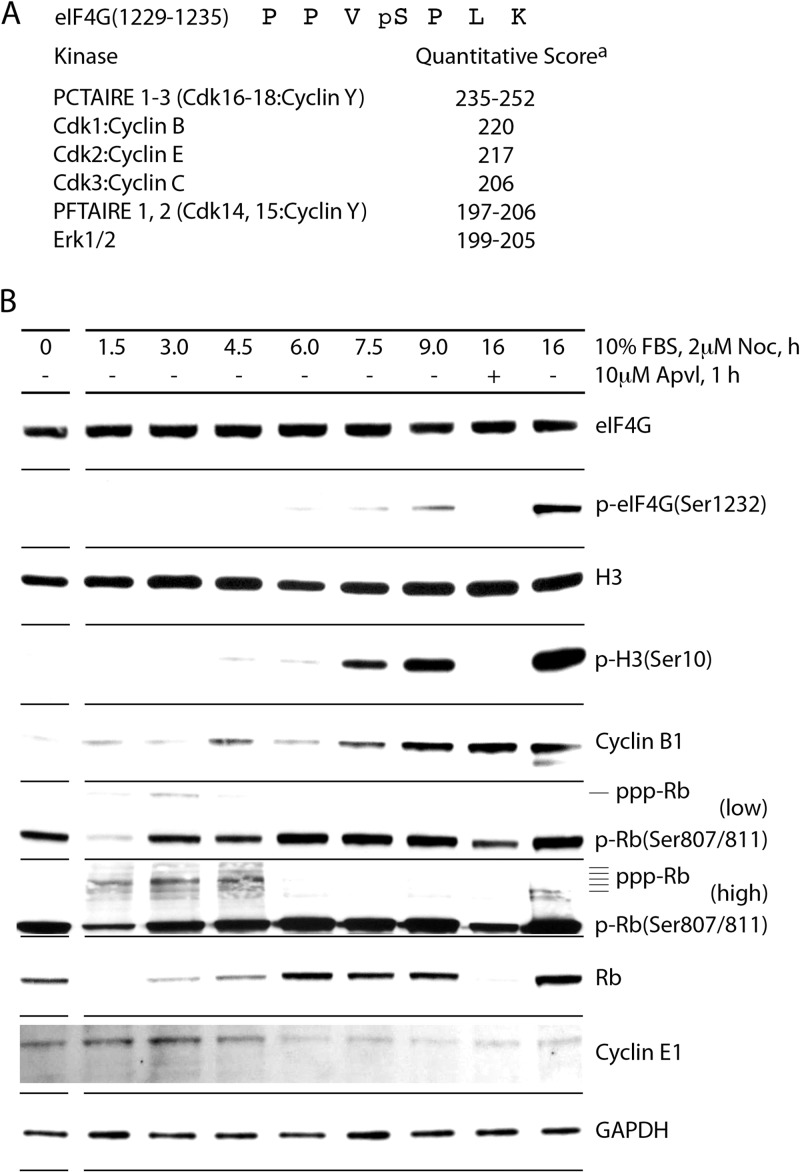
The sequence context surrounding eIF4G(Ser1232) closely resembles the consensus for MAPKs and Cdks (Fig. 3A) (33, 34). We reported previously that Ser1232 phosphorylation upon phorbol ester stimulation is due to Erk1/2 MAPKs (3, 4). In addition to Erk1/2, quantitative computational prediction tools identified a number of Cdks as potential candidates for mitotic phosphorylation of eIF4G (Fig. 3A). We performed a series of assays (Fig. 3 to 5) to systematically evaluate their involvement in this event. First, to examine a potential role for Cdk1 to -3, we conducted detailed kinetic analyses of cell cycle progression from G1/S through M phase (Fig. 3B). This indicated eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation in step with H3(S10) phosphorylation and accumulation of cyclin B1 (Fig. 3B), supporting involvement of Cdk1:cyclin B1 in mitotic eIF4G phosphorylation. Changes in cyclin E1 abundance and the time course of retinoblastoma protein (Rb) phosphorylation (at Cdk2:cyclin E substrate sites) did not match cyclin B1/p-Ser1232 accumulation (Fig. 3B), making Cdk2:cyclin E an unlikely candidate for eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation. We did not test Cdk3:cyclin C, but the kinetics of eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation (coincident with mitotic entry) all but excludes their involvement, because Cdk3:cyclin C is active in G0 exit (35).
FIG 3.
Kinetic analysis of mitotic phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) in vivo. (A) The sequence of eIF4G(1229-1335) and quantitative computer kinase prediction (athe quantitative score is based on deduced consensus phosphorylation site amino acid frequency scoring matrices that have been determined for each of the ∼500 different human protein kinases [51]). (B) Kinetic analysis of eIF4G phosphorylation and cell cycle progression from G1/S to M phase. HEK293 cells were arrested near the G1/S boundary by Th block (4 mM, 9 h) and released with growth medium in the presence of 2 μM NOC. Mitotic cells were treated with APVL (10 μM, 1 h). Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting. The assay was performed for a minimum of three times, and a representative series is shown.
FIG 5.
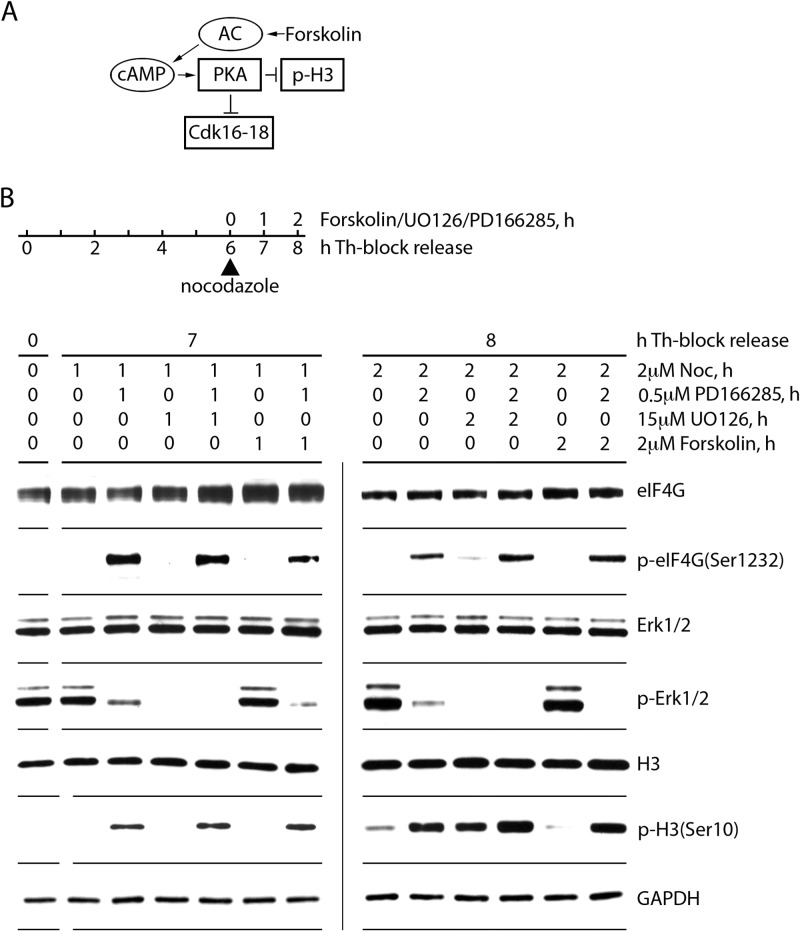
Inhibition of Erk1/2 or Cdk16-18 in mitosis does not prevent eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation. (A) Forskolin activates adenylate cyclase (AC), enhancing cAMP production. This stimulates protein kinase A (PKA), which causes inhibitory phosphorylation of Cdk16 to -18 by PKA. (B) HEK293 cells were synchronized by Th block (4 mM, 9 h) and released with growth medium for 6 h. Upon NOC arrest, the cells were treated with 500 nM PD166285 to stimulate mitotic entry, 2 μM NOC to prevent mitotic exit, or with 15 μM UO126 or forskolin to inhibit Erk1/2 or Cdk16 to -18 activity, respectively. Cells were collected after 1 (7 h after Th block release) and 2 (8 h after Th-block release) h of drug treatment and lysed. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. The assay was performed three times, and a representative series is shown.
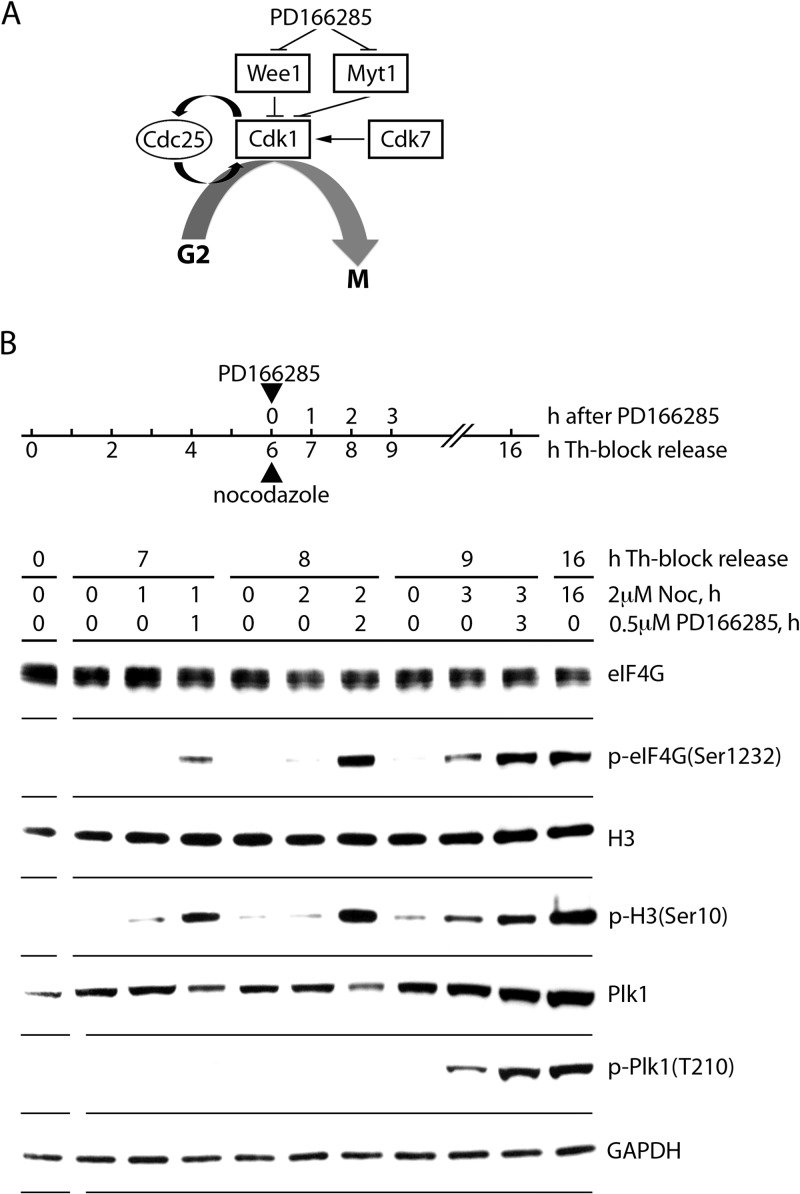
Next, to directly implicate Cdk1:cyclin B1 in eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation, we applied inhibitors that disrupt control over Cdk1 activation. Testing Cdk1's involvement in mitotic eIF4G phosphorylation in vivo cannot be studied with inhibitors of Cdk1 itself, because these may block eIF4G phosphorylation simply by preventing mitosis. As a case in point (Fig. 3B), the Cdk1 inhibitor aminopurvanalol A (APVL) inhibited Ser1232 phosphorylation but also prevented H3(Ser10) phosphorylation, indicating interference with mitotic entry. Entry into mitosis occurs upon the production of mitotic cyclins (e.g., cyclin B1 [Fig. 3B]), which form an active holoenzyme when associating with Cdk1. This process is controlled by the Cdk1 inhibitory Wee1/Myt1 kinases. Upon activation, Wee1 phosphorylates Cdk1(Thr14/Tyr15) (36), resulting in inhibition of Cdk1 activity/mitotic entry. This process is reversed by the Cdc25 phosphatase (37) (Fig. 4A). The tyrosine kinase inhibitor PD166285 inhibits Wee1/Myt1 and forces mitotic entry by removing constraints on Cdk1 activation (38). Accordingly, treating cells (synchronized with Th block) with PD166285 substantially enhanced phosphorylation of the mitotic marker H3(Ser10) compared to untreated cells (Fig. 4B). This was accompanied by a similar increase in eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation (Fig. 4B). Enhanced/accelerated mitotic entry was also evident as increased Plk1 phosphorylation upon PD166285 treatment (Plk1 is a downstream effector of Cdk1 [39]), albeit at a later time point (3 h) (Fig. 4B). Simultaneous phosphorylation of H3(S10) and eIF4G(S1232) occurs before Plk1 activation, suggesting that Cdk1 downstream effectors are unlikely to be involved in Ser1232 phosphorylation. Thus, enhanced eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation upon stimulation of Cdk1 activity upon Wee1/Myt1 inhibition strongly implicates Cdk1:cyclin B1 as the in vivo kinase targeting this site.
FIG 4.
Initiation of mitotic entrance by Wee1/Myt1 inhibition in G2-synchronized cells. (A) Schema of the Cdk1 regulatory network during G2/M progression. Cdk7 phosphorylates and stimulates, whereas Wee1/Myt1 kinases inhibit, Cdk1 activity. Also, Cdk1 phosphorylates and stimulates its activator Cdc25 for positive feedback. Direct inhibition of Wee1/Myt1 by PD166285 causes exponential activation of Cdk1 (forcing mitotic entry) due to the positive Cdc25 feedback loop. (B) HEK293 cells were synchronized by Th block (4 mM, 9 h) and released in growth medium for 6 h. Upon G2 entry, cells were treated with 2 μM NOC to prevent mitotic exit and with 500 nM PD166285. Cells were collected after 1, 2, or 3 h of drug treatment and lysed. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. The assay was performed three times, and a representative series is shown.
Lastly, to exclude Cdk16 to -18 and Erk1/2 in mitotic phosphorylation of eIF4G, we treated Th-synchronized cells with the adenylate cyclase activator forskolin (to inhibit Cdk16 to -18 [Fig. 5A]) or the Mek1 inhibitor UO126 (Fig. 5B). Forskolin treatment results in cyclic AMP (cAMP)-dependent activation of PKA, inhibition of H3(S10) phosphorylation, and inhibitory phosphorylation of Cdk16 to -18 at Ser153 (40). To enhance mitotic entry, synchronized cells were released from double Th block by growth medium exchange (6 h) and then simultaneously treated with NOC, PD166285, and other drugs (1 or 2 h), resulting in substantially increased eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation (Fig. 5B). UO126 treatment blocked Erk1/2 activation efficiently but had no effect on H3(S10) or eIF4G(S1232) phosphorylation. Treatment with PD166285 (2 h) and/or forskolin (Fig. 5B, right side) showed that forskolin alone inhibits phosphorylation of H3(Ser10) and, presumably, Cdk16 to -18 (p-Ser153 antibodies are not commercially available). Addition of PD166285 to forskolin-treated cells restored mitotic entry [H3(Ser10) phosphorylation] and Cdk1:cyclin B activity [eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation]. Neither forskolin nor UO126 had any effect on eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation in this test (Fig. 5B), excluding Cdk16 to -18 and Erk1/2 as possible kinases for mitotic eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation.
Phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) by Cdk1:cyclin B1 in vitro.
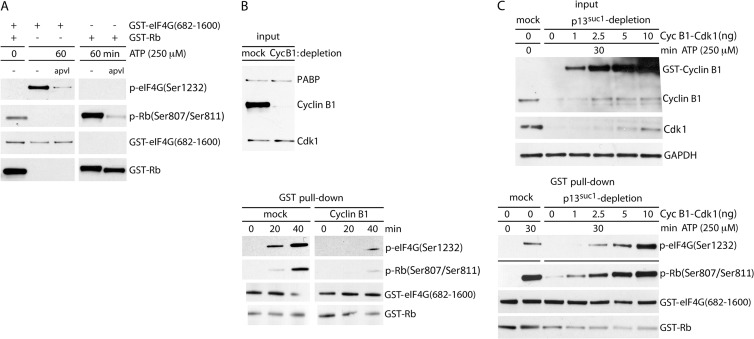
To further confirm our findings implicating Cdk1:cyclin B1 in mitotic eIF4G phosphorylation, we performed functional tests of eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation in vitro. First, we generated lysates from HEK 293 cells arrested in mitosis by NOC treatment and tested their ability to phosphorylate recombinant C-terminal fragments of eIF4G [GST-eIF4G(682-1600)] or GST-Rb (aa 773 to 928) (Fig. 6A). After 60 min of incubation with mitotic lysates, both recombinant GST fusion proteins were efficiently phosphorylated at the corresponding sites (Fig. 6A). This in vitro approach allowed us to use the Cdk1 inhibitor APVL to test an involvement of Cdk1 in eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation directly. The drug significantly reduced phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) and Rb(Ser807/11) (Fig. 6A), suggesting Cdk1 involvement in phosphorylation of these sites in vitro.
FIG 6.
Cdk1:cyclin B1 phosphorylates eIF4G at Ser1232 in vitro. (A) Recombinant GST-tagged C-terminal fragments of eIF4G and of Rb (GST-Rb) were incubated with mitotic cell extract from NOC-treated cells with or without APVL (10 μM) and then isolated using glutathione-sepharose. (B) Depletion of cyclin B1 and/or Cdk1 from mitotic lysate reduced in vitro phosphorylation of eIF4G at Ser1232. Cyclin B1 was depleted from mitotic lysate with anti-cyclin B1 antibody (top). Mock- and cyclin B1-depleted lysates were used to phosphorylate GST-eIF4G and GST-Rb for the indicated intervals (bottom). (C) p13suc1-Sepharose was used to deplete Cdk1:cyclin B1 from mitotic lysates. Lysates were reconstituted with increasing amounts of recombinant Cdk1:cyclin B1 (top) and used to phosphorylate GST-eIF4G and GST-Rb (bottom).
Next, we tested if Cdk1:cyclin B1 immunodepletion suppresses eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation in vitro. We were unable to codeplete Cdk1 with cyclin B1 IP, possibly because the antibody recognizes an epitope within the Cdk1 binding site. However, cyclin B1 depletion alone reduced eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation substantially (Fig. 6B). This supports a dependence of Ser1232 phosphorylation on Cdk1, since cyclin B1 is an essential cofactor specific to Cdk1. Finally, we depleted HEK293 cell lysates of all Cdks by incubating NOC-arrested lysates with yeast p13suc1, followed by reconstitution with recombinant Cdk1:cyclin B1 (Fig. 6C). Addition of 1 to 10 ng recombinant Cdk1:cyclin B1 restored eIF4G(S1232) phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner, indicating that Cdk1 can phosphorylate eIF4G(Ser1232) in the absence of all other Cdks. Reconstitution provided an excess of cyclin B1 and did not completely restore Cdk1 levels (Fig. 6C, top blot). Taken together, our observations suggest that Cdk1:cyclin B1 phosphorylates eIF4G directly at Ser1232 in mitosis.
eIF4G interactions with its binding partners in mitosis and effect of Ser1232 phosphorylation on initiation complex formation.
To investigate functional roles for eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation by Cdk1:cyclin B1 in translation during mitosis, we first validated our MS results of steady-state eIF4G-protein binding (Table 1). We compared lysates from HEK293eIF4G cells synchronized at different stages of the cell cycle by double Th and NOC block and release from NOC block into growth medium (Fig. 7). First, we confirmed eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation in step with H3(Ser10) phosphorylation during mitotic progression. As expected, phosphorylation of both H3(Ser10) and eIF4G(Ser1232) sites occurred in NOC-arrested and short-term-released (15 to 30 min) cells and disappeared after mitotic exit (180 min [Fig. 7A]). Second, we tested the expression of proteins with changed eIF4G interactions in mitosis, DDX3, eIF1A, and PDCD4, as well as Mnk1 and Cdk1 (Fig. 7A). Only PDCD4 exhibited altered expression in mitosis, in accordance with mitotic proteosomal degradation (Fig. 7A).
Cell lysates were subjected to Flag-IP, and eIF4G binding partners were assessed by immunoblotting followed by quantitative chemiluminescent detection (Fig. 7B). Relative eIF4G binding was determined as the ratio of signal to the intensity of chemiluminescence for immunoprecipitated myc-eIF4G (Fig. 7B). The interphase/metaphase binding differential of eIF3A and eIF4A to eIF4G was less than the standard deviation (±20%; quantitative data not shown). Cdk1 IP in mitosis revealed a faster-migrating band, possibly representing the catalytically active kinase without inhibitory phosphorylation on Thr14/Tyr15 (Fig. 7B). Binding of Cdk1 to eIF4G was increased during mitosis and decreased after mitotic exit, presumably due to proteosomal degradation of cyclin B1 (Fig. 7B). Mnk1, DDX3, and eIF1A, in accordance with our proteomic data (Table 1), showed enhanced binding to eIF4G in mitosis (Fig. 7B). Diminished PDCD4 binding to eIF4G during mitosis (Fig. 7B) correlates with its reduced expression in lysates (Fig. 7A).
eIF1A and DDX3 binding to eIF4G strongly correlates with eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation. Thus, to validate the functional role of eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation in mitosis, we used wt and Ser1232Ala eIF4G(1222-1600) fragments. These contain the structured HEAT2 and -3 domains, including ∼23 aa of the distal IDL, where Ser1232 is located (Fig. 8A). HEK293 cells were transfected with wt or mutant myc-eIF4G(1222-1600)-Flag fragments and synchronized and processed as described for Fig. 7. Immunoblotting of cell lysates confirmed in-step phosphorylation of endogenous eIF4G(Ser1232) and H3(Ser10) during mitosis (Fig. 8B). Flag-IP revealed that the wt eIF4G(1222-1600) fragment also was phosphorylated in mitosis but remained phosphorylated after mitotic exit (Fig. 8C), possibly due to poor substrate properties for the corresponding protein phosphatase(s). As expected, the Ser1232Ala mutant was not phosphorylated in the same assay (Fig. 8C). Co-IP tests failed to identify DDX3/eIF1A with both the wt eIF4G(1222-1600) fragment and the Ser1232Ala mutant (data not shown). This suggests that phosphorylation of Ser1232 by Cdk1 does not control altered eIF4G interactions with these proteins in mitosis.
We previously determined that the distal IDL (aa 1222 to 1245) contains a binding site for eIF4B, which is regulated by eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation by Erk1/2 (Fig. 8A) (4). Specifically, upon Erk1/2 activation, phosphorylation of Ser1232 resulted in eIF4B dissociation from the IDL (4). Our assays showed that Cdk1:cyclin B phosphorylation of the same residue may have a similar outcome in mitosis (Fig. 8C). In mitotic cells, eIF4B had dissociated from wt eIF4G(1222-1600), while this effect was substantially delayed with the Ser1232Ala variant (Fig. 8C).
Phosphorylation of Ser1232 strongly correlated with helicase eIF4A binding (Fig. 8C). For the wt eIF4G fragment, modest binding was observed in double-Th-block-synchronized cells, where eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation is low. Upon Ser1232 phosphorylation in mitosis, eIF4A binding was induced (Fig. 8C). The Ser1232Ala fragment had very low binding affinity for eIF4A independent of the state of cell cycle progression (Fig. 8C). We overexposed filters to detect delicate eIF4A co-IP with the eIF4G(Ser1232Ala) mutant fragment. This revealed substantially reduced mitotic eIF4A-HEAT2 binding upon Ser1232Ala substitution (Fig. 8C).
Tests with IDL truncation fragments showed that eIF4A binding to eIF4G-HEAT2 correlates with Mnk1 binding to HEAT3 (4). This is reflected in our data, as the increased eIF4A binding to wt eIF4G(1222-1600) in mitosis correlated with enhanced binding of Mnk1 to the same fragment (Fig. 7B and 8C). In contrast, the mutant Ser1232Ala fragment had decreased affinity for Mnk1 under all investigated conditions (Fig. 8C). Finally, the wt eIF4G(1222-1600) fragment, in contrast to the mutant isoform, showed enhanced binding with eIF3A and ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6) after mitotic exit, indicating increased interactions with small ribosomal subunits.
Ser1232Ala substitution in eIF4G stimulates the RNA-binding properties of the eIF4G/4A helicase complex.
Scanning or unwinding of mRNAs during translation initiation occurs through dynamic interactions of eIF4A/-4B with eIF4G HEAT1 and -2 in association with RNA templates. eIF4G and eIF4A have poor affinity for RNA alone, but they efficiently bind RNA in a ternary complex (29). Prior studies showed that eIF4A binding to eIF4G HEAT1 enables helicase associations with RNA, while binding to HEAT2 counteracts them (29). It is therefore plausible that increased eIF4A-HEAT2 binding in mitosis (Fig. 8C) correlates with suppressed RNA binding of the translation initiation helicase complex. To test this, we used RNA pulldown assays to evaluate the effect of mitotic eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation on RNA binding of the translation initiation helicase complex. Endogenous eIF4A1 to -3 are far more abundant than eIF4G (the eIF4A1 to -3/eIF4G1 ratio in U2OS osteosarcoma cells is ∼28:1 [41]). To bind most cellular eIF4A, we overexpressed eIF4G(682-1600) fragments. eIF4G(682-1600) was chosen for our assay because it lacks binding to eIF4E and PABP (Fig. 1A), which could mediate RNA contacts independent of eIF4A. Also, it contains all RNA binding determinants of eIF4G itself. We produced two cell lines, expressing wt myc-eIF4G(682-1600)-Flag or a Ser1232Ala substitution variant (Fig. 9A), for binding assays with biotinylated stem-loop RNA (Fig. 9B).
After NOC treatment, H3 was efficiently phosphorylated in both cell lines, whereas only the wt eIF4G fragment was phosphorylated at Ser1232 in mitosis (Fig. 9C). For the RNA pulldown assay, we controlled for the efficiency of RNA precipitation by quantifying coprecipitation of the double-stranded RNA binding protein 76 (DRBP76), which binds preferably with double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) (Fig. 9D). DRBP76 and myc-eIF4G were detected on the same immunoblot using the same secondary anti-species antibody under identical conditions, enabling quantitative assessment of the relative binding of these proteins with RNA. The Ser1232Ala substitution eIF4G fragment bound 2.1- and 3.2-fold stronger in interphase and mitosis, respectively, than the corresponding wt fragment (Fig. 9D). Association of the eIF4G/-4A translation initiation helicase complex with stem-loop RNA in mitosis was ∼3-fold stronger with the Ser1232Ala substitution eIF4G fragment than with the wt fragment (Fig. 9D). These observations correspond to our finding of enhanced eIF4G-HEAT2 binding to eIF4A due to Cdk1:cyclin B1 phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) in mitosis (Fig. 8C) and the previously reported effects of HEAT2/eIF4A binding on association of the translation initiation helicase complex with RNA (29).
eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation by Cdk1:cyclin B1 and mitotic translation repression.
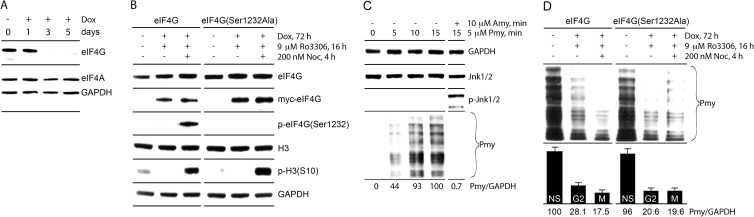
We next tested the involvement for eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation in the mitotic translation shift. First, to enable in vivo tests with mutant eIF4G(Ser1232Ala) while retaining authentic eIF4G levels, we used dox-inducible knockdown/knock-in HEK293 cell lines (see Materials and Methods). DOX induction of such cells for >3 days (i) achieved >90% depletion of endogenous eIF4G (Fig. 10A), (ii) restored total eIF4G to intrinsic levels (Fig. 10B), (iii) yielded efficient myc-eIF4G-Flag expression (Fig. 10B), and (iv) showed mitotic phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) only in the wt reconstituted cells (Fig. 10B). Thus, our approach almost completely replaces endogenous eIF4G with a mutated variant at constant expression levels. Second, we assessed global translation by labeling with the translation elongation inhibitor puromycin (PMY [42]). Conventional metabolic labeling with Met analogs requires Met starvation, which elicits stress responses with effects on protein synthesis. Short-term PMY pulsing does not require disruptive growth conditions, does not evoke stress-signaling responses (Fig. 10C), and leads to direct PMY incorporation into nascent polypeptides that are detectable with anti-PMY antibodies (Fig. 10C). The time course of PMY incorporation revealed a linear increase during the first 10 min of treatment and saturation at 15 min (Fig. 10C). Anisomycin (AMY), a competitive inhibitor of PMY binding to ribosomes, blocked PMY polypeptide incorporation (and activated Jnk1/2 [Fig. 10C]).
FIG 10.
Monitoring of global mitotic translation by PMY labeling in eIF4G knockout/knock-in cell lines. (A) Time course of DOX-inducible depletion of endogenous eIF4G. (B) HEK293 cell lines with DOX-inducible endogenous eIF4G depletion and myc-eIF4G/eIF4G(Ser1232Ala) reconstitution were induced for 3 days. During the last day, the cells were G2 arrested with Ro3306 and released to NOC-containing growth medium for mitotic arrest. (C) Time course of PMY incorporation into nascent polypeptide chains. Exponentially growing HEK293 cells were pretreated with DMSO or 10 μM AMY for 15 min and incubated with 5 μM PMY. To stop puromycylation, cells were washed with cold PBS at 4°C and lysed. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. The quantitative data represent an average value of PMY/GAPDH ratio from three independent experiments. Standard errors in all cases were less than 12% from the average value. (D) The effect of Ser1232Ala substitution in eIF4G on global mitotic translation (samples from assays shown in panel B were tested). Nonsynchronized (NS) cells and cells arrested in G2 and M phases were treated with 5 μM PMY for 15 min. The reaction was stopped, cells were lysed, and the lysates were subjected to PMY immunoblotting. The assay was repeated in three independent series, each consisting of three separate samples. The PMY/GAPDH ratio was quantified.
We used the puromycylation assay to compare global mitotic translation in knockdown/knock-in cell lines reconstituted with wt eIF4G or eIF4G(Ser1232Ala) (Fig. 10D). We used the conditions shown in Fig. 10B, with cell cycle arrest in G2 (with the specific Cdk1 inhibitor Ro3306 [43]) and release from G2 arrest to NOC-containing growth medium. Both cell lines were arrested in mitosis, as indicated by H3(S10) phosphorylation, but only wt eIF4G(Ser1232) was phosphorylated by Cdk1 (Fig. 10B). Puromycylation did not interfere with mitotic phosphorylation of H3 or eIF4G and resulted in accumulation of labeled polypeptides (Fig. 10D). The intensity of PMY labeling in nonsynchronized cells and in G2- and mitosis (M)-arrested cells was quantified and normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) levels (Fig. 10D). In agreement with prior metabolic labeling assays (44), global translation in G2- and M-arrested cells was inhibited by 75 to 80% relative to that in exponentially growing cells (Fig. 10D). Interphase translation in cells expressing eIF4G(Ser1232Ala) was moderately lower, while the level of mitotic translation was higher than in wt eIF4G-expressing cells (in mitosis, the difference is not statistically significant [Fig. 10D]). Our data are concordant with a translation-repressive function of eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation in mitosis, but they also indicate that this event alone is not sufficient for the steep decline of protein synthesis in mitosis. This outcome is expected since “…Cdk1 has hundreds of mitotic substrates…. The transition to metaphase is driven by many phosphorylation events, each one of which slightly biases a single protein toward its mitotic state, but no one of which is necessary or sufficient to drive mitosis. This complexity makes validating the importance of any single phosphorylation difficult…” (45).
DISCUSSION
In this study, to unravel cell cycle-dependent signals to translation machinery, we investigated eIF4G binding to its partners and phosphorylation in mitosis. Despite eIF4G's key roles as a translation initiation scaffold, ribosome adaptor, and signal integration node, it has not previously been implicated in mitotic translation. Out of 17 identified eIF4G phosphosites, 7 were elevated >5-fold in mitosis. We focused our efforts on Ser1232, since it (i) is a major phosphosite in eIF4G, (ii) is phosphorylated by Erk1/2 upon activation of Pkc/Raf signals, and (iii) exerts control over the eIF4G/-4A/-4B translation initiation helicase complex and its function in unwinding and scanning (4). The time course of eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation in synchronized cells strongly correlated with the accumulation of p-H3(Ser10) and cyclin B1 during mitosis. Modulation of Cdk1 activity in vivo, Cdk1 inhibitors in vitro, Cdk1:cyclin B1 depletion-reconstitution in vitro, and co-IP studies suggest that eIF4G(Ser1232) is a Cdk1:cyclin B1 substrate in mitosis.
Our analyses indicate that eIF4G-protein interactions are altered during mitosis and that phosphorylation of Ser1232 plays a role in regulating these events. DDX3, an RNA-dependent ATPase/DEAD box helicase, exhibits enhanced binding with eIF4G(41-1600) at the end of and after exit from mitosis. DDX3 is implicated in various aspects of protein synthesis control, such as translation initiation (46) and repression (47) or ribonucleoprotein rearrangements (28), but its precise functions remain unclear. Several translation initiation factors may interact with DDX3: eIF4G (in yeast [28]), eIF4E (47), PABP (48), and or eIF3 (49). We did not detect DDX3 binding with the eIF4G(1222-1600) fragment, excluding direct interactions of DDX3 with the C-terminal portion of eIF4G or its binding partners (eIF4A, -4B, or -3 or Mnk).
eIF4A has poor helicase activity on its own and requires a complex with eIF4G and the accessory protein eIF4B for optimal activity (1). eIF4B is part of the translation initiation helicase complex forming at eIF4G HEAT1 (29), but we previously identified a second binding site for eIF4B in the distal IDL (aa 1222 to 1245) (4), in direct proximity to the eIF4A binding site in HEAT2 (Fig. 1A and 8A) (29). Erk1/2-mediated phosphorylation of Ser1232 leads to dissociation of eIF4B from the IDL (4); our present evidence suggests that Cdk1:cyclin B1 phosphorylation of the same residue during mitosis has an identical effect. eIF4B is a downstream effector of major signaling pathways that control translation initiation. eIF4B(Ser406/422) are convergent substrates of the rpS6 kinase (downstream of mTOR) and Rsk (downstream of Erk1/2) (reviewed in reference 1). Our phosphoproteomic data suggest that eIF4B, which coimmunoprecipitated with eIF4G in mitosis (presumably due to binding to HEAT1), was not phosphorylated at the mitogen-activated Ser406/422 sites but showed >10-fold-enhanced phosphorylation at Ser214 and Tyr592 in mitosis. Meanwhile, phosphorylation of Ser459 and Ser462 was decreased in mitosis relative to interphase. The biological function of these events is unclear, but these events suggest that regulation of eIF4B binding to eIF4G during mitosis may involve simultaneous signals to both partners. Separately, formation of the translation initiation helicase complex may be codetermined by signals to eIF4B that control its interactions with eIF4A.
Binding of eIF4G HEAT2 with eIF4A is inhibitory for the unwinding and ATPase activities of eIF4A (29), due to ∼10-fold-decreased affinity of both ATP and RNA for eIF4A bound to HEAT2 (50). Our data suggest that mitotic phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) by Cdk1 stimulates binding of eIF4A with full-size eIF4G, due to increased eIF4G HEAT2-eIF4A interactions, and thereby inhibits RNA-binding properties of the translation initiation helicase complex. This conclusion is in agreement with an in vitro model (based on isothermal titration experiments) in which RNA binding of eIF4G HEAT2-eIF4A was anticooperative (29). Protein synthesis is the most energy-consuming process in the cell; idling the eIF4A helicase in an inactive complex with eIF4G HEAT2 during mitosis may preclude nonproductive ATPase activity. Our observation of a “frozen” eIF4G HEAT2-eIF4A complex in mitosis, due to Ser1232 phosphorylation by Cdk1:cyclin B1, agrees with profound, global translation repression in mitosis. We recently reported that phorbol ester-induced phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) by Erk1/2 causes dissociation of the eIF4G HEAT2 domain from the complex with initiation factors eIF4A/-4B/-3A and stimulates the association of HEAT3 domain with Mnk1 (4). Here, we showed that mitotic phosphorylation of the same residue by Cdk1:cyclin B1, while similarly increasing HEAT3-Mnk1 binding and IDL-eIF4B dissociation, exerts very different effects on other protein interactions with the eIF4G terminus. The key difference is a vast increase of eIF4G-HEAT2 binding to eIF4A compared to the nonphosphorylatable Ser1232Ala mutant. Thus, phosphorylation of the same site by different kinases at different stages of the cell cycle results in opposite effects on eIF4G-HEAT2 association with eIF4A.
In cells with endogenous eIF4G depletion/eIF4G(Ser1232Ala) reconstitution, interphase translation was slightly reduced, while mitotic translation was modestly increased. This indicates that eIF4G(Ser1232) phosphorylation by Cdk1:cyclin B1 participates in but cannot account for the mitotic translation shift alone. In mitotic mammalian cells, >1,000 proteins, including multiple translation initiation factors, translation elongation factors, accessory proteins, and ribosomal proteins, are targeted with over 14,000 phosphorylation events (26). It is inconceivable that any single one of these events controls the mitotic translation shift. Our research revealed a novel regulatory mechanism over translation initiation helicases in mitosis via phosphorylation of eIF4G(Ser1232) by Cdk1:cyclin B1. Our data shed light on a major convergent signaling node involved in cell cycle control and a mechanism contributing to translation repression in mitosis.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to Erik Soderblom, J. Will Thompson, Meredith E. Turner, and other members of the Proteomics Core Facility at Duke University for their help with phosphoproteomic analyses. We thank Pavel Nikitin for his assistance with FACS analyses.
This work was supported by PHS grants CA140510 and CA124756 (M.G.).
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 18 November 2013
REFERENCES
- 1.Parsyan A, Svitkin Y, Shahbazian D, Gkogkas C, Lasko P, Merrick WC, Sonenberg N. 2011. mRNA helicases: the tacticians of translational control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12:235–245. 10.1038/nrm3083 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Marintchev A, Wagner G. 2005. eIF4G and CBP80 share a common origin and similar domain organization: implications for the structure and function of eIF4G. Biochemistry 44:12265–12272. 10.1021/bi051271v [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dobrikov M, Dobrikova E, Shveygert M, Gromeier M. 2011. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G1 (eIF4G1) by protein kinase Cα regulates eIF4G1 binding to Mnk1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 31:2947–2959. 10.1128/MCB.05589-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dobrikov MI, Dobrikova EY, Gromeier M. 2013. Dynamic regulation of the translation initiation helicase complex by mitogenic signal transduction to eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G. Mol. Cell. Biol. 33:937–946. 10.1128/MCB.01441-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Konrad CG. 1963. Protein synthesis and Rna synthesis during mitosis in animal cells. J. Cell Biol. 19:267–277. 10.1083/jcb.19.2.267 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Prescott DM, Bender MA. 1962. Synthesis of RNA and protein during mitosis in mammalian tissue culture cells. Exp. Cell Res. 26:260–268. 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90176-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fan H, Penman S. 1970. Regulation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. II. Inhibition of protein synthesis at the level of initiation during mitosis. J. Mol. Biol. 50:655–670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wilker EW, van Vugt MA, Artim SA, Huang PH, Petersen CP, Reinhardt HC, Feng Y, Sharp PA, Sonenberg N, White FM, Yaffe MB. 2007. 14-3-3sigma controls mitotic translation to facilitate cytokinesis. Nature 446:329–332. 10.1038/nature05584 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sivan G, Aviner R, Elroy-Stein O. 2011. Mitotic modulation of translation elongation factor 1 leads to hindered tRNA delivery to ribosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 286:27927–27935. 10.1074/jbc.M111.255810 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pyronnet S, Dostie J, Sonenberg N. 2001. Suppression of cap-dependent translation in mitosis. Genes Dev. 15:2083–2093. 10.1101/gad.889201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hara K, Maruki Y, Long X, Yoshino K, Oshiro N, Hidayat S, Tokunaga C, Avruch J, Yonezawa K. 2002. Raptor, a binding partner of target of rapamycin (TOR), mediates TOR action. Cell 110:177–189. 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00833-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, King JE, Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Sabatini DM. 2002. mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell 110:163–175. 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00808-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pause A, Belsham GJ, Gingras AC, Donze O, Lin TA, Lawrence JC, Jr, Sonenberg N. 1994. Insulin-dependent stimulation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of a regulator of 5′-cap function. Nature 371:762–767. 10.1038/371762a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gwinn DM, Asara JM, Shaw RJ. 2010. Raptor is phosphorylated by cdc2 during mitosis. PLoS One 5:e9197. 10.1371/journal.pone.0009197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Heesom KJ, Gampel A, Mellor H, Denton RM. 2001. Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of the translational repressor eIF-4E binding protein-1 (4E-BP1). Curr. Biol. 11:1374–1379. 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00422-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ramírez-Valle F, Badura ML, Braunstein S, Narasimhan M, Schneider RJ. 2010. Mitotic raptor promotes mTORC1 activity, G(2)/M cell cycle progression, and internal ribosome entry site-mediated mRNA translation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30:3151–3164. 10.1128/MCB.00322-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Boyer D, Quintanilla R, Lee-Fruman KK. 2008. Regulation of catalytic activity of S6 kinase 2 during cell cycle. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 307:59–64. 10.1007/s11010-007-9584-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Petretti C, Savoian M, Montembault E, Glover DM, Prigent C, Giet R. 2006. The PITSLRE/CDK11p58 protein kinase promotes centrosome maturation and bipolar spindle formation. EMBO Rep. 7:418–424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cornelis S, Bruynooghe Y, Denecker G, Van Huffel S, Tinton S, Beyaert R. 2000. Identification and characterization of a novel cell cycle-regulated internal ribosome entry site. Mol. Cell 5:597–605. 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80239-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pyronnet S, Pradayrol L, Sonenberg N. 2000. A cell cycle-dependent internal ribosome entry site. Mol. Cell 5:607–616. 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80240-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shveygert M, Kaiser C, Bradrick SS, Gromeier M. 2010. Regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase occurs through modulation of Mnk1-eIF4G interaction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30:5160–5167. 10.1128/MCB.00448-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nesvizhskii AI, Keller A, Kolker E, Aebersold R. 2003. A statistical model for identifying proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 75:4646–4658. 10.1021/ac0341261 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Beausoleil SA, Villen J, Gerber SA, Rush J, Gygi SP. 2006. A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization. Nat. Biotechnol. 24:1285–1292. 10.1038/nbt1240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kaiser C, Dobrikova EY, Bradrick SS, Shveygert M, Herbert JT, Gromeier M. 2008. Activation of cap-independent translation by variant eukaryotic initiation factor 4G in vivo. RNA 14:2170–2182. 10.1261/rna.1171808 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zeng Y, Cai X, Cullen BR. 2005. Use of RNA polymerase II to transcribe artificial microRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 392:371–380. 10.1016/S0076-6879(04)92022-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dephoure N, Zhou C, Villen J, Beausoleil SA, Bakalarski CE, Elledge SJ, Gygi SP. 2008. A quantitative atlas of mitotic phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105:10762–10767. 10.1073/pnas.0805139105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hsu PP, Kang SA, Rameseder J, Zhang Y, Ottina KA, Lim D, Peterson TR, Choi Y, Gray NS, Yaffe MB, Marto JA, Sabatini DM. 2011. The mTOR-regulated phosphoproteome reveals a mechanism of mTORC1-mediated inhibition of growth factor signaling. Science 332:1317–1322. 10.1126/science.1199498 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hilliker A, Gao Z, Jankowsky E, Parker R. 2011. The DEAD-box protein Ded1 modulates translation by the formation and resolution of an eIF4F-mRNA complex. Mol. Cell 43:962–972. 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Marintchev A, Edmonds KA, Marintcheva B, Hendrickson E, Oberer M, Suzuki C, Herdy B, Sonenberg N, Wagner G. 2009. Topology and regulation of the human eIF4A/4G/4H helicase complex in translation initiation. Cell 136:447–460. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hornbeck PV, Kornhauser JM, Tkachev S, Zhang B, Skrzypek E, Murray B, Latham V, Sullivan M. 2012. PhosphoSitePlus: a comprehensive resource for investigating the structure and function of experimentally determined post-translational modifications in man and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:261–270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Raught B, Gingras AC, Gygi SP, Imataka H, Morino S, Gradi A, Aebersold R, Sonenberg N. 2000. Serum-stimulated, rapamycin-sensitive phosphorylation sites in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4GI. EMBO J. 19:434–444. 10.1093/emboj/19.3.434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Goto H, Tomono Y, Ajiro K, Kosako H, Fujita M, Sakurai M, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Okigaki T, Takahashi T, Inagaki M. 1999. Identification of a novel phosphorylation site on histone H3 coupled with mitotic chromosome condensation. J. Biol. Chem. 274:25543–25549. 10.1074/jbc.274.36.25543 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Songyang Z, Blechner S, Hoagland N, Hoekstra MF, Piwnica-Worms H, Cantley LC. 1994. Use of an oriented peptide library to determine the optimal substrates of protein kinases. Curr. Biol. 4:973–982. 10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00221-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Songyang Z, Lu KP, Kwon YT, Tsai LH, Filhol O, Cochet C, Brickey DA, Soderling TR, Bartleson C, Graves DJ, DeMaggio AJ, Hoekstra MF, Blenis J, Hunter T, Cantley LC. 1996. A structural basis for substrate specificities of protein Ser/Thr kinases: primary sequence preference of casein kinases I and II, NIMA, phosphorylase kinase, calmodulin-dependent kinase II, CDK5, and Erk1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:6486–6493 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ren S, Rollins BJ. 2004. Cyclin C/cdk3 promotes Rb-dependent G0 exit. Cell 117:239–251. 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00300-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Russell P, Nurse P. 1987. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell 49:559–567. 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Russell P, Nurse P. 1986. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell 45:145–153. 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Potapova TA, Sivakumar S, Flynn JN, Li R, Gorbsky GJ. 2011. Mitotic progression becomes irreversible in prometaphase and collapses when Wee1 and Cdc25 are inhibited. Mol. Biol. Cell 22:1191–1206. 10.1091/mbc.E10-07-0599 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Neef R, Gruneberg U, Kopajtich R, Li X, Nigg EA, Sillje H, Barr FA. 2007. Choice of Plk1 docking partners during mitosis and cytokinesis is controlled by the activation state of Cdk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 9:436–444. 10.1038/ncb1557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mikolcevic P, Sigl R, Rauch V, Hess MW, Pfaller K, Barisic M, Pelliniemi LJ, Boesl M, Geley S. 2012. Cyclin-dependent kinase 16/PCTAIRE kinase 1 is activated by cyclin Y and is essential for spermatogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 32:868–879. 10.1128/MCB.06261-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Beck M, Schmidt A, Malmstroem J, Claassen M, Ori A, Szymborska A, Herzog F, Rinner O, Ellenberg J, Aebersold R. 2011. The quantitative proteome of a human cell line. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7:549. 10.1038/msb.2011.82 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aviner R, Geiger T, Elroy-Stein O. 2013. Novel proteomic approach (PUNCH-P) reveals cell cycle-specific fluctuations in mRNA translation. Genes Dev. 27:1834–1844. 10.1101/gad.219105.113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vassilev LT, Tovar C, Chen S, Knezevic D, Zhao X, Sun H, Heimbrook DC, Chen L. 2006. Selective small-molecule inhibitor reveals critical mitotic functions of human CDK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103:10660–10665. 10.1073/pnas.0600447103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sivan G, Kedersha N, Elroy-Stein O. 2007. Ribosomal slowdown mediates translational arrest during cellular division. Mol. Cell. Biol. 27:6639–6646. 10.1128/MCB.00798-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rhind N, Russell P. 2012. Signaling pathways that regulate cell division. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. 4:a005942. 10.1101/cshperspect.a005942 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chuang RY, Weaver PL, Liu Z, Chang TH. 1997. Requirement of the DEAD-Box protein ded1p for messenger RNA translation. Science 275:1468–1471. 10.1126/science.275.5305.1468 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shih JW, Tsai TY, Chao CH, Wu Lee YH. 2008. Candidate tumor suppressor DDX3 RNA helicase specifically represses cap-dependent translation by acting as an eIF4E inhibitory protein. Oncogene 27:700–714. 10.1038/sj.onc.1210687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Soto-Rifo R, Rubilar PS, Limousin T, de Breyne S, Decimo D, Ohlmann T. 2012. DEAD-box protein DDX3 associates with eIF4F to promote translation of selected mRNAs. EMBO J. 31:3745–3756. 10.1038/emboj.2012.220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lee CS, Dias AP, Jedrychowski M, Patel AH, Hsu JL, Reed R. 2008. Human DDX3 functions in translation and interacts with the translation initiation factor eIF3. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:4708–4718. 10.1093/nar/gkn454 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Korneeva NL, First EA, Benoit CA, Rhoads RE. 2005. Interaction between the NH2-terminal domain of eIF4A and the central domain of eIF4G modulates RNA-stimulated ATPase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 280:1872–1881. 10.1074/jbc.M406168200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Trost B, Kusalik A. 2011. Computational prediction of eukaryotic phosphorylation sites. Bioinformatics 27:2927–2935. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]