Abstract
Lipid A, the toxic moiety of Gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins), is a glucosamine disaccharide to which fatty acid and phosphate residues are covalently attached. Recent studies of Salmonella lipid A indicate that 3-hydroxytetradecanoic acid (3-OH-14:0) residues are directly linked to the glucosamine backbone and the nonhydroxylated fatty acids (principally dodecanoic and tetradecanoic acids) are esterified to the hydroxyl groups of some of the 3-OH-14:0 molecules. We report here that the granule fraction of human neutrophils contains one or more enzymes that partially deacylate Salmonella typhimurium lipid A by removing the nonhydroxylated fatty acids, leaving almost all of the 3-OH-14:0 residues linked to glucosamine. The available evidence suggests that similar reactions also occur in living neutrophils that ingest lipopolysaccharides by antibody-dependent phagocytosis.
Full text
PDF
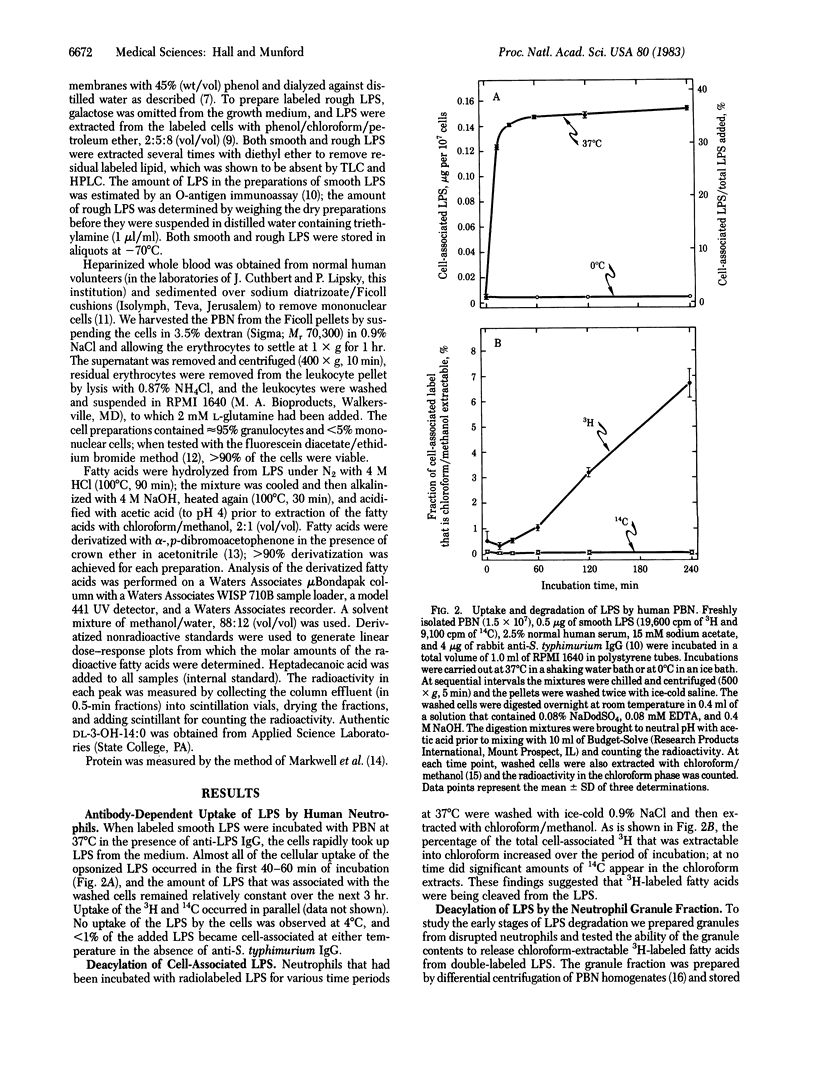
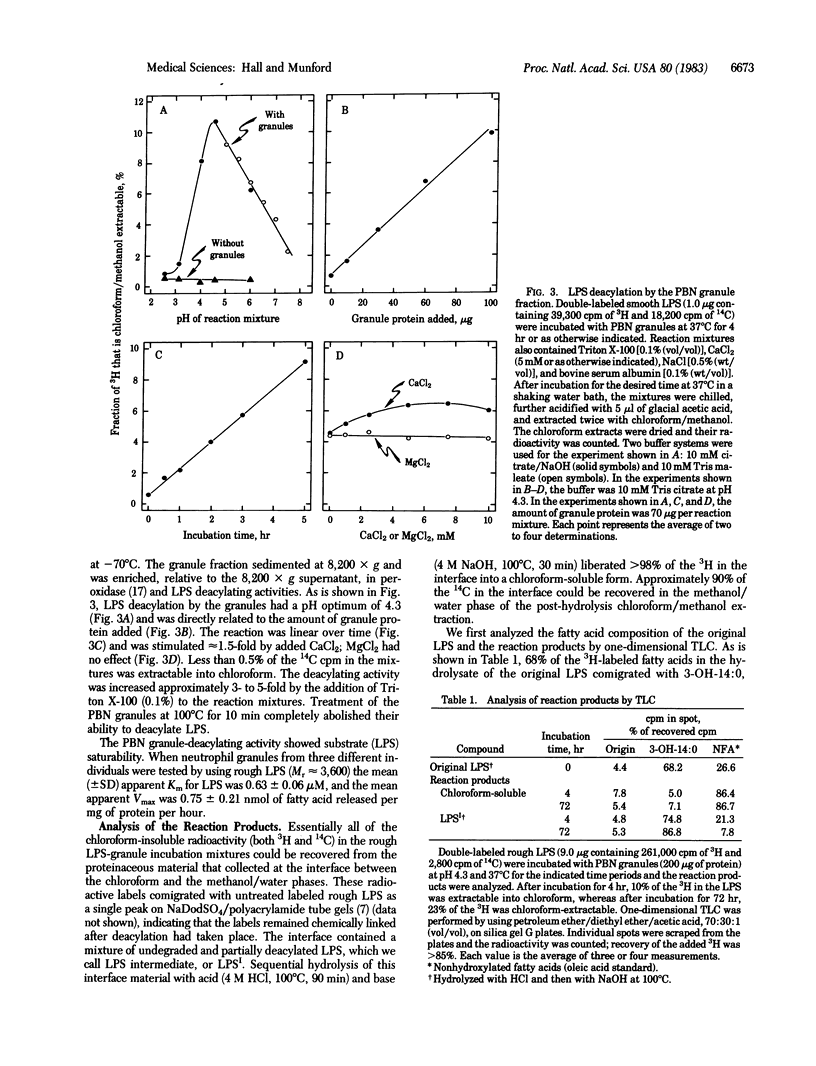
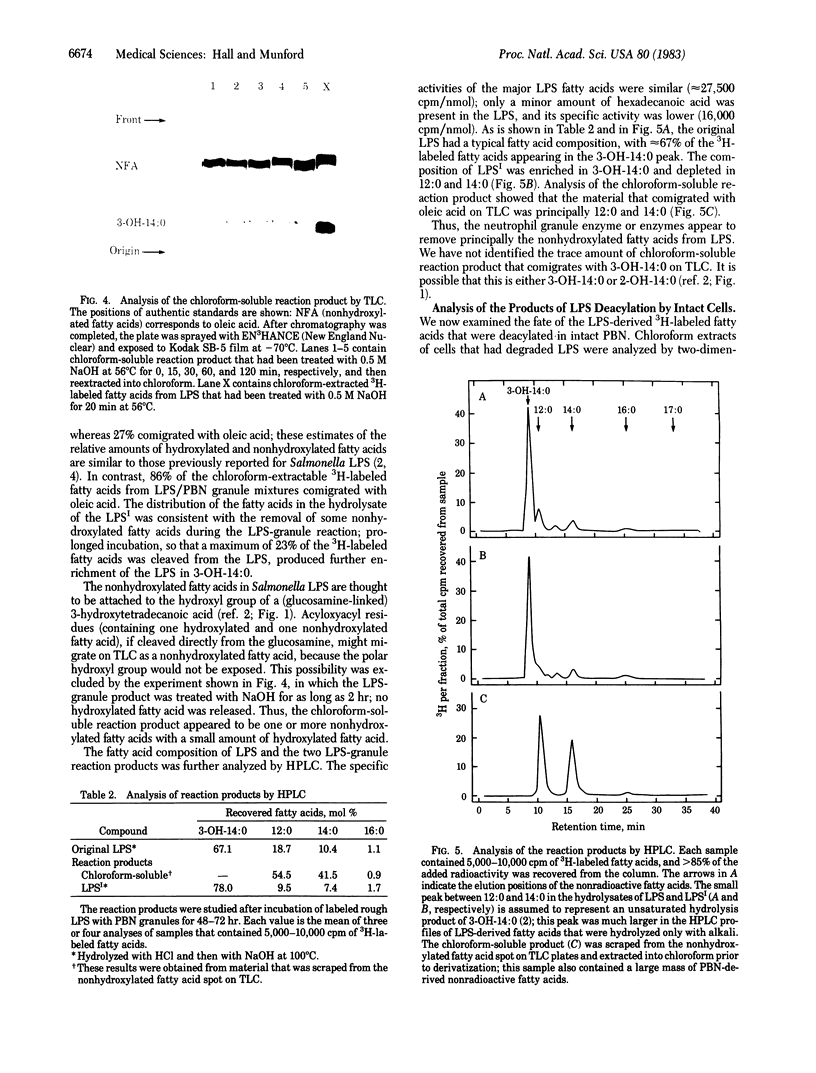

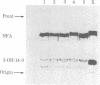
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Lipids of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: structure and metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):833–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.833-843.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durst H. D., Milano M., Kikta E. J., Jr, Connelly S. A., Grushka E. Phenacyl esters of fatty acids via crown ether catalysts for enhanced ultraviolet detection in liquid chromatography. Anal Chem. 1975 Sep;47(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1021/ac60361a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P. Degradation of microorganisms by phagocytic cells. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Jan-Feb;2(1):106–128. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Goldman J., Patriarca P. Phospholipid metabolism by phagocytic cells. VI. Observations on the fate of phospholipids of granulocytes and ingested Escherichia coli during phagocytosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 7;280(1):33–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimber P. E., Rafter G. W. The interaction of Escherichia coli endotoxin with leukocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90510-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiso M., Nishihori K., Hasegawa A., Okumura H., Azuma I. A new synthetic route to 2-(acylamino)-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl phosphates, and their endotoxic activity related to the Salmonella-type lipid A. Carbohydr Res. 1981 Sep 1;95(1):C5–C8. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Lastra R. Fatty acid biosynthesis in human leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1596–1602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L. Radioimmunoassay for Gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide O antigens: influence of antigen solubility. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):42–48. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.42-48.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Rick P. D. Size heterogeneity of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides in outer membranes and culture supernatant membrane fragments. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.630-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam V. N., Malchow D., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Die enzymatische Abspaltung langkettiger Fettsäuren aus bakteriellen Lipopolysacchariden mittels Extrakten aus der Amöbe von Dictyostelium discoideum. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Sep;351(9):1123–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A. Molecular aspects of endotoxic reactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Mar;33(1):72–98. doi: 10.1128/br.33.1.72-98.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Takayama K., Ribi E. Purification and structural determination of nontoxic lipid A obtained from the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11808–11815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. R., Verret R. C., Khorana H. G. The structure of lipopolysaccharide from an Escherichia coli heptose-less mutant. III. Two fatty acyl amidases from Dictyostelium discoideum and their action on lipopolysaccharide derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5926–5933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. The accessory function of phagocytic cells in human T cell and B cell responses. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1033–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Broady K. W., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T. The chemical structure of lipid A. Demonstration of amide-linked 3-acyloxyacyl residues in Salmonella minnesota Re lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]