Abstract
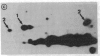
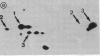
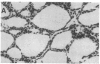
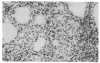
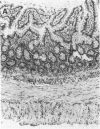
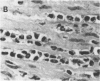
Evidence is accumulating that the development of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus involves autoimmune phenomena, both in the human and in the BB rat model. A strong association is observed in both cases with alleles of the class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Results of the present study show that autoimmune phenomena, as assessed by the presence of clinical diabetes or histological thyroiditis, are prevented by the injection of monoclonal antibodies to class II gene products in the BB rat. Immunosuppression was specifically obtained with a monoclonal antibody to the murine I-E equivalent, as opposed to the murine I-A equivalent, of the rat major histocompatibility complex. This represents indirect evidence for I-E subregion control of immune responses to islet cell and thyroid antigens in the BB rat model. The frequent occurrence of anaphylactic type deaths in young (1 month old) animals receiving more than six weekly injections of partially purified homologous (rat) monoclonal antibodies to rat class II gene products underscores the potential risks of this type of immunotherapy. The presumed immunologic mechanism (IgE antibody) and its specificity (anti-allotype, anti-idiotype, or anti-impurity) must be clarified to assess the risks and feasibility of this type of therapy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman N. E., Watling D. L., McDevitt H. O. Treatment of (NZB x NZW)F1 disease with anti-I-A monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1350–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Dyrberg T., Lernmark A. Autoantibodies to a 64-kilodalton islet cell protein precede the onset of spontaneous diabetes in the BB rat. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1348–1350. doi: 10.1126/science.6374896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer J., Reske K. Biochemical analysis of class II antigens. Identification of a two- and a three-polypeptide chain complex of I-A locus equivalent molecules in the rat. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jan;13(1):18–24. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenhorn E. P., Cecka J. M., Frelinger J., Götze D., Hood L. Structure of Ia antigens from the rat. Mouse alloantisera demonstrate at least two distinct molecular species. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Feb;10(2):145–151. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenhorn E. P., Symington F. W., Cramer D. V. Biochemical characterization of Ia antigens encoded by the RT1.B and RT1.D loci in the rat MHC. Immunogenetics. 1983;17(5):475–484. doi: 10.1007/BF00696871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buse J. B., Ben-Nun A., Klein K. A., Eisenbarth G. S., Seidman J. G., Jackson R. A. Specific class II histocompatibility gene polymorphism in BB rats. Diabetes. 1984 Jul;33(7):700–703. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.7.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, McDevitt H. O. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the initial lesion. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 11;304(24):1454–1465. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106113042403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colle E., Guttmann R. D., Seemayer T. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus syndrome in the rat. I. Association with the major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1237–1242. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyrberg T., Poussier P., Nakhooda F., Marliss E. B., Lernmark A. Islet cell surface and lymphocyte antibodies often precede the spontaneous diabetes in the BB rat. Diabetologia. 1984 Feb;26(2):159–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00281126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder M. E., Maclaren N. K. Identification of profound peripheral T lymphocyte immunodeficiencies in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1723–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C., Wright B. Rat x rat hybrid myelomas and a monoclonal anti-Fd portion of mouse IgG. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):131–133. doi: 10.1038/277131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. C. The major histocompatibility complex of the rat: a partial review. Metabolism. 1983 Jul;32(7 Suppl 1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(83)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Buse J. B., Rifai R., Pelletier D., Milford E. L., Carpenter C. B., Eisenbarth G. S., Williams R. M. Two genes required for diabetes in BB rats. Evidence from cyclical intercrosses and backcrosses. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1629–1636. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Auffray C., Korman A. J., Shackelford D. A., Strominger J. The class II molecules of the human and murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laupacis A., Stiller C. R., Gardell C., Keown P., Dupre J., Wallace A. C., Thibert P. Cyclosporin prevents diabetes in BB Wistar rats. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):10–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Kislauskis E., Williams R. R., Rossini A. A. Neonatal thymectomy prevents spontaneous diabetes mellitus in the BB/W rat. Science. 1982 May 7;216(4546):644–646. doi: 10.1126/science.7041259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Rossini A. A., Guberski D. L., Appel M. C., Williams R. M. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus: reversal and prevention in the BB/W rat with antiserum to rat lymphocytes. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.388619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Nakhooda A. F., Poussier P., Sima A. A. The diabetic syndrome of the 'BB' Wistar rat: possible relevance to type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes in man. Diabetologia. 1982 Apr;22(4):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00281296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O. Regulation of the immune response by the major histocompatibility system. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 25;303(26):1514–1517. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012253032606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naji A., Silvers W. K., Bellgrau D., Barker C. F. Spontaneous diabetes in rats: destruction of islets is prevented by immunological tolerance. Science. 1981 Sep 18;213(4514):1390–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.6791286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhooda A. F., Like A. A., Chappel C. I., Murray F. T., Marliss E. B. The spontaneously diabetic Wistar rat. Metabolic and morphologic studies. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):100–112. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. T., Adelman N. E., McDevitt H. O. In vivo effects of antibodies to immune response gene products. I. Haplotype-specific suppression of humoral immune responses with a monoclonal anti-I-A. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1694–1702. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini A. A., Slavin S., Woda B. A., Geisberg M., Like A. A., Mordes J. P. Total lymphoid irradiation prevents diabetes mellitus in the Bio-Breeding/Worcester (BB/W) rat. Diabetes. 1984 Jun;33(6):543–547. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.6.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemayer T. A., Colle E., Tannenbaum G. S., Oligny L. L., Guttmann R. D., Goldman H. Spontaneous diabetes mellitus syndrome in the rat. III. Pancreatic alterations in aglycosuric and untreated diabetic BB Wistar-derived rats. Metabolism. 1983 Jul;32(7 Suppl 1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(83)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L., Rosenbaum J. T., Sriram S., McDevitt H. O. In vivo effects of antibodies to immune response gene products: prevention of experimental allergic encephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7111–7114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternthal E., Like A. A., Sarantis K., Braverman L. E. Lymphocytic thyroiditis and diabetes in the BB/W rat. A new model of autoimmune endocrinopathy. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1058–1061. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldor M. K., Sriram S., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. In vivo therapy with monoclonal anti-I-A antibody suppresses immune responses to acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2713–2717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yale J. F., Marliss E. B. Altered immunity and diabetes in the BB rat. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]