Abstract
5-Azacytidine (azaC), a drug that induces decreased methylation of DNA in mammalian cells, was shown previously to induce differentiation of mesenchymal cell types in CHEF/18 cells (Chinese hamster embryo fibroblasts). This paper describes the effectiveness of azaC in inducing tumorigenicity in CHEF/18 cells, previously shown to be nontumorigenic stable diploids. A short exposure of growing cells to 3 microM azaC induced tumor-forming ability in CHEF/18 stem cells. Pre-adipocyte clones and subclones derived from CHEF/18 by prior treatment with azaC were also found to be tumorigenic. Pre-adipocytes previously induced by insulin in the absence of azaC were mostly nontumorigenic, but one clone produced tumors and gave rise to both tumorigenic and nontumorigenic subclones. Karyotype analysis of 41 clones and subclones from azaC-induced and insulin-induced pre-adipocytes revealed a complete correlation between tumor-forming ability and the presence of trisomy for chromosome 3q. In addition, the tumorigenic and tumor-derived lines were demethylated at specific C-C-G-G sites in the preproinsulin, Ha-ras, and Ki-ras genes as revealed by blot hybridization to Msp I- and Hpa II-digested DNAs, whereas the nontumorigenic lines resembled the CHEF/18 controls. This three-way correlation between tumorigenicity, trisomy for 3q, and specific demethylation suggests that decreased DNA methylation may be involved both in differentiation and in tumorigenicity, and that azaC may induce chromosomal aberrations as well as altering DNA methylation.
Full text
PDF


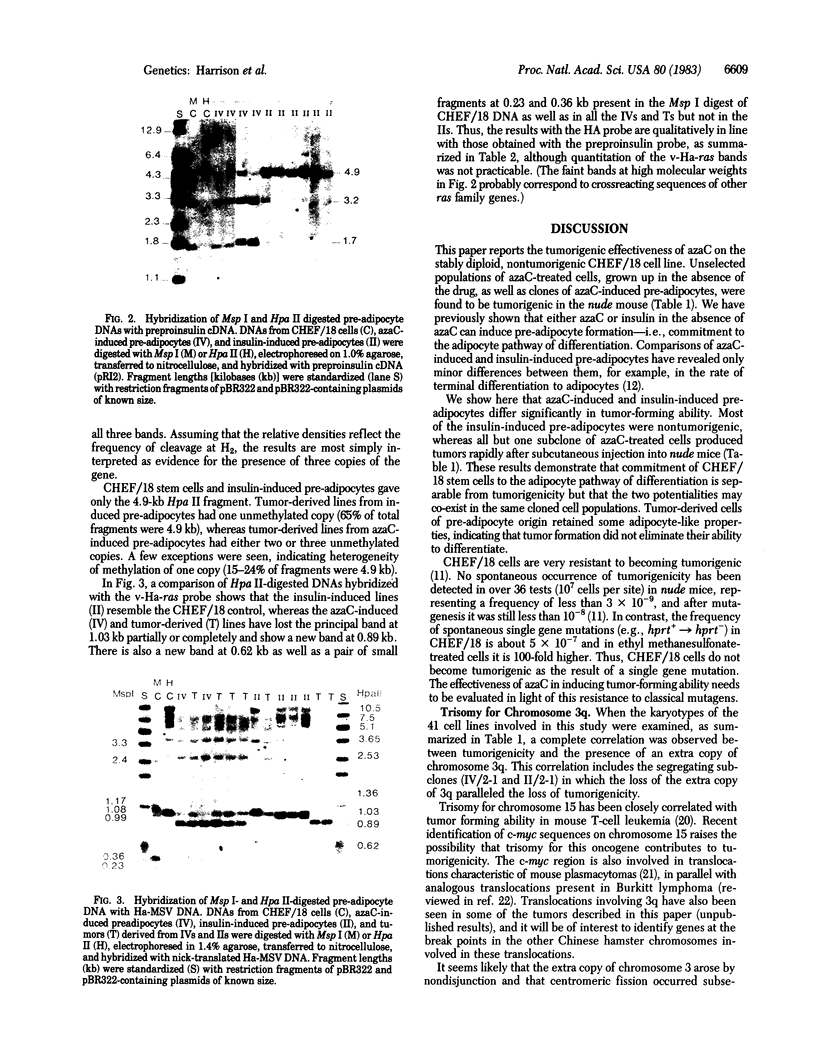

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloch-Shtacher N., Sachs L. Identification of a chromosome that controls malignancy in Chinese hamster cells. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Nov;93(2):205–212. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040930206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinides P. G., Taylor S. M., Jones P. A. Phenotypic conversion of cultured mouse embryo cells by aza pyrimidine nucleosides. Dev Biol. 1978 Sep;66(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Cooper G. M. Transfection by exogenous and endogenous murine retrovirus DNAs. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Taylor S. M. Hemimethylated duplex DNAs prepared from 5-azacytidine-treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2933–2947. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin R. M., Gadi I. K., Smith B. L., Sager R. Genetic analysis of tumorigenesis: X. Chromosome studies of transformed mutants and tumor-derived CHEF/18 cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Sep;8(5):677–689. doi: 10.1007/BF01542860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin R. M., Sager R. Genetic analysis of tumorigenesis: V. Chromosomal analysis of tumorigenic and nontumorigenic diploid chinese hamster cell lines. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Jan;6(1):75–87. doi: 10.1007/BF01538697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin R. M., Sager R. Genetic analysis of tumorigenesis: VI. Chromosome rearrangements in tumors derived from diploid premalignant Chinese hamster cells in nude mice. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Sep;6(5):615–630. doi: 10.1007/BF01538641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Specific chromosomal translocations and the genesis of B-cell-derived tumors in mice and men. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90449-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. The role of gene dosage and genetic transpositions in carcinogenesis. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):313–318. doi: 10.1038/294313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley T. J., DeSimone J., Anagnou N. P., Keller G. H., Humphries R. K., Turner P. H., Young N. S., Keller P., Nienhuis A. W. 5-azacytidine selectively increases gamma-globin synthesis in a patient with beta+ thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 9;307(24):1469–1475. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212093072401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Schimke R. T. Structure and genomic organization of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S. J., Nash W. G., Goodwin J. L., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Dispersion of the ras family of transforming genes to four different chromosomes in man. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):839–842. doi: 10.1038/302839a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F., Efstratiadis A., Lomedico P., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Dodgson J. The evolution of genes: the chicken preproinsulin gene. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Friedman J. DNA methylation and its possible biological roles. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:33–52. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60482-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougeon F., Mach B. Cloning and amplification of alpha and beta mouse globin gene sequences synthesised in vitro. Gene. 1977 May;1(3-4):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Anisowicz A., Howell N. Genomic rearrangements in a mouse cell line containing integrated SV40 DNA. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Kovac P. E. Genetic analysis of tumorigenesis: I. Expression of tumor-forming ability in hamster hybrid cell lines. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 May;4(3):375–392. doi: 10.1007/BF01542849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Kovac P. Pre-adipocyte determination either by insulin or by 5-azacytidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):480–484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki J. H., McCredie K. B., Vietti T. J., Hewlett J. S., Morrison F. S., Costanzi J. J., Stuckey W. J., Whitecar J., Hoogstraten B. 5-azacytidine in acute leukemia. Cancer. 1978 Nov;42(5):2111–2114. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197811)42:5<2111::aid-cncr2820420505>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi D. V., Garrett C. E., Barr P. J. On the mechanism of inhibition of DNA-cytosine methyltransferases by cytosine analogs. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. L., Sager R. Multistep origin of tumor-forming ability in Chinese hamster embryo fibroblast cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Feb;42(2):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira J., Wiener F., Babonits M., Gamble J., Miller J., Klein G. The role of chromosome 15 in murine leukemogenesis. I. Contrasting behavior of the tumor vs. normal parent-derived chromosomes No. 15 in somatic hybrids of varying tumorigenicity. Int J Cancer. 1981 Dec;28(6):785–798. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. M., Jones P. A. Multiple new phenotypes induced in 10T1/2 and 3T3 cells treated with 5-azacytidine. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):771–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90317-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Shih C., Weinberg R. A., Francke U. Oncogene from human EJ bladder carcinoma is located on the short arm of chromosome 11. Science. 1983 Feb 4;219(4584):498–501. doi: 10.1126/science.6297001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]