Abstract
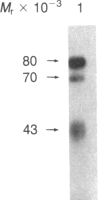
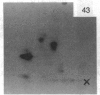
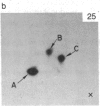
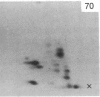
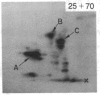
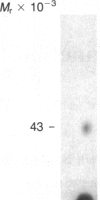
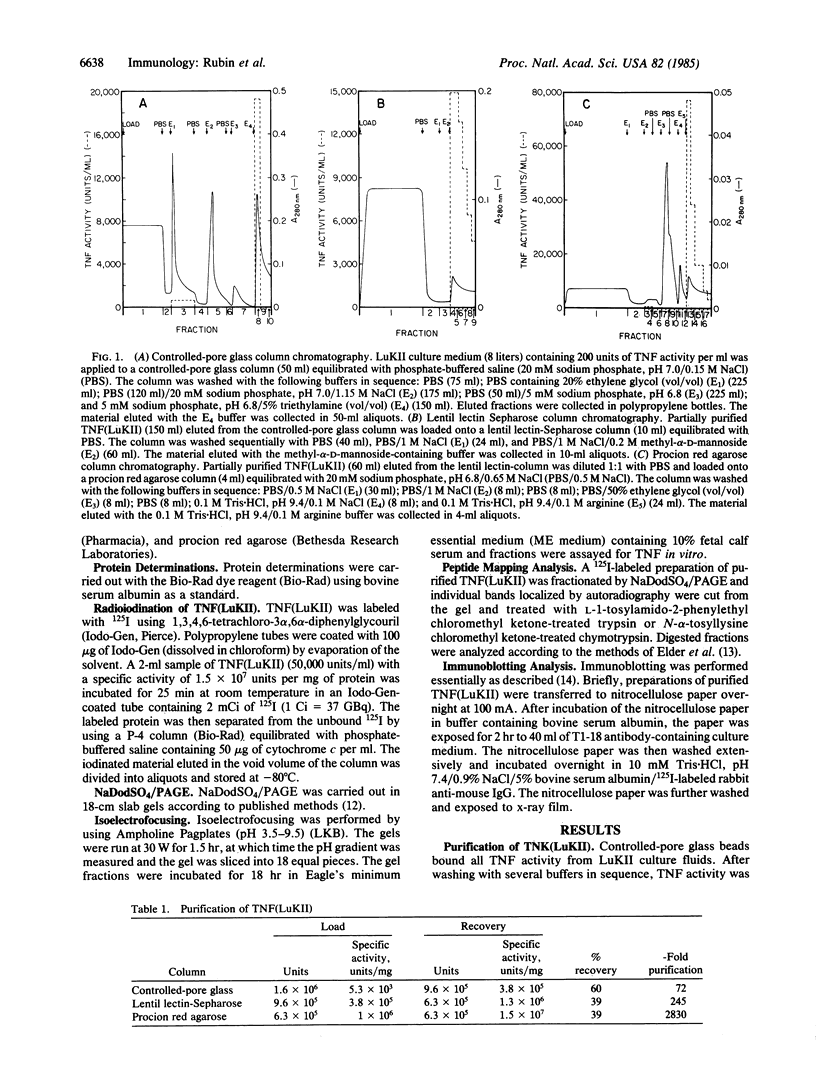
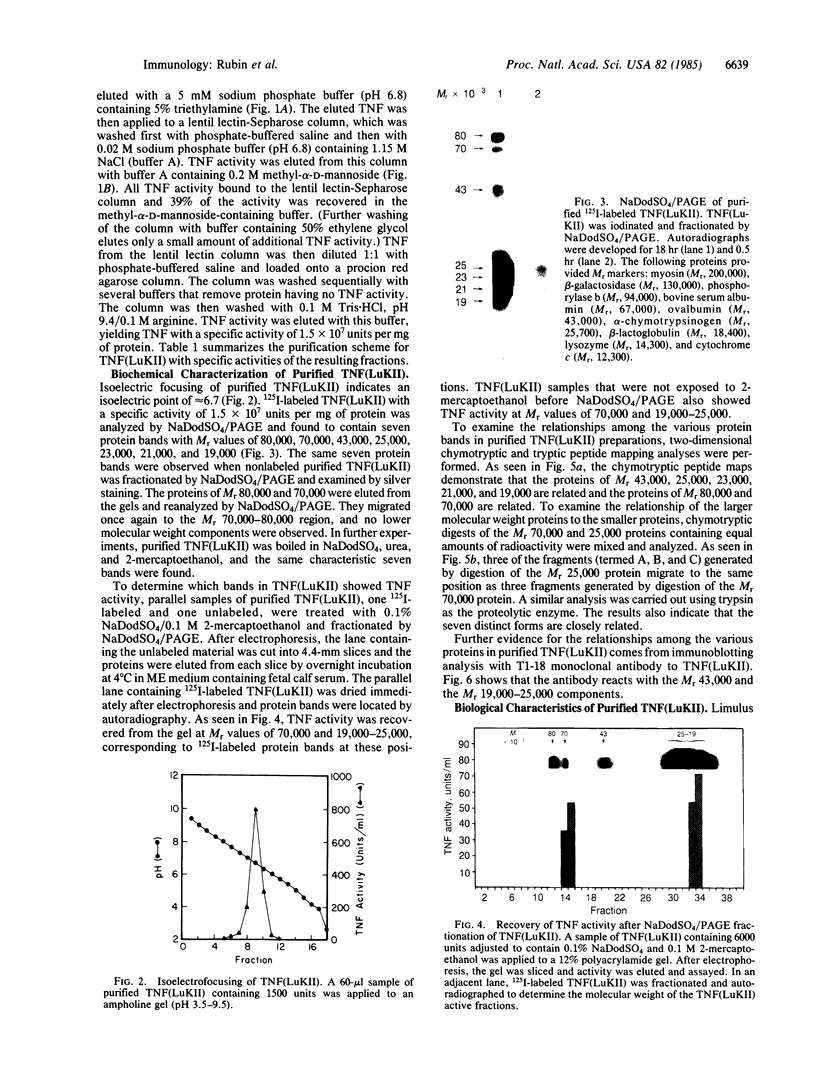
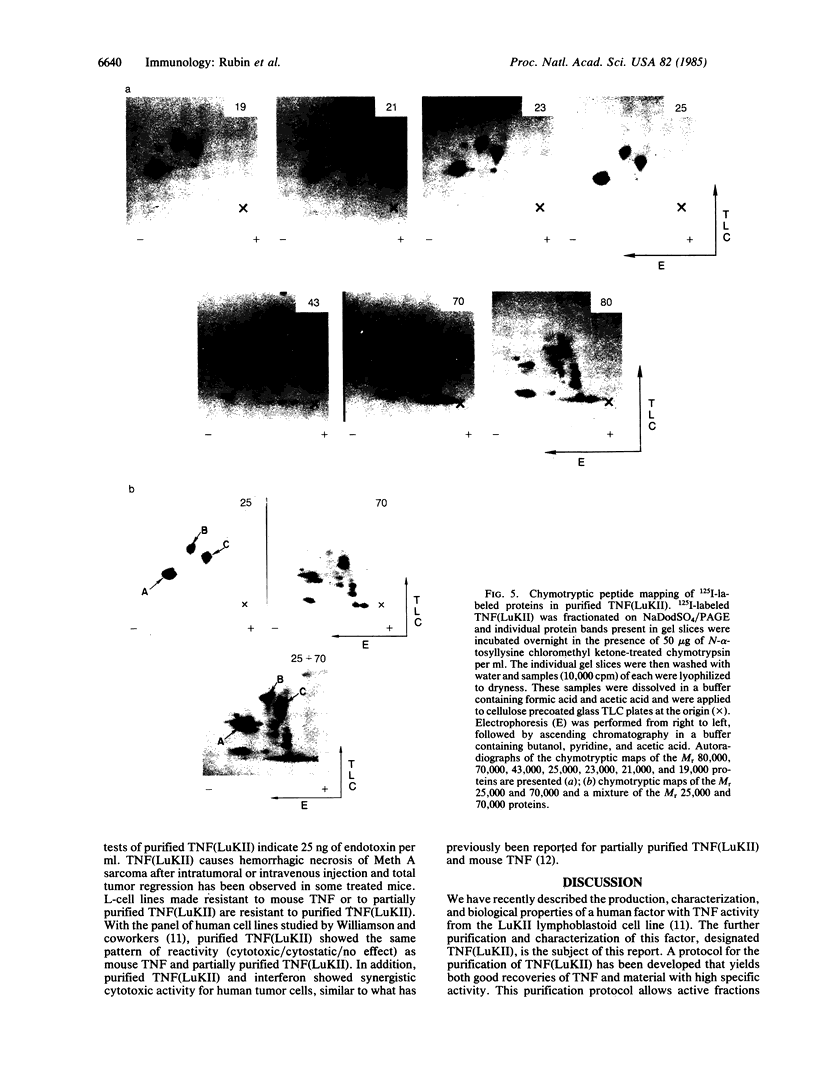
A factor with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity produced by the LuKII human lymphoblastoid cell line [designated TNF(LuKII)] was purified sequentially by using controlled-pore glass, lentil lectin-Sepharose, and procion red agarose chromatography, yielding TNF with a specific activity of 1.5 X 10(7) units per mg of protein and an isoelectric point of approximately equal to 6.7. Purified TNF(LuKII) fractionated by NaDodSO4/PAGE under reducing as well as nonreducing conditions was found to contain seven protein bands of Mr 80,000, 70,000, 43,000, 25,000, 23,000, 21,000, and 19,000. The proteins of Mr 80,000 and 70,000 could not be dissociated into lower molecular weight components. Peptide mapping analysis and immunoblotting analysis revealed that the seven protein bands in the purified TNF(LuKII) preparations are related. After fractionation of TNF(LuKII) by NaDodSO4/PAGE under reducing conditions, TNF activity was recovered from the regions of Mr 70,000 and 19,000-25,000. Purified human TNF(LuKII) (i) produces hemorrhagic necrosis of Meth A mouse sarcoma in the standard in vivo mouse TNF assay; (ii) has the same pattern of reactivity as mouse TNF (cytotoxic/cytostatic/no effect) on a panel of human cancer cell lines; and (iii) has its anticellular effect potentiated by interferon, also a feature of mouse TNF.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Henzel W. J., Moffat B., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N. Primary structure of human lymphotoxin derived from 1788 lymphoblastoid cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2334–2344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal B. B., Moffat B., Harkins R. N. Human lymphotoxin. Production by a lymphoblastoid cell line, purification, and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):686–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Jensen F. C., Bryant M. L., Lerner R. A. Polymorphism of the major envelope glycoprotein (gp70) of murine C-type viruses: virion associated and differentiation antigens encoded by a multi-gene family. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):23–28. doi: 10.1038/267023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A., Yamamoto R. S., Fair D. S., Hiserodt J. C. The human LT system. I. Physical-chemical heterogeneity of LT molecules released by mitogen activated human lymphocytes in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jul;38(2):388–402. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Aggarwal B. B., Benton C. V., Bringman T. S., Henzel W. J., Jarrett J. A., Leung D. W., Moffat B., Ng P., Svedersky L. P. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human lymphotoxin, a lymphokine with tumour necrosis activity. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):721–724. doi: 10.1038/312721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Dobrjansky A., Carswell E. A., Kassel R. L., Old L. J., Fiore N., Schwartz M. K. Partial purification of a serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haranaka K., Satomi N. Cytotoxic activity of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) on human cancer cells in vitro. Jpn J Exp Med. 1981 Jun;51(3):191–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helson L., Green S., Carswell E., Old L. J. Effect of tumour necrosis factor on cultured human melanoma cells. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):731–732. doi: 10.1038/258731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Cuatrecasas P. Preliminary characterization of the tumor cell cytotoxin in tumor necrosis serum. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1279–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Ryley H. C., Neale M. L. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. IV. Purification and chemical characterization. Br J Cancer. 1980 Sep;42(3):416–422. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Watkins J. F. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. I. Mode of action, specificity and physicochemical properties. Br J Cancer. 1978 Aug;38(2):302–309. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Meltzer M. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Generation and characterization of a lipopolysaccharide-induced and serum-derived cytotoxic factor for tumor cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.204-211.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrove J. M., Gifford G. E. Stimulation of RNA synthesis in L-929 cells by rabbit tumor necrosis factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Mar;160(3):354–358. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenau W. Lymphotoxin: properties, role and mode of action. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1981;3(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(81)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M. R., Gifford G. E. Purification and physico-chemical characterization of rabbit tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1671–1677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Yamaguchi H., Ito H., Todd C. W., Wallace R. B. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene for human tumour necrosis factor. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):803–806. doi: 10.1038/313803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson B. D., Carswell E. A., Rubin B. Y., Prendergast J. S., Old L. J. Human tumor necrosis factor produced by human B-cell lines: synergistic cytotoxic interaction with human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5397–5401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]