Abstract
The interaction of terminal complement proteins (C5-C9) with normal erythrocytes and type III paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes (PNH-E) has been compared in terms of binding of the C5-9 complex, C9 polymerization, and C9 insertion into membranes. Complement components C5, C7, and C8 bind equally well to both types of erythrocytes, whereas the binding of C9 to PNH-E is 5-6 times greater than that to normal erythrocytes. The kinetics of C9 binding was compared with the kinetics of lysis for both types of cells under conditions leading to 100% lysis. There was a noticeable lag time between C9 binding and lysis of normal erythrocytes, but the lysis of PNH-E proceeded without a lag and the kinetics of lysis more closely paralleled C9 binding. The efficiency of C9 insertion was similar for both types of cells, but C9 polymerization was significantly enhanced on PNH-E. These data indicate that the enhanced susceptibility of type III PNH-E toward lysis by C5-9 can be correlated with abnormally high C9 binding and increased formation of poly(C9).
Full text
PDF



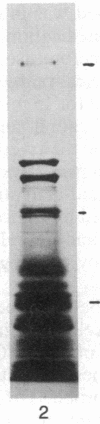
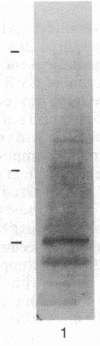
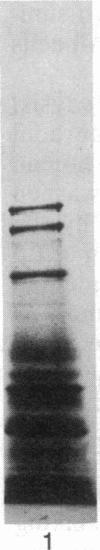
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J., Klump O. The terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement. Evidence for the existence of multiple protease-resistant polypeptides that form the trans-membrane complement channel. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2451–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. On the cause and nature of C9-related heterogeneity of terminal complement complexes generated on target erythrocytes through the action of whole serum. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1453–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Borsos T. Studies on the terminal stages of immune hemolysis. V. Evidence that not all complement-produced transmembrane channels are equal. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DACIE J. V. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Proc R Soc Med. 1963 Jul;56:587–596. doi: 10.1177/003591576305600723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert J. R., Esser A. F. Proteolytic modification of human complement protein C9: loss of poly(C9) and circular lesion formation without impairment of function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2128–2132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham T. H., Dingle J. H. STUDIES ON DESTRUCTION OF RED BLOOD CELLS. II. CHRONIC HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA WITH PAROXYSMAL NOCTURNAL HEMOGLOBINURIA: CERTAIN IMMUNOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF THE HEMOLYTIC MECHANISM WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO SERUM COMPLEMENT. J Clin Invest. 1939 Nov;18(6):657–672. doi: 10.1172/JCI101081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. C., Jenkins D. E. The "sugar-water" test for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jul 21;275(3):155–157. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196607212750308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu V. W., Esser A. F., Podack E. R., Wisnieski B. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: photolabeling reveals insertion of terminal proteins into target membrane. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):380–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu V. W., Holmes R. K. Evidence for direct insertion of fragments A and B of diphtheria toxin into model membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12226–12233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu V. W., Shin M. L. Species-restricted target cell lysis by human complement: complement-lysed erythrocytes from heterologous and homologous species differ in their ratio of bound to inserted C9. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2133–2137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu V. W., Wisnieski B. J. Photoreactive labeling of M13 coat protein in model membranes by use of a glycolipid probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5460–5464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Hammer C. H., Mayer M. M., Shin M. L. Activation of the fifth and sixth component of the complement system: similarities between C5b6 and C(56)a with respect to lytic enhancement by cell-bound C3b or A2C, and species preferences of target cell. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):999–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata K. K., Manweiler C. A., Bramhall J., Wisnieski B. J. Photoreactive probes for high resolution mapping of membrane proteins. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1978;22:579–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. M., Shin M. L., Mayer M. M. On the lysis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes by complement: dual role of C3b. Blut. 1982 Oct;45(4):249–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00320192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular analysis of the membrane attack mechanism of complement. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):549–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Kinoshita T., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of complement activation on the surface of cells after incorporation of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) into their membranes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1558–1578. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., March J. P., Rosenfeld S. I., Austen K. F. Affected erythrocytes of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria are deficient in the complement regulatory protein, decay accelerating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman C. H., Rosenfeld S. I., Jenkins D. E., Jr, Thiem P. A., Leddy J. P. Complement lysis of human erythrocytes. Differeing susceptibility of two types of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells to C5b-9. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):428–433. doi: 10.1172/JCI109479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Deficiency of an erythrocyte membrane protein with complement regulatory activity in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5430–5434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschoop J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular organization of C9 within the membrane attack complex of complement. Induction of circular C9 polymerization by the C5b-8 assembly. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):268–282. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschopp J. Circular polymerization of the ninth component of complement. Ring closure of the tubular complex confers resistance to detergent dissociation and to proteolytic degradation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15204–15212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Whitlow M. B., Mayer M. M. Transmembrane channel formation by complement: functional analysis of the number of C5b6, C7, C8, and C9 molecules required for a single channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4751–4755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb M., Nichols J. C., Whoriskey S. K., Murphy J. R. Isolation of hybridoma cell lines and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against cholera enterotoxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):267–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.267-272.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Jenkins D. E., Jr, Leddy J. P. Enhanced reactive lysis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes by C5b-9 does not involve increased C7 binding or cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Packman C. H., Jenkins D. E., Jr, Countryman J. K., Leddy J. P. Complement lysis of human erythrocytes. III. Differing effectiveness of human and guinea pig C9 on normal and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2063–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Dacie J. V. Immune lysis of normal human and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) red blood cells. I. The sensitivity of PNH red cells to lysis by complement and specific antibody. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):736–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI105388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Logue G. L., Adams J., Crookston J. H. Mechanisms of immune lysis of the red cells in hereditary erythroblastic multinuclearity with a positive acidified serum test and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):31–43. doi: 10.1172/JCI107551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria--present status and future prospects. West J Med. 1980 Mar;132(3):219–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F. Variations in the red cells in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol. 1973 Mar;24(3):327–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria revisited. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 22;309(12):723–725. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309223091209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steckel E. W., Welbaum B. E., Sodetz J. M. Evidence of direct insertion of terminal complement proteins into cell membrane bilayers during cytolysis. Labeling by a photosensitive membrane probe reveals a major role for the eighth and ninth components. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4318–4324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J. Ultrastructure of the membrane attack complex of complement. Heterogeneity of the complex caused by different degree of C9 polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7857–7863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]