Abstract
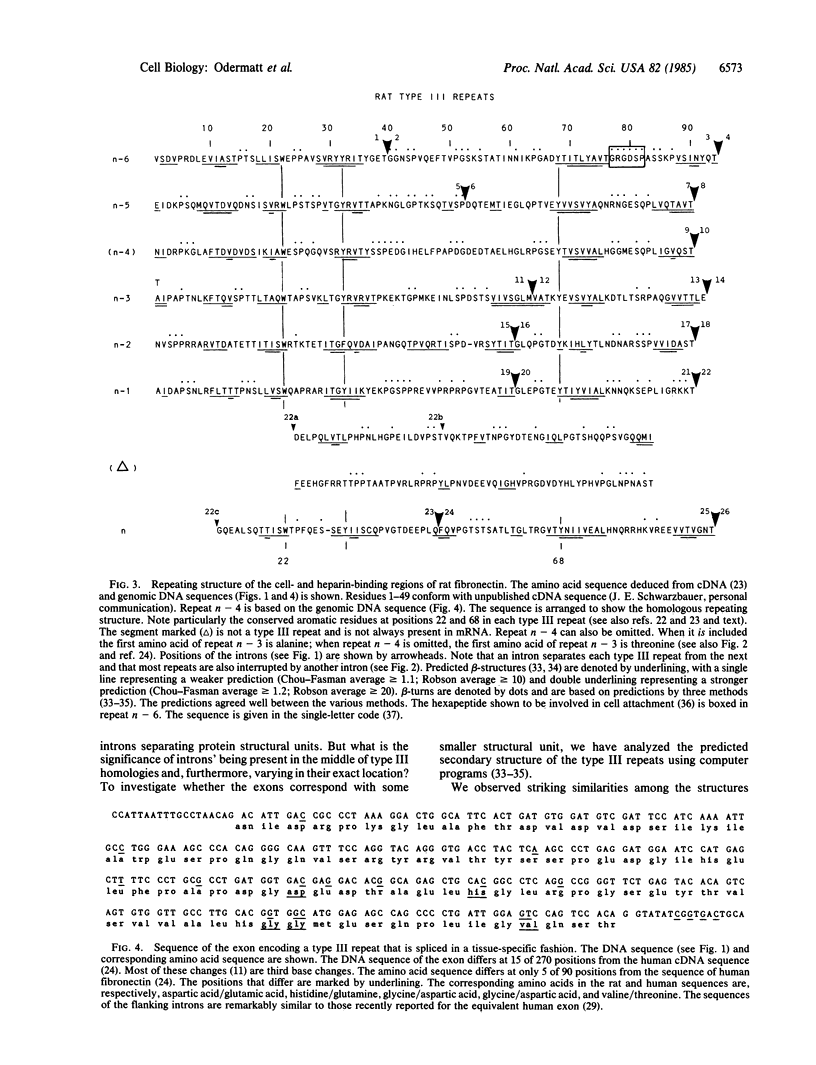
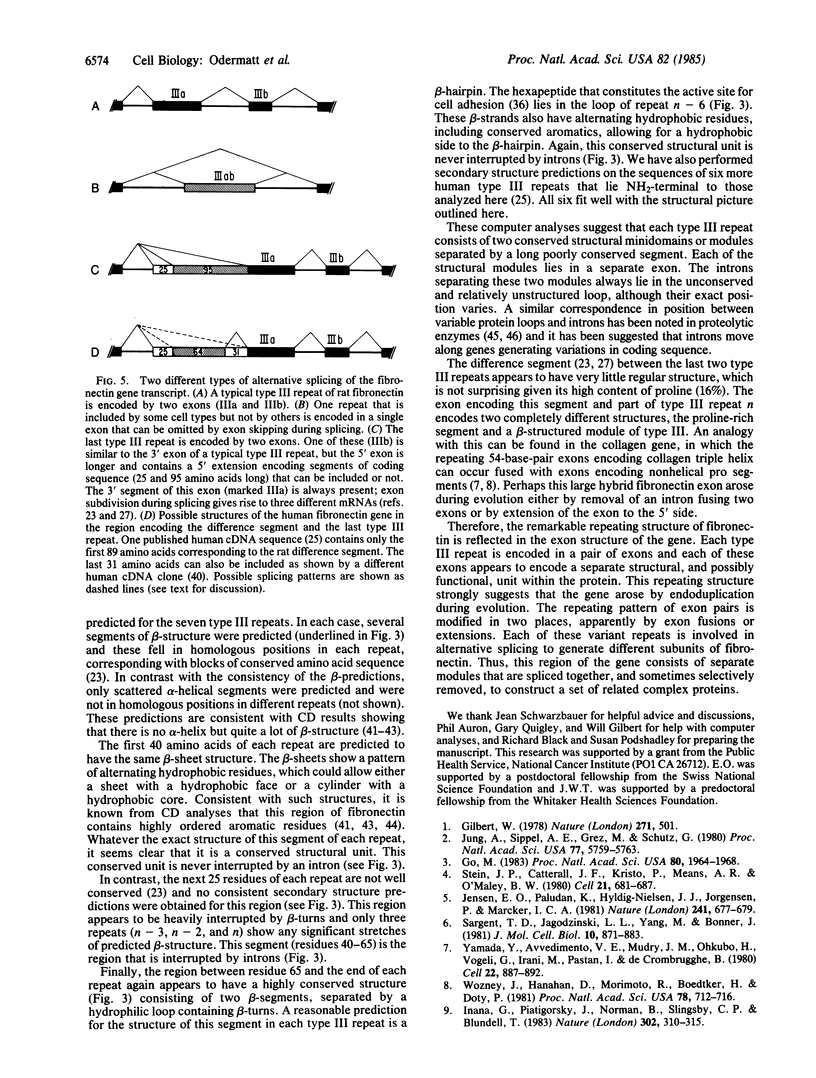
Analysis of the exon-intron structure of the rat fibronectin gene shows that exons correspond precisely with repeating structural units in the protein and that alternative use of some exons produces fibronectin subunits that differ by the presence or absence of certain structural modules. Secondary structure predictions suggest that the repeating structure of the protein is further subdivided into smaller structural units and that these also correspond with exons in the gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander S. S., Jr, Colonna G., Edelhoch H. The structure and stability of human plasma cold-insoluble globulin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1501–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Place A. R., Powers D. A., Sofer W. Alcohol dehydrogenase gene of Drosophila melanogaster: relationship of intervening sequences to functional domains in the protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2717–2721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard M. P., Kolbe M., Weil D., Chu M. L. Human cellular fibronectin: comparison of the carboxyl-terminal portion with rat identifies primary structural domains separated by hypervariable regions. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2698–2704. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. E., Abarbanel R. M., Kuntz I. D., Fletterick R. J. Secondary structure assignment for alpha/beta proteins by a combinatorial approach. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):4894–4904. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Rutter W. J., Fletterick R. Splice junctions: association with variation in protein structure. Science. 1983 Jun 10;220(4602):1125–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6344214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Sprang S., Fletterick R., Rutter W. J. Intron-exon splice junctions map at protein surfaces. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):180–182. doi: 10.1038/299180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A. Multigene families encoding actin and tubulin. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):6–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90494-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go M. Modular structural units, exons, and function in chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1964–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano H., Yamada Y., Sullivan M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I., Yamada K. M. Isolation of genomic DNA clones spanning the entire fibronectin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T. Immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:499–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Goodenow R. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):685–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Yamada K. M. Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):369–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inana G., Piatigorsky J., Norman B., Slingsby C., Blundell T. Gene and protein structure of a beta-crystallin polypeptide in murine lens: relationship of exons and structural motifs. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):310–315. doi: 10.1038/302310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Sippel A. E., Grez M., Schütz G. Exons encode functional and structural units of chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. Protein structural domains in the Caenorhabditis elegans unc-54 myosin heavy chain gene are not separated by introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4253–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: cell specific alternative mRNA splicing generates polypeptide chains differing in the number of internal repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5853–5868. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: molecular cloning evidence for two mRNA species differing by an internal segment coding for a structural domain. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):221–226. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human and bovine fibronectins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding human rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4851–4855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Elgh F., Lund B. The structure of the human tissue-type plasminogen activator gene: correlation of intron and exon structures to functional and structural domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5355–5359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt E., Engle J., Richter H., Hörmann H. Shape, conformation and stability of fibronectin fragments determined by electron microscopy, circular dichroism and ultracentrifugation. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):109–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. I., Hynes R. O. Multiple fibronectin subunits and their post-translational modifications. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13477–13487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen T. E., Thøgersen H. C., Skorstengaard K., Vibe-Pedersen K., Sahl P., Sottrup-Jensen L., Magnusson S. Partial primary structure of bovine plasma fibronectin: three types of internal homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):137–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Rogers J. H., Hüppi K., Brack C., Traunecker A., Maki R., Wall R., Tonegawa S. Domains and the hinge region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain are encoded in separate DNA segments. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):627–633. doi: 10.1038/277627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Jagodzinski L. L., Yang M., Bonner J. Fine structure and evolution of the rat serum albumin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;1(10):871–883. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.10.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Paul J. I., Hynes R. O. On the origin of species of fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1424–1428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Catterall J. F., Kristo P., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Ovomucoid intervening sequences specify functional domains and generate protein polymorphism. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Hynes R. O. Plasma fibronectin is synthesized and secreted by hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4641–4647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Schwarzbauer J. E., Hynes R. O. A single rat fibronectin gene generates three different mRNAs by alternative splicing of a complex exon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooney N. M., Amrani D. L., Homandberg G. A., McDonald J. A., Mosesson M. W. Near ultraviolet circular dichroism spectroscopy of plasma fibronectin and fibronectin fragments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 15;108(3):1085–1091. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibe-Pedersen K., Kornblihtt A. R., Baralle F. E. Expression of a human alpha-globin/fibronectin gene hybrid generates two mRNAs by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2511–2516. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh E. J., Frangou S. A., Morris E. R., Rees D. A., Chavin S. I. Tyrosine optical activity as a probe of the conformation and interactions of fibronectin. Biopolymers. 1983 Mar;22(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Morimoto R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Fine structural analysis of the chicken pro alpha 2 collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):712–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Cell surface interactions with extracellular materials. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:761–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Avvedimento V. E., Mudryj M., Ohkubo H., Vogeli G., Irani M., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. The collagen gene: evidence for its evolutinary assembly by amplification of a DNA segment containing an exon of 54 bp. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):887–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90565-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


