Abstract
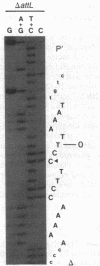
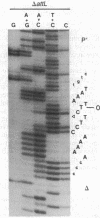
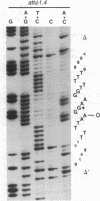
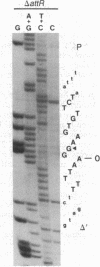
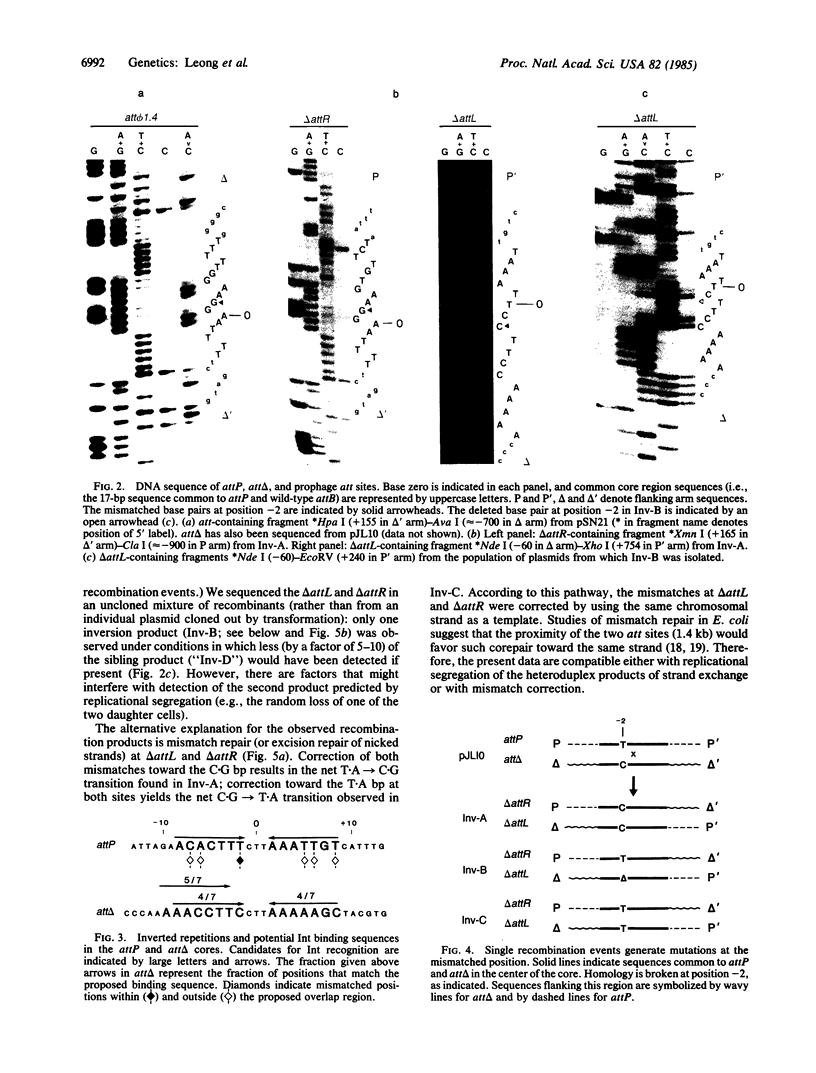
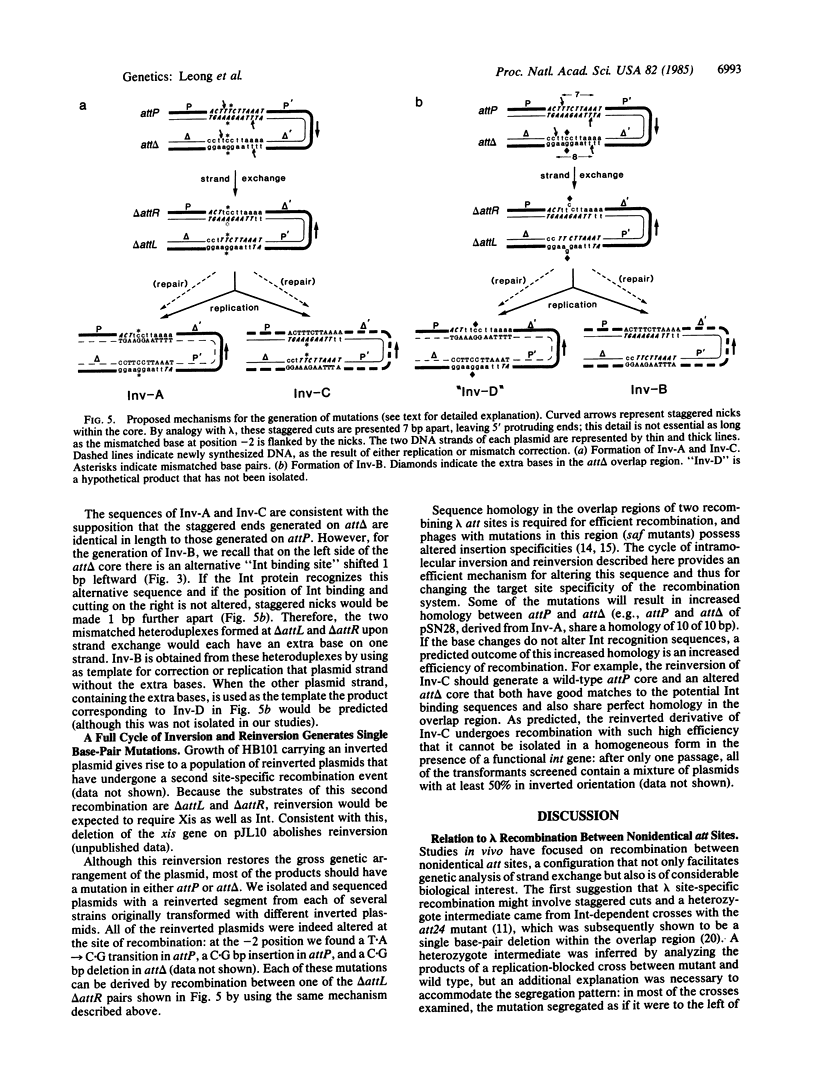
The sequence analysis of both products of individual phi 80 site-specific recombination events in vivo shows that recombination with a secondary attachment (att) site generates several different novel joints at the mismatched position: one recombination event resulted in a single base-pair deletion and two other recombination events resulted in two different single base-pair substitutions. The characterized products of recombination can be straightforwardly interpreted as the outcome of strand exchange involving staggered nicks bracketing the heterology within an overlap region of five to nine base pairs. In comparison, more complex segregation patterns have been observed in previous studies of lambda recombination between nonidentical att sites; the nature of the overlap region heterology may have a significant effect on the segregation patterns. To recover both products of a single recombination event, we used a plasmid that carries the phi 80 int and xis genes and both att sites. Because the two att sites are situated in opposite orientation, intramolecular recombination between them inverts rather than deletes the intervening segment of DNA. Although subsequent reinversion restores the original gross genetic arrangement, single base-pair insertions, deletions, and substitutions are introduced at the sites of recombination. One of the mutations improves the recombination efficiency of the secondary att site and thereby converts a formerly "stable" sequence to an efficient target for rearrangement, and other mutations are predicted to alter the specificity of recombination. These pathways may also provide useful models for the efficient generation of localized sequence diversity on a development (as well as evolutionary) time scale.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer C. E., Hesse S. D., Gardner J. F., Gumport R. I. DNA interactions during bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:699–705. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. E. coli integration host factor binds to specific sites in DNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. The mechanism of phage lambda site-specific recombination: site-specific breakage of DNA by Int topoisomerase. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Flamm E., Weisberg R. A. An Escherichia coli mutant unable to support site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Nunes-Düby S., Lesser C. F., Youderian P., Susskind M. M., Landy A. The phi 80 and P22 attachment sites. Primary structure and interaction with Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4468–4477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Weisberg R., Enquist L., Mizuuchi M., Buraczynska M., Foeller C., Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. Structure and function of the phage lambda att site: size, int-binding sites, and location of the crossover point. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):429–437. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda: the mechanism of conservation site specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:143–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Patterns of lambda Int recognition in the regions of strand exchange. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Shulman M., Landy A. Biochemical analysis of att-defective mutants of the phage lambda site-specific recombination system. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):505–522. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Gottesman M. Attachment site mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 25;81(4):461–482. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90517-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely E., Simon M. DNA sequence adjacent to flagellar genes and evolution of flagellar-phase variation. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.74-81.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., Jr, Meselson M. Repair tracts in mismatched DNA heteroduplexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4135–4139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg R. A., Enquist L. W., Foeller C., Landy A. Role for DNA homology in site-specific recombination. The isolation and characterization of a site affinity mutant of coliphage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):319–342. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Studier F. W., Dorgai L., Appelbaum E., Weisberg R. A. Enzymes and sites of genetic recombination: studies with gene-3 endonuclease of phage T7 and with site-affinity mutants of phage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:715–726. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]