Fig. 7.
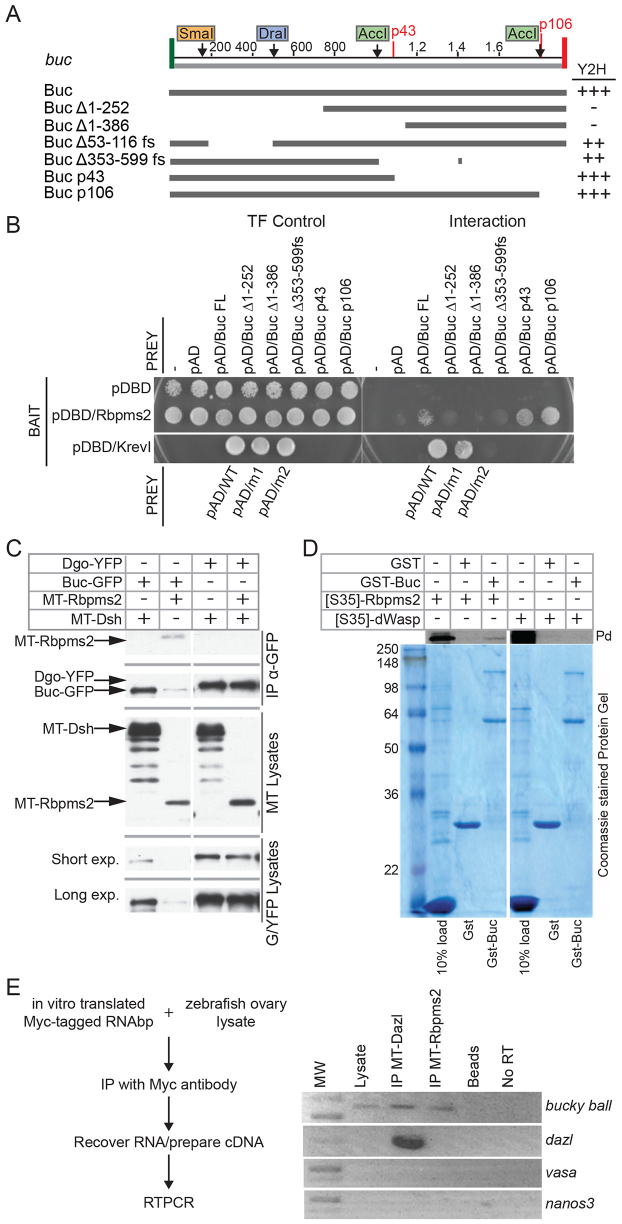
Buc protein interacts with the RNAbp Rbpms2. (A) Summary of buc deletion constructs used in the yeast two-hybrid analyses in B. Buc interacts with Rbpms2 via the N-terminus of Buc. The transformation (TF) control plates select for bait (pDBD) and prey (pAD) plasmids, whereas the interaction plates select for binding between the bait and prey proteins. Control baits and preys were KrevI and a strongly interacting prey Ral/GDS (wt) and two mutants: Ral/GDSm1 (moderate/medium interaction with Krev) and Ral/GDSm2 (weak/no interaction with KrevI). (C) Rbpms2 co-immunoprecipitates with Buc in HEK293 lysates. Top panels indicate transfected plasmids. Long exposure reveals proteins with lower expression levels. (D) Pull-down assay with GST- and 35S-labeled GFP fusion proteins. (pd, pull down). GST fusion protein inputs were visualized with Coomassie Blue. (E) RNA IP experiments using in vitro synthesized Myc-tagged RNAbps. The RNAs that co-immunoprecipitated with Myc-tagged RNAbps were amplified by RT-PCR. MT-Rbpms2 immunoprecipitated buc but not nanos2, vasa or dazl. MT-Dazl associated with buc and dazl mRNAs.