Abstract
Bats are known to host viruses closely related to important human coronaviruses (HCoVs), such as HCoV-229E, severe-acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), and Middle East respiratory syndrome CoV (MERS-CoV). As RNA viruses may coevolve with their hosts, we sought to investigate the closest sister taxon to bats, the Eulipotyphla, and screened European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) from Germany for CoV by nested reverse transcriptase PCR. A novel betacoronavirus species in a phylogenetic sister relationship to MERS-CoV and clade c bat CoVs was detected and characterized on the whole-genome level. A total of 58.9% of hedgehog fecal specimens were positive for the novel CoV (EriCoV) at 7.9 log10 mean RNA copies per ml. EriCoV RNA concentrations were higher in the intestine than in other solid organs, blood, or urine. Detailed analyses of the full hedgehog intestine showed the highest EriCoV concentrations in lower gastrointestinal tract specimens, compatible with viral replication in the lower intestine and fecal-oral transmission. Thirteen of 27 (48.2%) hedgehog sera contained non-neutralizing antibodies against MERS-CoV. The animal origins of this betacoronavirus clade that includes MERS-CoV may thus include both bat and nonbat hosts.
TEXT
The Coronaviridae subfamily Coronavirinae contains the four genera Alpha-, Beta-, Gamma- and Deltacoronavirus (1, 2). Betacoronaviruses are further discriminated into clades a to d. Until recently, five human coronaviruses (HCoVs) were known, namely, the alphacoronaviruses HCoV-229E and HCoV-NL63 and the betacoronaviruses HCoV-OC43, HCoV-HKU1 (both clade a), and Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV, clade b) (3–8). In 2012, a highly pathogenic novel HCoV termed Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) emerged (9–11). MERS-CoV belongs to the Betacoronavirus clade c, which previously contained only bat CoVs (BtCovs) (12–17). Because of the high number of bat CoVs newly described in the aftermath of SARS, it was assumed that all mammalian CoVs originated in the order Chiroptera (18). The majority of these novel bat CoVs were found in insectivorous bats (18). Therefore, we speculated that other insectivorous mammals could also harbor CoVs. This might specifically apply to the animal order Eulipotyphla, which includes hedgehogs, moles, solenodons, and shrews, because this and the order Chiroptera are phylogenetically related (19). For this reason, we analyzed fecal samples from 248 European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) for CoVs. A novel betacoronavirus clade c species was found and described using molecular and immunologic tools.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection, processing, and screening for coronavirus RNA.
Fecal samples from European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) kept in an animal shelter in northern Germany because of poor physical condition or injuries were sampled noninvasively and stored in RNAlater (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) at −20°C until further investigation. For the initial CoV screening, fecal samples of 10 individual animals were pooled. RNA purification and CoV detection using two different nested reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) assays targeting the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) gene were done as described previously (16, 20, 21). Individual specimens in positive pools were identified using a strain-specific real-time RT-PCR (oligonucleotide sequences available upon request) based on the nucleotide sequences obtained from sequencing of initial PCR amplicons. For phylogenetic analyses, sequences from the PCR screening assays were extended to an 816-nucleotide (nt) RdRp fragment (22). In addition, carcasses from 27 hedgehogs that died in the animal shelter during their stay were collected and stored at −20°C until dissection. Samples from the brain, heart, lung, liver, kidney, spleen, and intestine were taken. The intestines of five additional CoV-positive animals were cleaned and dissected in 10 portions taken in equal intervals immediately after the stomach and until the anal orifice.
Blood was sampled from inside the heart and urine from inside the bladder by puncture of these organs before removal. Quantification of viral RNA was done using strain-specific assays and photometrically quantified in vitro cRNA transcripts as described previously (10, 23).
Whole-genome sequencing.
RNA extracts of two positive samples were determined and prepared for 454 next-generation sequencing (NGS) as described previously (24, 25). Sequences obtained from 454-NGS were reproduced on individual samples and connected by long-range reverse transcription-PCR using specific oligonucleotide primers (available upon request). Determination of the 5′ and 3′ genome ends was done using a rapid amplification of cDNA ends kit (Roche, Penzberg, Germany). PCR products were sequenced by dye terminator chemistry (Seqlab, Goettingen, Germany).
Genome analyses.
The nucleotide sequences of the genomes and the amino acid sequences of the presumed open reading frames (ORFs) were compared to other c clade betacoronaviruses for which full-length genome sequences were available. Nucleic acid alignments were done based on the amino acid coding using the MAFFT algorithm (26) in the geneious software package (Biomatters, Auckland, New Zealand). Phylogenetic analyses of the extended screening fragments, as well as the presumed ORFs, were done using MrBayes version 3.1 (27) using a WAG amino acid substitution model and 4,000,000 generations sampled every 100 steps. Trees were annotated using a burn-in of 10,000 in TreeAnnotator version 1.5 and visualized with FigTree version 1.4 from the BEAST package (28). The pairwise identities of all ORFs and predicted proteins of the two Erinaceus CoVs (EriCoV) were calculated using MEGA5 (29). Similarity plots were generated using SSE version 1.0 (30) using a sliding window of 400 and a step size of 40 nucleotides.
Virus isolation attempts.
Isolation of virus from those specimens containing the highest RNA concentrations was attempted on Vero E6 cells, which are known to support MERS-CoV infection (31). In addition, immortalized kidney cells of a Pipistrellus bat and immortalized lung cells from Crocidura suaveolens from the animal order Eulipotyphla were used for isolation attempts (our own unpublished cell lines).
Serology.
Blood samples obtained during dissection of the 27 hedgehog carcasses were tested for antibodies against MERS-CoV using a commercially available indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA; Euromimmun AG, Lübeck, Germany) with slight modifications. A rabbit anti-suncus immunoglobulin G (IgG) adapted for cross-recognition of hedgehog Ig was used as a secondary antibody at a 1:200 dilution. Detection was done with a cyanine 3-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Dianova, Hamburg, Germany). Virus neutralization tests against MERS-CoV were done as described previously (32). Briefly, blood samples were serially diluted from 1:20 to 1:2,560 in serum-free medium, mixed with 100 PFU, and preincubated for 1 h at 37°C before being added to a Vero B4 cell monolayer. After adsorption for 1 h at 37°C, the serum-virus mixture was discarded and fresh medium (Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium) was added to the cells. Cytopathogenic effects were visualized 3 days postinfection by fixation and staining with crystal violet solution.
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
The four virus sequences obtained from European hedgehog fecal samples were deposited in GenBank with accession numbers KC545383 to KC545386.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Fecal specimens from 248 European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) were tested for CoVs by broad-range nested RT-PCRs. This approach yielded four different virus sequences. These sequences (GenBank accession numbers KC545383 to KC545386) were classifiable as clade c betacoronaviruses in initial BLAST comparisons and were named Erinaceus CoV (EriCoV). Within EriCoVs, two different clades separated by 3.1 to 3.4% nucleotide distance in an 816-nt RdRp fragment were identified. Figure 1 shows a Bayesian phylogeny of this RdRp fragment. All EriCoVs grouped phylogenetically within the Betacoronavirus clade c. The EriCoVs clustered in sister relationship to a clade defined by the bat CoVs HKU4 and HKU5, the MERS-CoV-related viruses, and a clade of Nycteris bat CoVs. The amino acid distances to the clade c prototype viruses HKU4, HKU5, and MERS-CoV were 7.7 to 8.8% in the translated 816-nt RdRp fragment. The distance from the Nycteris CoV was 8.5 to 9.2%. In our previous proposal to tentatively classify CoVs into RdRp-grouping units (RGU), which are predictive of species classification, betacoronavirus species were at least 6.3% different on the amino acid level in this sequence fragment (22). EriCoVs therefore represented a novel tentative betacoronavirus clade c species.
FIG 1.

Betacoronavirus phylogeny, including the novel viruses from European hedgehogs. Bayesian phylogeny of an 816-nucleotide RdRp gene sequence fragment corresponding to positions 14822 to 15637 in MERS-CoV strain EMC/2012 (GenBank accession no. JX869059). The novel Erinaceus viruses are shown in red, and MERS-CoVs in blue.
For an estimate of EriCoV prevalence and an assessment of viral RNA concentrations, all specimens were retested using strain-specific real-time RT-PCR assays. EriCoVs were now detected in 146 of 248 individual specimens (58.9%). Viral RNA concentrations were high, with a mean of 7.9 log10 copies per ml of fecal suspension (range, 4.2 to 11). Isolation of virus was attempted unsuccessfully on three different cell lines for those specimens containing the highest RNA concentrations.
The high detection rate and virus concentrations in feces appeared compatible with replication in the intestine. Therefore, 27 hedgehog carcasses were dissected and the intestines were tested using specific real-time RT-PCR assays. EriCoV RNA was found in intestinal specimens from 12 of these 27 animals (44.4%). The difference in detection rates between feces and intestinal specimens was not statistically significant (corrected χ2 = 1.5, P = 0.2). The data in Fig. 2A show that intestinal virus concentrations in these 12 animals were high, 6.78 log10 mean RNA copies per gram of tissue (range, 3.9 to 11.8). The mean virus concentrations in all other solid organs, urine, and blood from these 12 animals were at least 10-fold lower. This and the high EriCoV detection rate in feces might be compatible with a fecal-oral route of transmission. Furthermore, the high EriCoV concentrations were compatible with virus replication in the intestinal tract. This was comparable to viruses replicating in the human gut, such as Aichi, rota- and noroviruses (33). We could not determine if infection was associated with clinical disease in hedgehogs. While gastroenteritis caused by CoVs is not rare in animals (34), intestinal virus replication could also be asymptomatic or associated with nonenteric disease, similar to, e.g., human enteroviruses (35).
FIG 2.

Erinaceus CoV RNA concentrations in solid organs, urine, and blood, and virus distribution within the intestine. (A) Virus concentrations in solid organs, urine, and blood of 12 EriCoV-positive animals are given in log10 RNA copies per milliliter or gram of tissue. Horizontal bars represent mean virus concentrations per organ category. Missing bars represent negative test results. For all organs, specimens from 12 individual animals were available, except urine, where no specimen was available from animal 12. Colors represent individual animals as identified in the key. (B) Ranges of EriCoV concentrations in 10 different intestinal sections of five RNA-positive individuals are given in log10 RNA copies per gram of tissue. Black horizontal bars represent mean virus concentrations; ***, P < 0.005 according to Mann-Whitney U test.
Because only small fragments of the intestine of the initial 27 animals had been collected upon dissection, it was impossible to determine in which portion of the gastrointestinal tract the virus might replicate. Therefore, five additional EriCoV-positive intestines were identified by testing of 10 additional hedgehog carcasses. The entire intestines of these animals were cut into 10 equal-sized pieces starting from the stomach, and EriCoV RNA concentrations were determined in each portion. The data in Fig. 2B show that the highest concentrations were detected in distal (aboral) parts. The virus concentrations in these sections were significantly higher than those toward the stomach (Mann-Whitney U test, P < 0.005). This was comparable to the higher PCR positivity rates in aboral than in oral intestine sections in a previous study on Leschenault's rousette bats fed CoV-positive tissue from other bats (36).
To determine antigenic relatedness to MERS-CoV, hedgehog sera and secondary anti-suncus immunoglobulin (Ig) were adapted for use with a commercially available MERS-CoV IFA. At a serum dilution of 1:10, 13 of 27 (48.2%) blood specimens were reactive. The median IFA endpoint titers were 1:100 (range, 1:10 to 1:400). The images in Fig. 3 exemplify the IFA reaction patterns of positive and negative sera. To analyze whether the observed antibodies were indeed directed against MERS-CoV, all IFA-positive sera were tested in a MERS-CoV neutralization assay. None of the IFA-positive sera contained MERS-CoV neutralizing antibodies in dilutions higher than 1:20. This was compatible with cross-reactivity of anti-EriCoV antibodies with MERS-CoV, which they bound but did not neutralize, similar to cross-reactive anti-HCoV antibodies in humans (37, 38). The high frequency of EriCoV infection and the absence of other CoV sequences in hedgehogs in our study could indicate that all detected antibody titers were indeed specific for EriCoV. Six of the 13 IFA-positive animals (46.2%) showed concomitant detection of EriCoV RNA, implying that some hedgehogs may have cleared EriCoV infection or that a different CoV hypothetically elicited the observed antibody response. On the other hand, 6 of 12 PCR-positive animals (50%) showed no detectable antibodies, compatible with sampling before seroconversion.
FIG 3.

Serologic testing of hedgehog blood. (Top) Reaction patterns of a reactive (23) and a nonreactive (22) hedgehog serum with MERS-CoV-infected Vero cells at 1:10 screening dilution. (Bottom) Endpoint dilution of serum sample 23. Scale bar, 20 μm.
To confirm the RGU-based tentative species classification and to investigate the genetic relatedness between EriCoV and MERS-CoV, one whole-genome sequence was generated for each of the two EriCoV subclades (represented by viruses EriCoV/2012-174 and EriCoV/2012-216). The sizes of the two EriCoV genomes were 30,137 and 30,164 nt, with a G+C content of 37%. The numbers and locations of EriCoV ORFs, as well as seven transcription regulatory sequences (TRS) preceding them, were characteristic for clade c betacoronaviruses (2, 39). Figure 4 shows the genome organization of EriCoV and other clade c betacoronaviruses. Table 1 provides details on the TRS and their genomic localizations. The predicted leader TRS of EriCoV (AACUCUUGUUUUAACGAACUUAA) differed by only three nucleotides from those of the betacoronavirus clade c prototype viruses HKU4, HKU5, and MERS-CoV [AACUUUG(U/A)UUUUAACGAACUUAA] (40, 41). The predicted AUG codons of ORF3b, ORF4b, and ORF8b were not preceded by separate body TRS elements and may be translated from bicistronic mRNAs, as discussed for other CoVs, including MERS-CoV (39, 42, 43). In ORF1a/ORF1ab, a ribosomal frameshift was predicted based on the tentative slippery sequence UUUAAAC (indicated by an arrow in Fig. 4) (39, 44). Table 2 provides details on the sizes and genomic locations of the 16 predicted ORF1ab nonstructural proteins (nsp).
FIG 4.
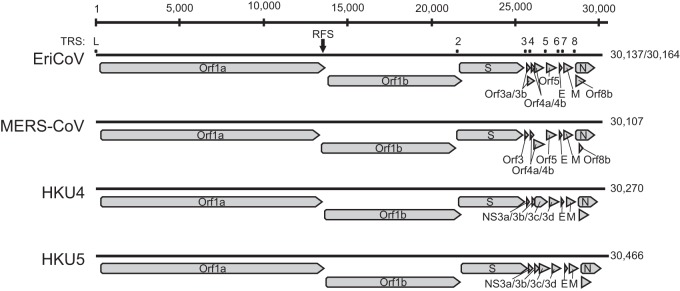
Genome organization of EriCoV and other clade c betacoronaviruses. Genomes are represented by black lines, and ORFs are indicated by gray arrows. The ribosomal frameshift site (RFS) at nucleotide positions 13578 to 13584 (EriCoV/2012-174) and 13605 to 13611 (EriCoV/2012-216) is marked with a black arrow. The locations of transcription regulatory core sequences (TRS) are marked by labeled dots.
TABLE 1.
Coding of potential and putative transcription regulatory sequences of the EriCoV genome sequences

TABLE 2.
Prediction of the putative polyprotein pp1a/pp1ab cleavage sites of hedgehog coronaviruses based on sequence comparison with MERS-CoV strain EMC/2012
| NSP | First–last amino acid residuesa of EriCoV/2012-174b | Protein size (aa) | First–last amino acid residues of EriCoV/2012-216c | Protein size (aa) | Putative functional domain(s)d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Met1–Gly200 | 200 | Met1–Gly200 | 200 | |
| 2 | Asp201–Gly859 | 659 | Asp201–Gly859 | 659 | |
| 3 | Ala860–Gly2805 | 1,946 | Ala860–Gly2814 | 1,955 | ADRP, PL2pro |
| 4 | Ser2806–Gln3310 | 505 | Ser2815–Gln3319 | 505 | |
| 5 | Ser3311–Gln3616 | 306 | Ser3320–Gln3625 | 306 | 3CLpro |
| 6 | Ser3617–Gln3908 | 292 | Ser3626–Gln3917 | 292 | |
| 7 | Ser3909–Gln3991 | 83 | Ser3918–Gln4000 | 83 | |
| 8 | Ser3992–Gln4190 | 199 | Ser4001–Gln4199 | 199 | Primase |
| 9 | Asn4191–Gln4300 | 110 | Asn4200–Gln4309 | 110 | |
| 10 | Ala4301–His4440 | 140 | Ala4310–His4449 | 140 | |
| 11 | Ser4441–Leu4454 | 14 | Ser4450–Leu4463 | 14 | Short peptide at the end of ORF1a |
| 12 | Ser4441–Gln5374 | 934 | Ser4450–Gln5383 | 934 | RdRp |
| 13 | Ala5375–Gln5972 | 598 | Ala5384–Gln5981 | 598 | Hel, NTPase |
| 14 | Ser5973–Gln6496 | 524 | Ser5982–Gln6505 | 524 | ExoN, NMT |
| 15 | Gly6497–Gln6839 | 343 | Gly6506–Gln6848 | 343 | NendoU |
| 16 | Ala6840–Cys7150 | 311 | Ala6849–Cys7159 | 311 | OMT |
Superscript numbers indicate positions in polyprotein pp1a/pp1ab, with the supposition of a ribosomal frameshift resulting in a peptide bond between Asn4448/Arg4449 (EriCoV/2012-174/GER/2012) and Asn4457/Arg4458 (EriCoV/2012-216/GER/2012) for the expression of ORF1ab.
GenBank accession number KC545383.
GenBank accession number KC545386.
ADRP, ADP-ribose 1″-phosphatase; PL2pro, papain-like protease 2; 3CLpro, coronavirus nsp5 protease; Hel, helicase; NTPase, nucleoside triphosphatase; ExoN, exoribonuclease; NMT, N7 methyltransferase; NendoU, endoribonuclease; OMT, 2′ O-methyltransferase.
A separate comparison of the amino acid sequences of seven conserved ORF1ab domains, as suggested by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) for formal CoV species delineation, is shown in Table 3. The sequence identities of the seven concatenated domains compared to those of other clade c viruses (82.4 to 86.9%) were well below the 90% threshold proposed by the ICTV (41), confirming the presence of a separate new CoV species.
TABLE 3.
Comparison of amino acid identities of seven conserved replicase domains of the hedgehog coronavirus and prototype clade c betacoronaviruses for species delineation
| Domain | % amino acid sequence identity (range): |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within EriCoVa | Of EriCoV compared to: |
|||
| MERS-CoVb | HKU4c | HKU5d | ||
| ADRP | 96.9–100 | 71.3 | 57.5–59.4 | 61.3–61.9 |
| NSP5 (3CLpro) | 99.0–100 | 79.1–79.7 | 72.9–73.5 | 76.8–77.1 |
| NSP12 (RdRp) | 99.0–100 | 88.9–89.4 | 87.2–88.1 | 88.1–88.7 |
| NSP13 (Hel, NTPase) | 99.6–100 | 91.1–91.5 | 89.5–90.0 | 90.3–90.8 |
| NSP14 (ExoN, NMT) | 99.6–100 | 89.5–89.9 | 83.2–84.3 | 88.0–88.4 |
| NSP15 (NendoU) | 97.1–100 | 82.5–83.1 | 74.3–75.4 | 78.4–79.3 |
| NSP16 (OMT) | 99.0–100 | 86.5–87.5 | 81.5–82.1 | 83.8–85.1 |
| Concatenated domains | 98.9–100 | 86.9 | 82.4–82.8 | 84.8–85 |
Figure 5 shows a comparison of the complete genomic nucleotide sequences of EriCoVs and HKU4, HKU5, and MERS-CoV. The EriCoVs shared 96.9% overall nucleotide identity across the two whole genomes (red line). They were almost equidistant from the prototype clade c betacoronaviruses (orange and pale and dark blue lines). Table 4 summarizes the amino acid sequence identities between the predicted proteins of EriCoV and other clade c betacoronaviruses. The highest amino acid sequence identity between EriCoV and the other clade c CoVs was observed for the membrane protein, with 78.0 to 79.4% identity, and the lowest identity was observed within ORF3a, with 26.7 to 28.9% identity. These values were similar to values found in sequence comparisons between MERS-CoV and the prototype clade c betacoronaviruses HKU4 and HKU5 (41).
FIG 5.
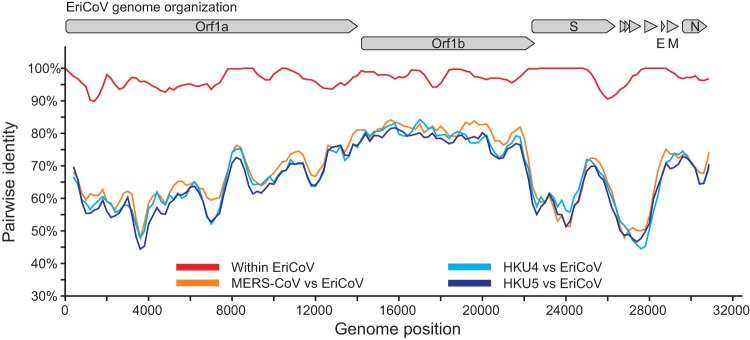
Genomic sequence identity between EriCoVs and other clade c betacoronaviruses. Similarity plots were generated using SSE version 1.0 (38) using a sliding window of 400 and a step size of 40 nucleotides.
TABLE 4.
Identities between open reading frames of the novel hedgehog coronavirus and prototype clade c betacoronaviruses
| Annotation in EriCoV | Annotation in MERS-CoV/EMC | Annotation in BtCoV-HKU4 and BtCoV-HKU5 | % amino acid identitya: |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within EriCoV | Of MERS-CoVb to EriCoV | Of HKU4-1c to EriCoV | Of HKU5-1d to EriCoV | |||
| ORF1ab | ORF1ab | ORF1ab | 97.4 | 73.9–74.0 | 68.8–69.1 | 71.0–71.1 |
| S | S | S | 98.5 | 57.9–58.2 | 58.4–58.6 | 58.2–58.3 |
| ORF3a | ORF3 | NS3a | 92.3 | 26.7–28.9 | 28.2 | 27.8–28.9 |
| ORF3b | ORF4a | NS3b | 93.6 | 39.5 | 39.5 | 44.3 |
| ORF4a | ORF4a | NS3b | 97.5 | 39.5 | 39.5 | 44.3 |
| ORF4b | ORF4b | NS3c | 96.0 | 39.3–39.7 | 29.3 | 27.8 |
| ORF5 | ORF5 | NS3d | 100.0 | 52.2 | 38.3 | 45.1 |
| E (ORF6) | E | E | 100.0 | 72.0 | 62.2 | 59.8 |
| M (ORF7) | M | M | 99.5 | 78.9–79.4 | 78.0–78.4 | 78.9–79.4 |
| N (ORF8) | N | N | 98.6 | 71.9–72.1 | 71.1 | 69.4 |
| ORF8b | ORF8b | Undescribed | 93.5 | 53.6 | 41.2–42.8 | 46.6–47.6 |
Pairwise identities of all ORFs and predicted proteins of the two EriCoVs were calculated using alignments based on amino acid coding by the MAFFT algorithm (20) in the geneious software package (Biomatters) and MEGA5 (29).
Accession number JX869059.
Accession number EF065505.
Accession number EF065509.
Bayesian phylogenies of all EriCoV ORFs are shown in Fig. 6. EriCoVs clustered as a sister clade to all previously known bat-associated clade c CoVs and MERS-CoV. As in previous sequence comparisons between MERS-CoV and HKU4 and HKU5 (45), different topologies were observed for individual ORFs, in particular the envelope and nucleocapsid genes. While this might indicate ancient recombination, it could as well result from differential selective pressures acting on different genome portions, causing slightly deviating inferences of apical phylogenies in those closely related viruses. Analysis by Bootscans on nearly complete genome alignments identified no obvious signs of recombination.
FIG 6.
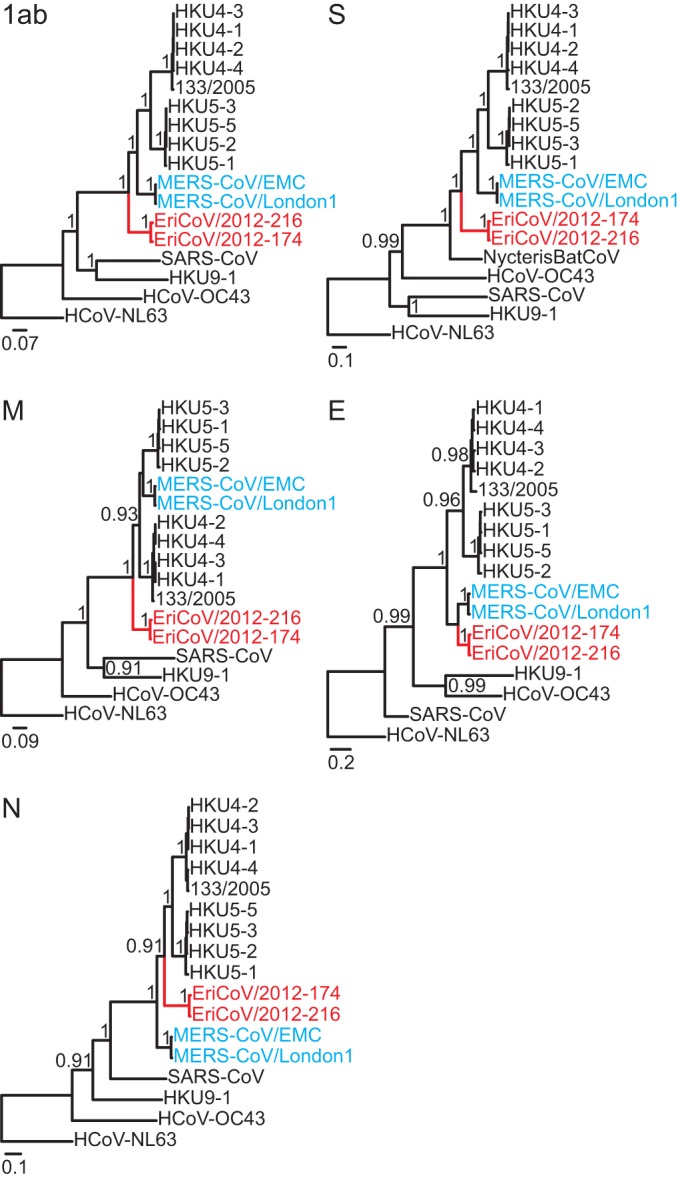
Phylogenies of all ORFs, including the novel hedgehog betacoronaviruses. Statistical support of grouping from Bayesian posterior probabilities is shown at deep nodes. For graphical reasons, only values above 0.7 are shown. Scale bar represents genetic distance. The novel Erinaceus viruses are shown in red, and MERS-CoVs in blue.
The failure to isolate EriCoV might predict a low potential to replicate in heterologous host cells, unlike MERS-CoV, which in cell culture shows relatively little host restriction (31). An analysis of the spike gene sequence indicated that EriCoV cellular entry may differ from that of MERS-CoV, because the receptor binding domain (RBD) of MERS-CoV (46–48) and the corresponding region of EriCoV showed only 36.7% amino acid identity (88 of 240 residues). Whether the corresponding region in the EriCoV Spike protein can interact with the MERS-CoV receptor dipeptidyl peptidase 4 or its hedgehog-specific homologue remains to be determined (49). The detailed genomic analysis of EriCoV may facilitate the generation of recombinant clade c viruses once reverse genetic systems for this betacoronavirus clade become available to clarify the zoonotic potential of EriCoV and identify potential virulence factors.
There is close phylogenetic relatedness between the mammalian orders Chiroptera, which includes bats, and Eulipotyphla, which includes hedgehogs (19, 50, 51). The phylogenetic clustering of EriCoV inside the bat-dominated clade c might hint at an exchange of viruses between bats and hedgehogs in the past, and yet, a divergence of EriCoV from bat CoVs during the formation of the eulipotyphlan stem lineage cannot be excluded. Further studies on putative CoVs in other insectivorous mammals, e.g., shrews or moles, in addition to CoVs in bats and an expansion of the nidovirus diversity in insects may therefore allow further hints at the evolutionary origins of CoVs. The detection of clade c betacoronaviruses in Chiroptera, Eulipotyphla, and primate hosts (humans) may be compatible with the high replicative capacity of MERS-CoV on different mammalian cell lines (31) and could imply that both bat and nonbat hosts should be investigated to elucidate the origins of MERS-CoV.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Monika Eschbach-Bludau, Tobias Bleicker, and Leonardo Calderón Obaldía (Institute of Virology, Bonn) for technical assistance. We are grateful to Manfred Göpner and the whole team of the Igel-Schutz-Initiative Laatzen e.V. for their help collecting samples. We also thank Sander van Boheemen and Ron A. M. Fouchier at Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, for providing MERS-CoV sequence alignments and Rainer Ulrich and Mathias Schlegel at Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut, Greifswald—Insel Riems for providing anti-suncus immunoglobulin.
This study was supported by the European Union FP7 projects EMPERIE (contract number 223498) and ANTIGONE (contract number 278976) and a grant from the German Centre for Infection Research (DZIF) to C.D.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 16 October 2013
REFERENCES
- 1.Adams MJ, Carstens EB. 2012. Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2012). Arch. Virol. 157:1411–1422. 10.1007/s00705-012-1299-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Perlman S, Netland J. 2009. Coronaviruses post-SARS: update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7:439–450. 10.1038/nrmicro2147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hamre D, Procknow JJ. 1966. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 121:190–193. 10.3181/00379727-121-30734 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van der Hoek L, Pyrc K, Jebbink MF, Vermeulen-Oost W, Berkhout RJ, Wolthers KC, Wertheim-van Dillen PM, Kaandorp J, Spaargaren J, Berkhout B. 2004. Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat. Med. 10:368–373. 10.1038/nm1024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S, Rabenau H, Panning M, Kolesnikova L, Fouchier RA, Berger A, Burguiere AM, Cinatl J, Eickmann M, Escriou N, Grywna K, Kramme S, Manuguerra JC, Muller S, Rickerts V, Sturmer M, Vieth S, Klenk HD, Osterhaus AD, Schmitz H, Doerr HW. 2003. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 348:1967–1976. 10.1056/NEJMoa030747 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fouchier RA, Hartwig NG, Bestebroer TM, Niemeyer B, de Jong JC, Simon JH, Osterhaus AD. 2004. A previously undescribed coronavirus associated with respiratory disease in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101:6212–6216. 10.1073/pnas.0400762101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McIntosh K, Dees JH, Becker WB, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM. 1967. Recovery in tracheal organ cultures of novel viruses from patients with respiratory disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 57:933–940. 10.1073/pnas.57.4.933 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Woo PC, Lau SK, Chu CM, Chan KH, Tsoi HW, Huang Y, Wong BH, Poon RW, Cai JJ, Luk WK, Poon LL, Wong SS, Guan Y, Peiris JS, Yuen KY. 2005. Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel coronavirus, coronavirus HKU1, from patients with pneumonia. J. Virol. 79:884–895. 10.1128/JVI.79.2.884-895.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. 2012. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 367:1814–1820. 10.1056/NEJMoa1211721 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Corman VM, Eckerle I, Bleicker T, Zaki A, Landt O, Eschbach-Bludau M, van Boheemen S, Gopal R, Ballhause M, Bestebroer TM, Muth D, Muller MA, Drexler JF, Zambon M, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RM, Drosten C. 2012. Detection of a novel human coronavirus by real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Euro Surveill. 17:pii20285 http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=20285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.de Groot RJ, Baker SC, Baric RS, Brown CS, Drosten C, Enjuanes L, Fouchier RA, Galiano M, Gorbalenya AE, Memish Z, Perlman S, Poon LL, Snijder EJ, Stephens GM, Woo PC, Zaki AM, Zambon M, Ziebuhr J. 2013. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): announcement of the Coronavirus Study Group. J. Virol. 87:7790–7792. 10.1128/JVI.01244-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Woo PC, Wang M, Lau SK, Xu H, Poon RW, Guo R, Wong BH, Gao K, Tsoi HW, Huang Y, Li KS, Lam CS, Chan KH, Zheng BJ, Yuen KY. 2007. Comparative analysis of twelve genomes of three novel group 2c and group 2d coronaviruses reveals unique group and subgroup features. J. Virol. 81:1574–1585. 10.1128/JVI.02182-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Anthony S, Ojeda-Flores R, Rico-Chavez O, Navarrete-Macias I, Zambrana-Torrelio C, Rostal MK, Epstein JH, Tipps T, Liang E, Sanchez-Leon M, Sotomayor-Bonilla J, Aguirre AA, Avila R, Medellin RA, Goldstein T, Suzan G, Daszak P, Lipkin WI. 2013. Coronaviruses in bats from Mexico. J. Gen. Virol. 94(Pt 5):1028–1038. 10.1099/vir.0.049759-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tang XC, Zhang JX, Zhang SY, Wang P, Fan XH, Li LF, Li G, Dong BQ, Liu W, Cheung CL, Xu KM, Song WJ, Vijaykrishna D, Poon LL, Peiris JS, Smith GJ, Chen H, Guan Y. 2006. Prevalence and genetic diversity of coronaviruses in bats from China. J. Virol. 80:7481–7490. 10.1128/JVI.00697-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Reusken CB, Lina PH, Pielaat A, de Vries A, Dam-Deisz C, Adema J, Drexler JF, Drosten C, Kooi EA. 2010. Circulation of group 2 coronaviruses in a bat species common to urban areas in Western Europe. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 10:785–791. 10.1089/vbz.2009.0173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Annan A, Baldwin HJ, Corman VM, Klose SM, Owusu M, Nkrumah EE, Badu EK, Anti P, Agbenyega O, Meyer B, Oppong S, Sarkodie YA, Kalko EK, Lina PH, Godlevska EV, Reusken C, Seebens A, Gloza-Rausch F, Vallo P, Tschapka M, Drosten C, Drexler JF. 2013. Human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012-related viruses in bats, Ghana and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 19:456–459. 10.3201/eid1903.121503 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ithete NL, Stoffberg S, Corman VM, Cottontail VM, Richards LR, Schoeman MC, Drosten C, Drexler JF, Preiser W. 2013. Close relative of human Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in South African bat. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 19:1697–1699. 10.3201/eid1910.130946 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Woo PC, Lau SK, Huang Y, Yuen KY. 2009. Coronavirus diversity, phylogeny and interspecies jumping. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 234:1117–1127. 10.3181/0903-MR-94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bininda-Emonds OR, Cardillo M, Jones KE, MacPhee RD, Beck RM, Grenyer R, Price SA, Vos RA, Gittleman JL, Purvis A. 2007. The delayed rise of present-day mammals. Nature 446:507–512. 10.1038/nature05634 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Corman VM, Muller MA, Costabel U, Timm J, Binger T, Meyer B, Kreher P, Lattwein E, Eschbach-Bludau M, Nitsche A, Bleicker T, Landt O, Schweiger B, Drexler JF, Osterhaus AD, Haagmans BL, Dittmer U, Bonin F, Wolff T, Drosten C. 2012. Assays for laboratory confirmation of novel human coronavirus (hCoV-EMC) infections. Euro Surveill. 17:pii20334 http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=20334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.de Souza Luna LK, Heiser V, Regamey N, Panning M, Drexler JF, Mulangu S, Poon L, Baumgarte S, Haijema BJ, Kaiser L, Drosten C. 2007. Generic detection of coronaviruses and differentiation at the prototype strain level by reverse transcription-PCR and nonfluorescent low-density microarray. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45:1049–1052. 10.1128/JCM.02426-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Drexler JF, Gloza-Rausch F, Glende J, Corman VM, Muth D, Goettsche M, Seebens A, Niedrig M, Pfefferle S, Yordanov S, Zhelyazkov L, Hermanns U, Vallo P, Lukashev A, Muller MA, Deng H, Herrler G, Drosten C. 2010. Genomic characterization of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus in European bats and classification of coronaviruses based on partial RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene sequences. J. Virol. 84:11336–11349. 10.1128/JVI.00650-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Drexler JF, Corman VM, Wegner T, Tateno AF, Zerbinati RM, Gloza-Rausch F, Seebens A, Muller MA, Drosten C. 2011. Amplification of emerging viruses in a bat colony. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 17:449–456. 10.3201/eid1703.100526 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Drexler JF, Corman VM, Muller MA, Maganga GD, Vallo P, Binger T, Gloza-Rausch F, Rasche A, Yordanov S, Seebens A, Oppong S, Adu Sarkodie Y, Pongombo C, Lukashev AN, Schmidt-Chanasit J, Stocker A, Carneiro AJ, Erbar S, Maisner A, Fronhoffs F, Buettner R, Kalko EK, Kruppa T, Franke CR, Kallies R, Yandoko ER, Herrler G, Reusken C, Hassanin A, Kruger DH, Matthee S, Ulrich RG, Leroy EM, Drosten C. 2012. Bats host major mammalian paramyxoviruses. Nat. Commun. 3:796. 10.1038/ncomms1796 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Palacios G, Quan PL, Jabado OJ, Conlan S, Hirschberg DL, Liu Y, Zhai J, Renwick N, Hui J, Hegyi H, Grolla A, Strong JE, Towner JS, Geisbert TW, Jahrling PB, Buchen-Osmond C, Ellerbrok H, Sanchez-Seco MP, Lussier Y, Formenty P, Nichol MS, Feldmann H, Briese T, Lipkin WI. 2007. Panmicrobial oligonucleotide array for diagnosis of infectious diseases. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 13:73–81. 10.3201/eid1301.060837 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K, Miyata T. 2002. MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:3059–3066. 10.1093/nar/gkf436 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP. 2003. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Drummond AJ, Rambaut A. 2007. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 7:214. 10.1186/1471-2148-7-214 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. 2011. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28:2731–2739. 10.1093/molbev/msr121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Simmonds P. 2012. SSE: a nucleotide and amino acid sequence analysis platform. BMC Res. Notes 5:50. 10.1186/1756-0500-5-50 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Muller MA, Raj VS, Muth D, Meyer B, Kallies S, Smits SL, Wollny R, Bestebroer TM, Specht S, Suliman T, Zimmermann K, Binger T, Eckerle I, Tschapka M, Zaki AM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA, Haagmans BL, Drosten C. 2012. Human coronavirus EMC does not require the SARS-coronavirus receptor and maintains broad replicative capability in mammalian cell lines. mBio 3(6):e00515–12. 10.1128/mBio.00515-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Reusken CB, Haagmans BL, Muller MA, Gutierrez C, Godeke GJ, Meyer B, Muth D, Raj VS, Vries LS, Corman VM, Drexler JF, Smits SL, El Tahir YE, De Sousa R, van Beek J, Nowotny N, van Maanen K, Hidalgo-Hermoso E, Bosch BJ, Rottier P, Osterhaus A, Gortazar-Schmidt C, Drosten C, Koopmans MP. 2013. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus neutralising serum antibodies in dromedary camels: a comparative serological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 13:859–866. 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70164-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Drexler JF, Baumgarte S, de Souza Luna LK, Eschbach-Bludau M, Lukashev AN, Drosten C. 2011. Aichi virus shedding in high concentrations in patients with acute diarrhea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 17:1544–1548 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Saif LJ. 2004. Animal coronaviruses: what can they teach us about the severe acute respiratory syndrome? Rev. Sci. Tech. 23:643–660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tapparel C, Siegrist F, Petty TJ, Kaiser L. 2013. Picornavirus and enterovirus diversity with associated human diseases. Infect. Genet. Evol. 14:282–293. 10.1016/j.meegid.2012.10.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Watanabe S, Masangkay JS, Nagata N, Morikawa S, Mizutani T, Fukushi S, Alviola P, Omatsu T, Ueda N, Iha K, Taniguchi S, Fujii H, Tsuda S, Endoh M, Kato K, Tohya Y, Kyuwa S, Yoshikawa Y, Akashi H. 2010. Bat coronaviruses and experimental infection of bats, the Philippines. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 16:1217–1223. 10.3201/eid1608.100208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Buchholz U, Muller MA, Nitsche A, Sanewski A, Wevering N, Bauer-Balci T, Bonin F, Drosten C, Schweiger B, Wolff T, Muth D, Meyer B, Buda S, Krause G, Schaade L, Haas W. 2013. Contact investigation of a case of human novel coronavirus infection treated in a German hospital, October-November 2012. Euro Surveill. 18:pii20406 http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=20406 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chan KH, Chan JF, Tse H, Chen H, Lau CC, Cai JP, Tsang AK, Xiao X, To KK, Lau SK, Woo PC, Zheng BJ, Wang M, Yuen KY. 2013. Cross-reactive antibodies in convalescent SARS patients' sera against the emerging novel human coronavirus EMC (2012) by both immunofluorescent and neutralizing antibody tests. J. Infect. 67:130–140. 10.1016/j.jinf.2013.03.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Brian DA, Baric RS. 2005. Coronavirus genome structure and replication. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 287:1–30. 10.1007/3-540-26765-4_1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kindler E, Jonsdottir HR, Muth D, Hamming OJ, Hartmann R, Rodriguez R, Geffers R, Fouchier RA, Drosten C, Muller MA, Dijkman R, Thiel V. 2013. Efficient replication of the novel human betacoronavirus EMC on primary human epithelium highlights its zoonotic potential. mBio 44(1):e00611–12. 10.1128/mBio.00611-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.van Boheemen S, de Graaf M, Lauber C, Bestebroer TM, Raj VS, Zaki AM, Osterhaus AD, Haagmans BL, Gorbalenya AE, Snijder EJ, Fouchier RA. 2012. Genomic characterization of a newly discovered coronavirus associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans. mBio 3(6):e00473–12. 10.1128/mBio.00473-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Weiss SR, Navas-Martin S. 2005. Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 69:635–664. 10.1128/MMBR.69.4.635-664.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pasternak AO, Spaan WJ, Snijder EJ. 2006. Nidovirus transcription: how to make sense? J. Gen. Virol. 87:1403–1421. 10.1099/vir.0.81611-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Masters PS. 2006. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 66:193–292. 10.1016/S0065-3527(06)66005-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lau SK, Li KS, Tsang AK, Lam CS, Ahmed S, Chen H, Chan KH, Woo PC, Yuen KY. 2013. Genetic characterization of Betacoronavirus lineage C viruses in bats revealed marked sequence divergence in the spike protein of Pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5 in Japanese pipistrelle: implications on the origin of the novel Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 87:8638–8650. 10.1128/JVI.01055-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lu G, Hu Y, Wang Q, Qi J, Gao F, Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Yuan Y, Bao J, Zhang B, Shi Y, Yan J, Gao GF. 2013. Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor CD26. Nature 500:227–231. 10.1038/nature12328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang N, Shi X, Jiang L, Zhang S, Wang D, Tong P, Guo D, Fu L, Cui Y, Liu X, Arledge KC, Chen YH, Zhang L, Wang X. 2013. Structure of MERS-CoV spike receptor-binding domain complexed with human receptor DPP4. Cell Res. 23:986–993. 10.1038/cr.2013.92 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jiang S, Lu L, Du L, Debnath AK. 2013. A predicted receptor-binding and critical neutralizing domain in S protein of the novel human coronavirus HCoV-EMC. J. Infect. 66:464–466. 10.1016/j.jinf.2012.12.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Raj VS, Mou H, Smits SL, Dekkers DH, Muller MA, Dijkman R, Muth D, Demmers JA, Zaki A, Fouchier RA, Thiel V, Drosten C, Rottier PJ, Osterhaus AD, Bosch BJ, Haagmans BL. 2013. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 495:251–254. 10.1038/nature12005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Meredith RW, Janecka JE, Gatesy J, Ryder OA, Fisher CA, Teeling EC, Goodbla A, Eizirik E, Simao TL, Stadler T, Rabosky DL, Honeycutt RL, Flynn JJ, Ingram CM, Steiner C, Williams TL, Robinson TJ, Burk-Herrick A, Westerman M, Ayoub NA, Springer MS, Murphy WJ. 2011. Impacts of the Cretaceous terrestrial revolution and KPg extinction on mammal diversification. Science 334:521–524. 10.1126/science.1211028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Cuthill JH, Charleston MA. 2013. A simple model explains the dynamics of preferential host switching among mammal RNA viruses. Evolution 67:980–990. 10.1111/evo.12064 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Chen SC, Olsthoorn RC. 2010. Group-specific structural features of the 5′-proximal sequences of coronavirus genomic RNAs. Virology 401:29–41. 10.1016/j.virol.2010.02.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


