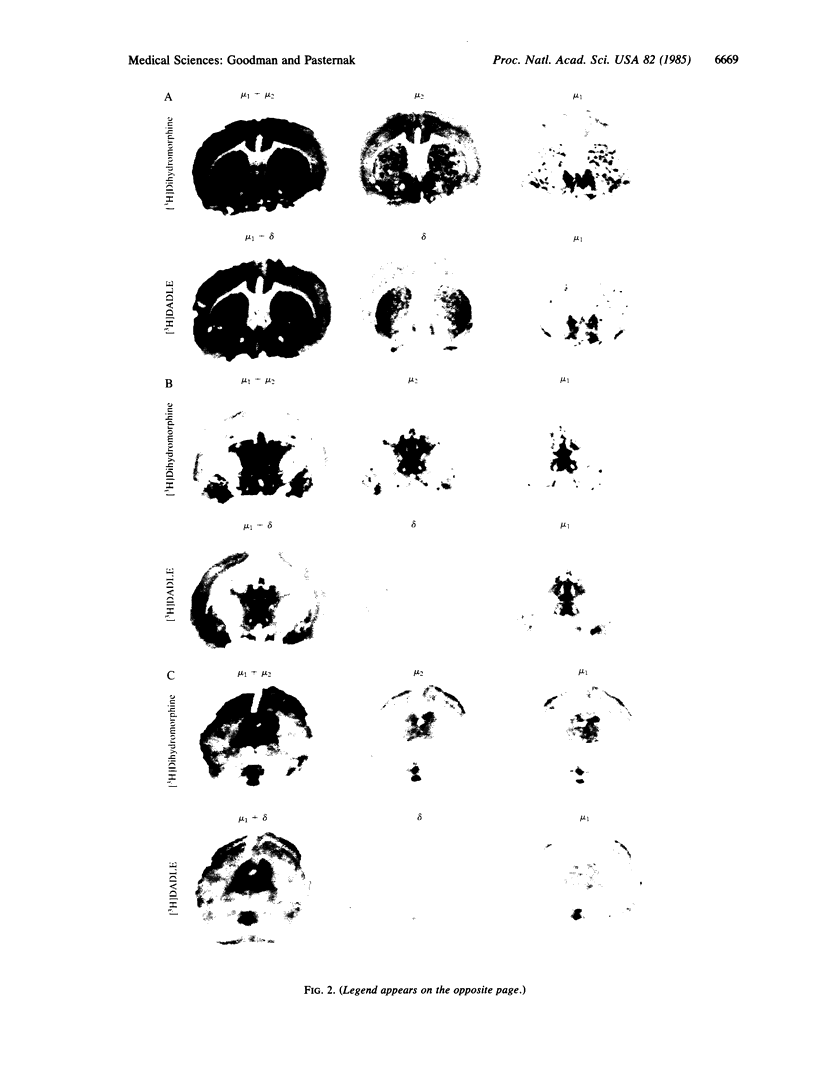
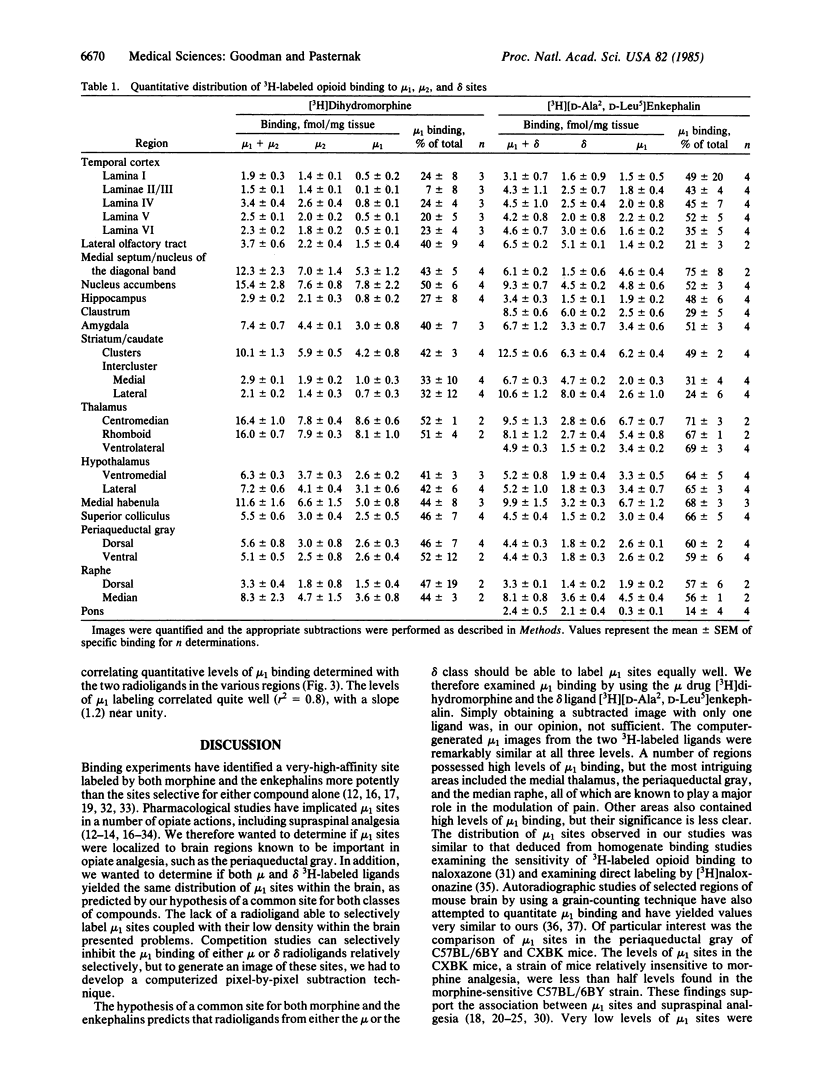
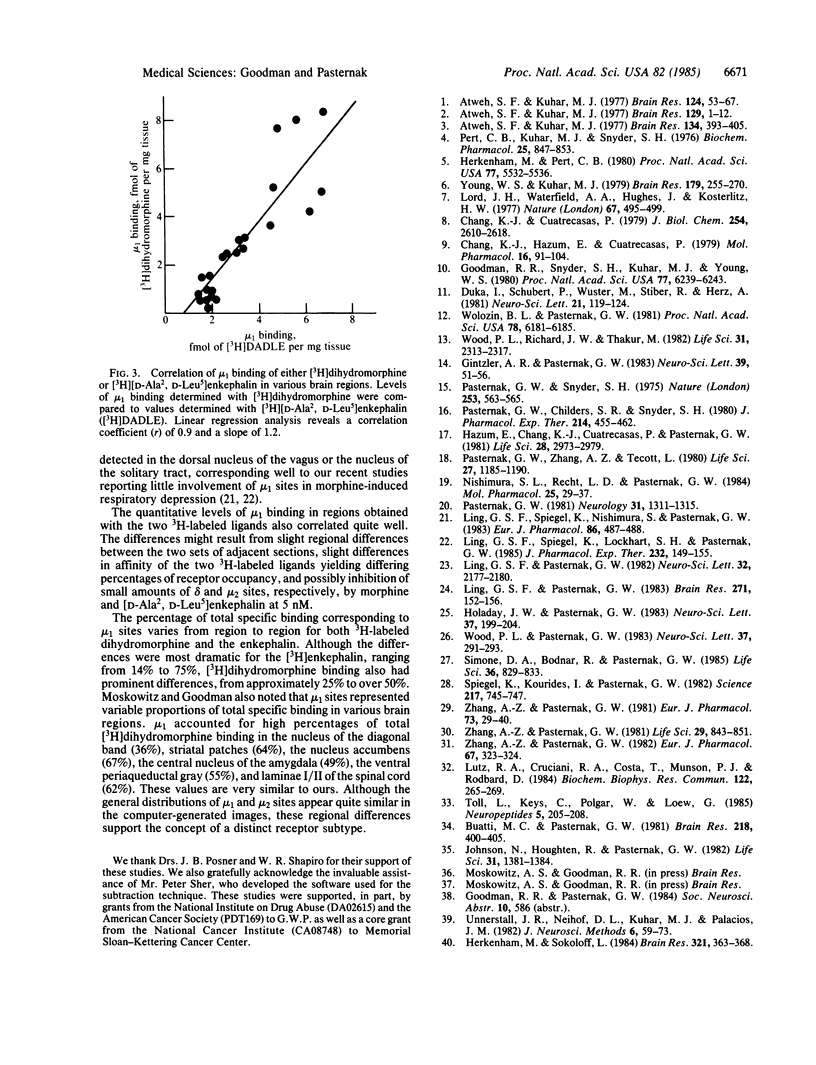
Abstract
We have developed a quantitative computerized subtraction technique to demonstrate in rat brain the regional distribution of mu1 sites, a common very-high-affinity binding site for both morphine and the enkephalins. Low concentrations of [D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin selectively inhibit the mu1 binding of [3H]dihydromorphine, leaving mu2 sites, while low morphine concentrations eliminate the mu1 binding of [3H][D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin, leaving delta sites. Thus, quantitative differences between images of sections incubated in the presence and absence of these low concentrations of unlabeled opioid represent mu1 binding sites. The regional distributions of mu1 sites labeled with [3H]dihydromorphine were quite similar to those determined by using [3H][D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin. High levels of mu1 binding were observed in the periaqueductal gray, medial thalamus, and median raphe, consistent with the previously described role of mu1 sites in analgesia. Other regions with high levels of mu1 binding include the nucleus accumbens, the clusters and subcallosal streak of the striatum, hypothalamus, medial habenula, and the medial septum/diagonal band region. The proportion of total specific binding corresponding to mu1 sites varied among the regions, ranging from 14% to 75% for [3H][D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin and 20% to 52% for [3H]dihydromorphine.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. I. Spinal cord and lower medulla. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90863-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. II. The brain stem. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 24;129(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90965-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III. The telencephalon. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 14;134(3):393–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90817-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buatti M. C., Pasternak G. W. Multiple opiate receptors: phylogenetic differences. Brain Res. 1981 Aug 10;218(1-2):400–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Cooper B. R., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. Multiple opiate receptors: different regional distribution in the brain and differential binding of opiates and opioid peptides. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):91–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Multiple opiate receptors. Enkephalins and morphine bind to receptors of different specificity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2610–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duka T., Schubert P., Wüster M., Stoiber R., Herz A. A selective distribution pattern of different opiate receptors in certain areas of rat brain as revealed by in vitro autoradiography. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jan 20;21(2):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90368-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gintzler A. R., Pasternak G. W. Multiple mu receptors: evidence for mu2 sites in the guinea pig ileum. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Aug 19;39(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H., Kuhar M. J., Young W. S., 3rd Differentiation of delta and mu opiate receptor localizations by light microscopic autoradiography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6239–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazum E., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P., Pasternak G. W. Naloxazone irreversibly inhibits the high affinity binding of [125I]D-ala2-D-leu5-enkephalin. Life Sci. 1981 Jun 29;28(26):2973–2979. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Pert C. B. In vitro autoradiography of opiate receptors in rat brain suggests loci of "opiatergic" pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5532–5536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Sokoloff L. Quantitative receptor autoradiography: tissue defatting eliminates differential self-absorption of tritium radiation in gray and white matter of brain. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 12;321(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holaday J. W., Pasternak G. W., Faden A. I. Naloxazone pretreatment modifies cardiorespiratory, temperature, and behavioral effects of morphine. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jun 16;37(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson N., Houghten R., Pasternak G. W. Binding of 3H-beta-endorphin in rat brain. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1381–1384. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. S., Pasternak G. W. Spinal and supraspinal opioid analgesia in the mouse: the role of subpopulations of opioid binding sites. Brain Res. 1983 Jul 18;271(1):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. S., Spiegel K., Lockhart S. H., Pasternak G. W. Separation of opioid analgesia from respiratory depression: evidence for different receptor mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jan;232(1):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. S., Spiegel K., Nishimura S. L., Pasternak G. W. Dissociation of morphine's analgesic and respiratory depressant actions. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):487–488. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz R. A., Cruciani R. A., Costa T., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. A very high affinity opioid binding site in rat brain: demonstration by computer modeling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90469-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura S. L., Recht L. D., Pasternak G. W. Biochemical characterization of high-affinity 3H-opioid binding. Further evidence for Mu1 sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;25(1):29–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. Naloxazone, a long-acting opiate antagonist: effects on analgesia in intact animals and on opiate receptor binding in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Sep;214(3):455–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W. Opiate, enkephalin, and endorphin analgesia: relations to a single subpopulation of opiate receptors. Neurology. 1981 Oct;31(10):1311–1315. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.10.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Snyder S. H. Identification of novel high affinity opiate receptor binding in rat brain. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):563–565. doi: 10.1038/253563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Zhang A., Tecott L. Developmental differences between high and low affinity opiate binding sites: their relationship to analgesia and respiratory depression. Life Sci. 1980 Sep 29;27(13):1185–1190. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor binding--enhancement by opiate administration in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Apr 1;25(7):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simone D. A., Bodnar R. J., Goldman E. J., Pasternak G. W. Involvement of opioid receptor subtypes in rat feeding behavior. Life Sci. 1985 Mar 4;36(9):829–833. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel K., Kourides I. A., Pasternak G. W. Prolactin and growth hormone release by morphine in the rat: different receptor mechanisms. Science. 1982 Aug 20;217(4561):745–747. doi: 10.1126/science.6285470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toll L., Keys C., Polgar W., Loew G. The use of computer analysis in describing multiple opiate receptors. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unnerstall J. R., Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J., Palacios J. M. Quantitative receptor autoradiography using [3H]ultrofilm: application to multiple benzodiazepine receptors. J Neurosci Methods. 1982 Jul;6(1-2):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(82)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolozin B. L., Pasternak G. W. Classification of multiple morphine and enkephalin binding sites in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L., Pasternak G. W. Specific mu 2 opioid isoreceptor regulation of nigrostriatal neurons: in vivo evidence with naloxonazine. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jun 30;37(3):291–293. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90446-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L., Richard J. W., Thakur M. Mu opiate isoreceptors: differentiation with kappa agonists. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 15;31(20-21):2313–2317. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. A new method for receptor autoradiography: [3H]opioid receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. Z., Pasternak G. W. Ontogeny of opioid pharmacology and receptors: high and low affinity site differences. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. Z., Pasternak G. W. Opiates and enkephalins: a common binding site mediates their analgesic actions in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 24;29(8):843–851. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. Z., Pasternak G. W. mu- and delta-opiate receptors: correlation with high and low affinity opiate binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 17;67(2-3):323–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90518-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








