Abstract
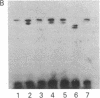
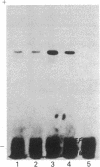
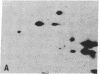
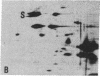
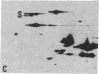
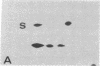
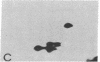
The S antigen of a Papua New Guinean isolate of Plasmodium falciparum was identified by immunoblotting as the dominant antigen in culture supernatants. An antigen identical in molecular weight (Mr 220,000), isoelectric point (pI 4.2), and immunoreactivity with sera from individuals exposed to malaria was expressed by four Papua New Guinean isolates and one isolate of unknown origin. The Mr 220,000 antigen was not detected in culture supernatants derived from two isolates from Thailand and one from Ghana. The Mr 220,000, pI 4.2 S antigen may characterize a subpopulation of parasites common to many isolates of P. falciparum, which is selected for by continuous culture in vitro. A variant S antigen, 30 kilodaltons larger but with similar immunoreactivity, was expressed by 1 of 26 clonal populations derived by limit-dilution culture from one of the Papua New Guinean isolates of P. falciparum. The characteristics of the S antigen, defined by immunoblotting, allowed it to be identified in two-dimensional separations of [35S]methionine-labeled parasite proteins, thus confirming the parasite origin of the antigen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Knowles G. Differential effect of immunoglobulin on the in vitro growth of several isolates of Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1228–1235. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1228-1235.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn P., Gilbert H., Newcombe J., Cuzner M. L. Rapid analysis of immunoglobulin isoelectric focusing patterns with cellulose nitrate sheets and immunoperoxidase staining. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jun 11;51(2):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride J. S., Walliker D., Morgan G. Antigenic diversity in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1982 Jul 16;217(4556):254–257. doi: 10.1126/science.6178159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor I. A., Wilson R. J. Precipitating antibodies and immunoglobulins in P. falciparum infections in The Gambia, West Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65(2):136–151. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(71)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield L., Saul A., Myler P., Kidson C. Antigenic differences among isolates of Plasmodium falciparum demonstrated by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):893–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.893-897.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait A. Analysis of protein variation in Plasmodium falciparum by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Feb;2(3-4):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J. Antigens and antibodies associated with Plasmodium falciparum infections in West Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1970;64(4):547–554. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(70)90076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Bartholomew R. K. The release of antigens by Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitology. 1975 Oct;71(2):183–192. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000046631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Ling I. Fractionation and characterization of Plasmodium falciparum antigens. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57 (Suppl 1):123–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., McGregor I. A., Hall P. J. Persistence and recurrence of S-antigen in Plasmodium falciparum infections in man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1975;69(5-6):460–467. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(75)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., McGregor I. A., Hall P., Williams K., Bartholomew R. Antigens associated with Plasmodium falciparum infections in man. Lancet. 1969 Jul 26;2(7613):201–205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91437-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., McGregor I. A., Williams K. Occurrence of S-antigens in serum in Plasmodium falciparum infections in man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1975;69(5-6):453–459. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(75)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., McGregor I. A., Wilson M. E. The stability and fractionation of malarial antigens from the blood of Africans infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Int J Parasitol. 1973 Jul;3(4):511–520. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(73)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J. Serotyping Plasmodium falciparum malaria with S-antigens. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):451–452. doi: 10.1038/284451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J. The production of antigens by Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. Int J Parasitol. 1974 Oct;4(5):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(74)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Voller A. A comparison of malarial antigens from human and Aotus monkey blood infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitology. 1972 Apr;64(2):191–195. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000029620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]