Abstract
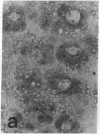
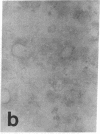
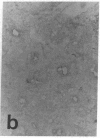
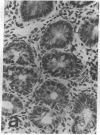
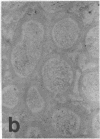
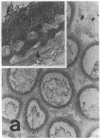
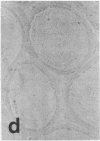
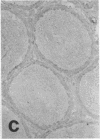
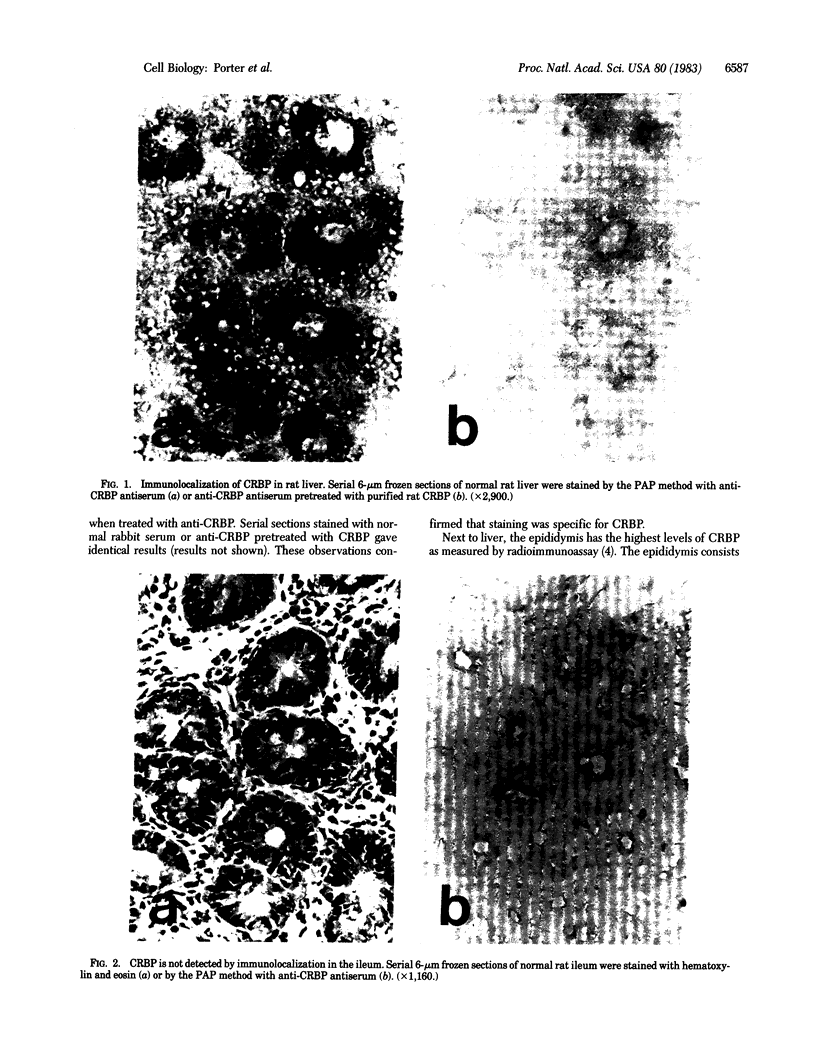
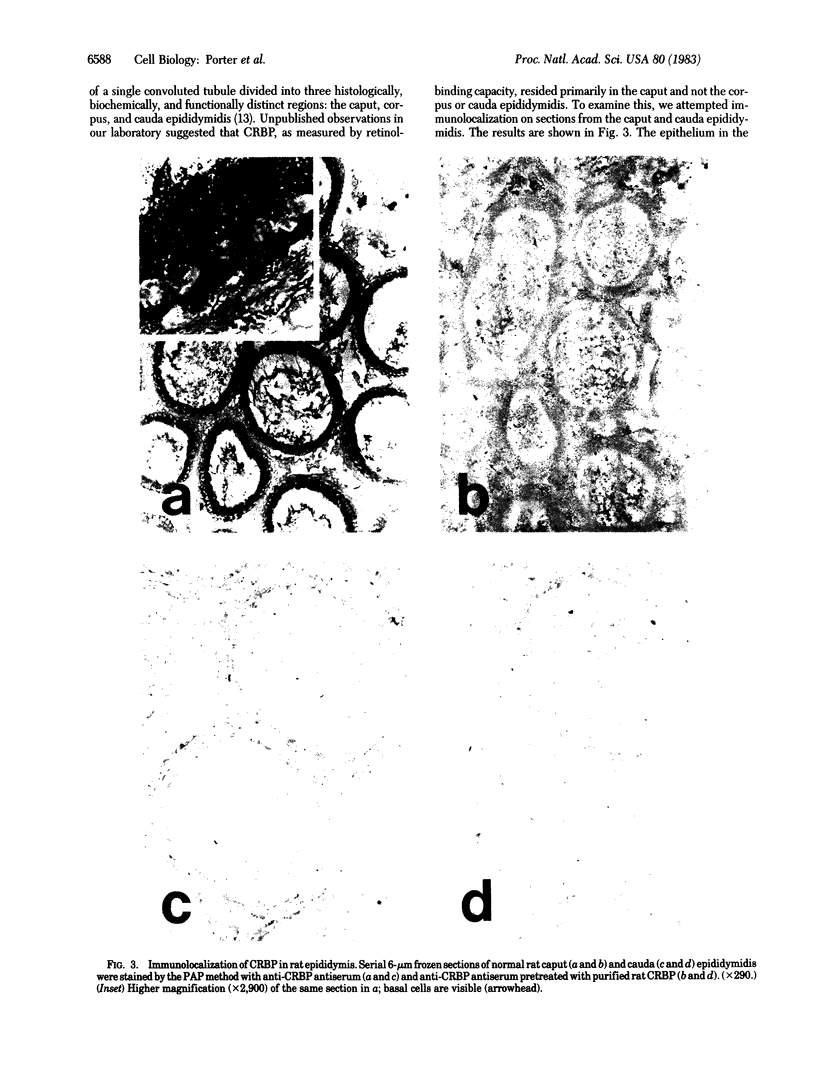
The distribution of cellular retinol-binding protein (CRBP) in rat liver, ileum, and epididymis was examined by the peroxidase-antiperoxidase immunolocalization technique. Positive cytoplasmic staining was seen in the liver when antiserum prepared against purified CRBP was used but not when antiserum absorbed with purified CRBP was used. Ileal mucosa, a tissue that contains no detectable CRBP, showed no positive staining. The epididymis showed strong positive staining in the caput but not in the cauda. Staining was present in principal and basal cells but not in peritubular or interstitial cells. Radioimmunoassay revealed that the CRBP within the caput epididymidis was localized in the initial segment and proximal region, areas known to be involved in the synthesis and secretion of factors necessary for sperm maturation. The results demonstrate that the expression of CRBP may vary within the same cell type, as well as between different cell types within the same tissue.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi N., Smith J. E., Sklan D., Goodman D. S. Radioimmunoassay studies of the tissue distribution and subcellular localization of cellular retinol-binding protein in rats. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9471–9476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashor M. M., Toft D. O., Chytil F. In vitro binding of retinol to rat-tissue components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3483–3487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E. Effect of androgens on protein synthesis and secretion in various regions of the rat epididymis, as analysed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1983 Mar;29(3):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(83)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E., Higgins S. J. Characterization and androgen-dependence of proteins associated with luminal fluid and spermatozoa in the rat epididymis. J Reprod Fertil. 1980 Jul;59(2):363–375. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0590363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E. Influence of incubation conditions, tunicamycin and castration on incorporation of [3H]mannose and [3H]fucose into rat epididymal glycoproteins in vitro. J Reprod Fertil. 1983 Jan;67(1):97–105. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0670097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E. Secretion of proteins and glycoproteins by the rat epididymis: regional differences, androgen-dependence, and effects of protease inhibitors, procaine, and tunicamycin. Biol Reprod. 1981 Dec;25(5):1099–1117. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod25.5.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F., Ong D. E. Cellular retinol- and retinoic acid-binding proteins in vitamin A action. Fed Proc. 1979 Oct;38(11):2510–2514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F., Ong D. E. Cellular vitamin A binding proteins. Vitam Horm. 1978;36:1–32. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60980-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggenvik J., Griswold M. D. Retinol binding protein in rat testicular cells. J Reprod Fertil. 1981 Mar;61(2):403–408. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0610403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. C., Kennedy M., Chiba N. Vitamin A and nuclear RNA synthesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969 Aug;22(8):1048–1058. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/22.8.1048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Brown C. R., Von Glós K. I., Parker M. G. Hormonal regulation of protein synthesis in the rat epididymis. Characterization of androgen-dependent and testicular fluid-dependent proteins. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):667–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1880667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohane A. C., Cameo M. S., Piñeiro L., Garberi J. C., Blaquier J. A. Distribution and site of production of specific proteins in the rat epididymis. Biol Reprod. 1980 Aug;23(1):181–187. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod23.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau G., Ong D. E., Chytil F. Interaction of the retinol/cellular retinol-binding protein complex with isolated nuclei and nuclear components. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):63–68. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omori M., Chytil F. Mechanism of vitamin A action. Gene expression in retinol-deficient rats. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14370–14374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Chytil F. Cellular retinol-binding protein from rat liver. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):828–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Chytil F. Changes in levels of cellular retinol- and retinoic-acid-binding proteins of liver and lung during perinatal development of rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3976–3978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Chytil F. Presence of cellular rentinol and retinoic acid binding proteins in experimental rumors. Cancer Lett. 1976 Sep;2(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(76)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Crow J. A., Chytil F. Radioimmunochemical determination of cellular retinol- and cellular retinoic acid-binding proteins in cytosols of rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13385–13389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Goodwin W. J., Jesse R. H., Griffin A. C. Presence of cellular retinol and retinoic acid-binding proteins in epidermoid carcinoma of the oral cavity and oropharynx. Cancer. 1982 Apr 1;49(7):1409–1412. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820401)49:7<1409::aid-cncr2820490717>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Markert C., Chiu J. F. Cellular binding proteins for vitamin A in colorectal adenocarcinoma of rat. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4422–4426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takase S., Ong D. E., Chytil F. Cellular retinol-binding protein allows specific interaction of retinol with the nucleus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2204–2208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. H., Chytil F. Effect of vitamin A deficiency on RNA synthesis in isolated rat liver nuclei. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 9;23(14):1461–1471. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. C., Buck R. C. An electron microscopic study of metaplasia of the rat tracheal epithelium in vitamin A deficiency. Lab Invest. 1971 Jan;24(1):55–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachman R. D. The stimulation of RNA synthesis in vivo and in vitro by retinol (vitamin A) in the intestine of vitamin A deficient rats. Life Sci. 1967 Oct 15;6(20):2207–2213. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]