Abstract
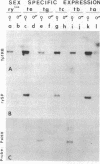
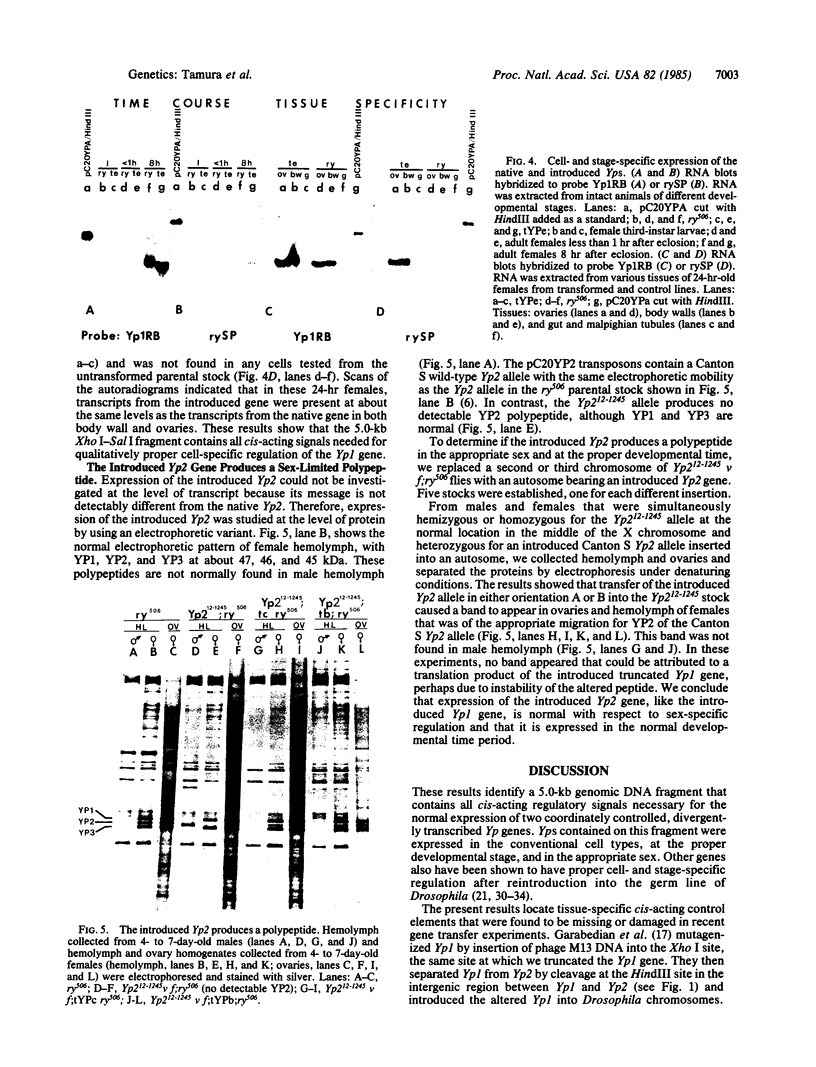
To find whether cis-acting regulatory sequences necessary for sex- and cell-specific expression of two yolk polypeptide genes (Yps) reside near the structural genes themselves, we introduced a 5.0-kilobase genomic DNA segment containing a 3' truncated Yp1 and a complete Yp2 into five different autosomal locations by P-element-mediated gene transfer. Transcripts from the introduced Yp1 were not found in male flies but appeared on a normal developmental schedule in adult females, accumulating in their body walls and ovarian follicles but not in guts or malpighian tubules. Protein from the introduced Yp2 allele was present in female hemolymph and vitellogenic ovaries but was lacking from male hemolymph. We conclude that sequences necessary for the correct stage-, cell-, and sex-specific expression of the Yp1 and Yp2 genes are included in this genomic fragment. These results combined with published work suggest that two tissue-specific, cis-acting, bidirectional, positive regulatory elements placed on either side of a centrally located HindIII site govern expression of both Yp genes--one element specific for fat body and the other specific for ovarian follicle cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker B. S., Belote J. M. Sex determination and dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:345–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett T., Pachl C., Gergen J. P., Wensink P. C. The isolation and characterization of Drosophila yolk protein genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belote J. M., Handler A. M., Wolfner M. F., Livak K. J., Baker B. S. Sex-specific regulation of yolk protein gene expression in Drosophila. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90148-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourouis M., Richards G. Remote regulatory sequences of the Drosophila glue gene sgs3 as revealed by P-element transformation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownes M., Hames B. D. Accumulation and degradation of three major yolk proteins in Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Zool. 1977 Apr;200(1):149–156. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402000118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownes M., Nöthiger R. Sex determining genes and vitellogenin synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):222–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00269661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. D., Weiner A. J., Goralski T. J., Mahowald A. P. The follicle cells are a major site of vitellogenin synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1982 Jan;89(1):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Hung M. C., Wensink P. C. Independent control elements that determine yolk protein gene expression in alternative Drosophila tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Klemenz R., Weber U., Kloter U. Functional analysis of the white gene of Drosophila by P-factor-mediated transformation. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2077–2085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T. Correct developmental expression of a cloned alcohol dehydrogenase gene transduced into the Drosophila germ line. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Gillam I. C., Delaney A. D., Tener G. M. Acetylation of chromosome squashes of Drosophila melanogaster decreases the background in autoradiographs from hybridization with [125I]-labeled RNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Aug;26(8):677–679. doi: 10.1177/26.8.99471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelrigg T., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Transformation of white locus DNA in drosophila: dosage compensation, zeste interaction, and position effects. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovemann B., Galler R., Walldorf U., Küpper H., Bautz E. K. Vitellogenin in Drosophila melanogaster: sequence of the yolk protein I gene and its flanking regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4721–4734. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
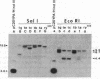
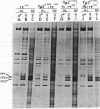
- Hung M. C., Barnett T., Woolford C., Wensink P. C. Transcript maps of Drosophila yolk protein genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 5;154(4):581–602. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jowett T., Postlethwait J. H. The Regulation of yolk polypeptide synthesis in Drosophila ovaries and fat body by 20-hydroxyecdysone and a juvenile hormone analog. Dev Biol. 1980 Nov;80(1):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRK R. L., LAI L. Y., MAHMOOD S., SINGH R. B. Haptoglobin types in South-East Asia. Nature. 1960 Jan 16;185:185–186. doi: 10.1038/185185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimble J., Sharrock W. J. Tissue-specific synthesis of yolk proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1983 Mar;96(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler J. D. Developmental genetics of the Drosophila egg. I. Identification of 59 sex-linked cistrons with maternal effects on embryonic development. Genetics. 1977 Feb;85(2):259–272. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota T., Fukunaga A., Kawabe M., Oishi K. Interactions between sex-transformation mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Hemolymph vitellogenins and gonad morphology. Genetics. 1981 Nov-Dec;99(3-4):429–441. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.3-4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwait J. H., Bownes M., Jowett T. Sexual phenotype and vitellogenin synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G., Cassab A., Bourouis M., Jarry B., Dissous C. The normal developmental regulation of a cloned sgs3 'glue' gene chromosomally integrated in Drosophila melanogaster by P element transformation. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2137–2142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell D. C., Higgins M. J., McMillan B. J., White B. N. Structural analysis of the three vitellogenin genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1323–1338. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholnick S. B., Morgan B. A., Hirsh J. The cloned dopa decarboxylase gene is developmentally regulated when reintegrated into the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirk P. D., Minoo P., Postlethwait J. H. 20-Hydroxyecdysone stimulates the accumulation of translatable yolk polypeptide gene transcript in adult male Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):186–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. The effect of chromosomal position on the expression of the Drosophila xanthine dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TELFER W. H. Immunological studies of insect metamorphosis. II. The role of a sex-limited blood protein in egg formation by the Cecropia silkworm. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Mar;37(4):539–558. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Smith D. F. Vitellogenesis: a versatile model for hormonal regulation of gene expression. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1979;35:47–95. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571135-7.50006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]