Abstract
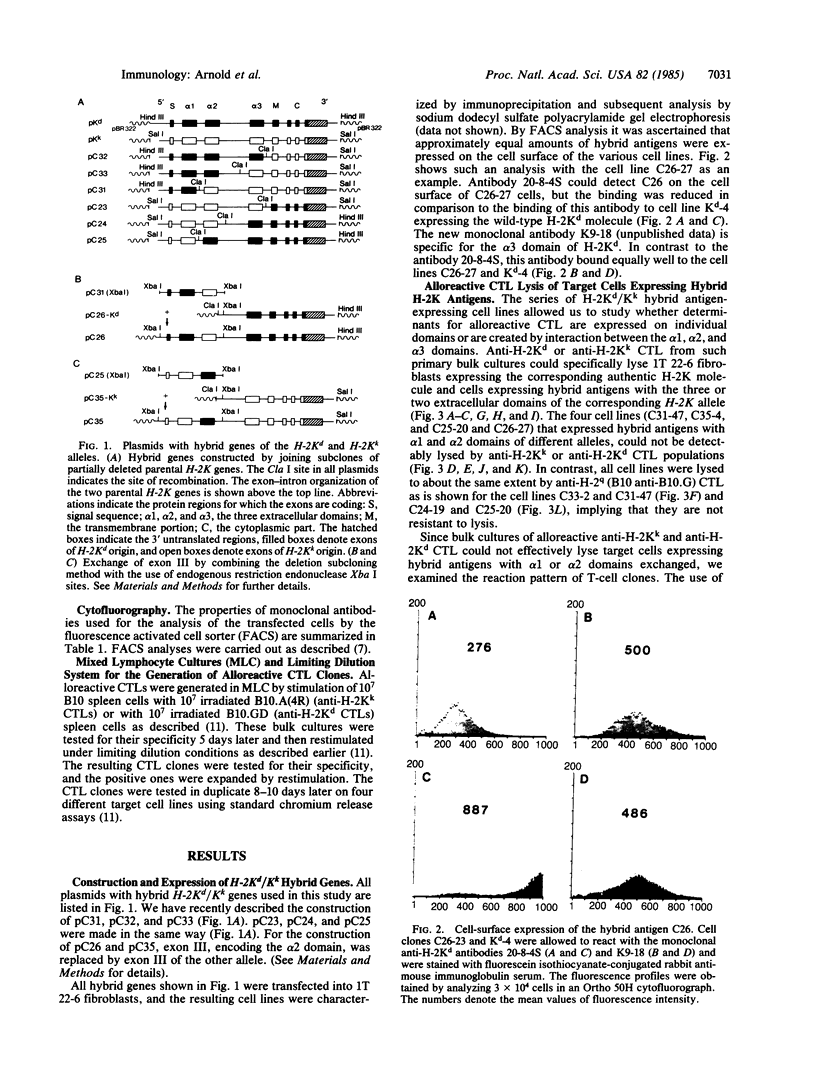
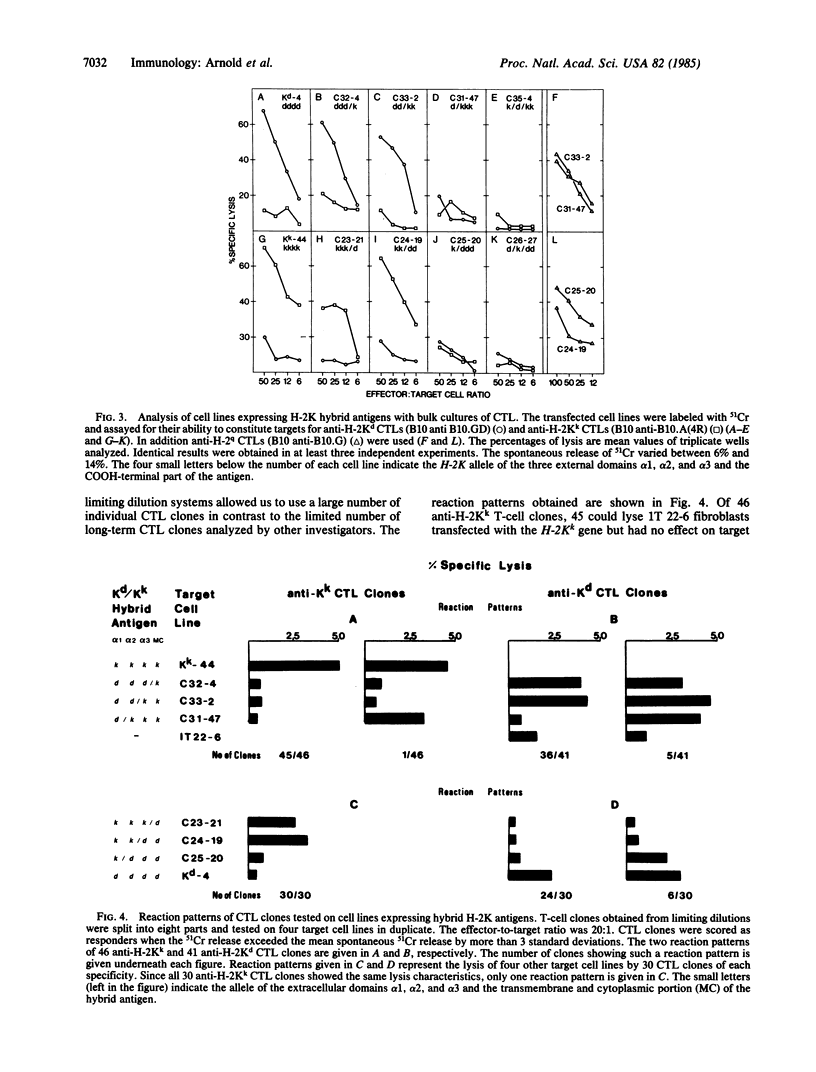
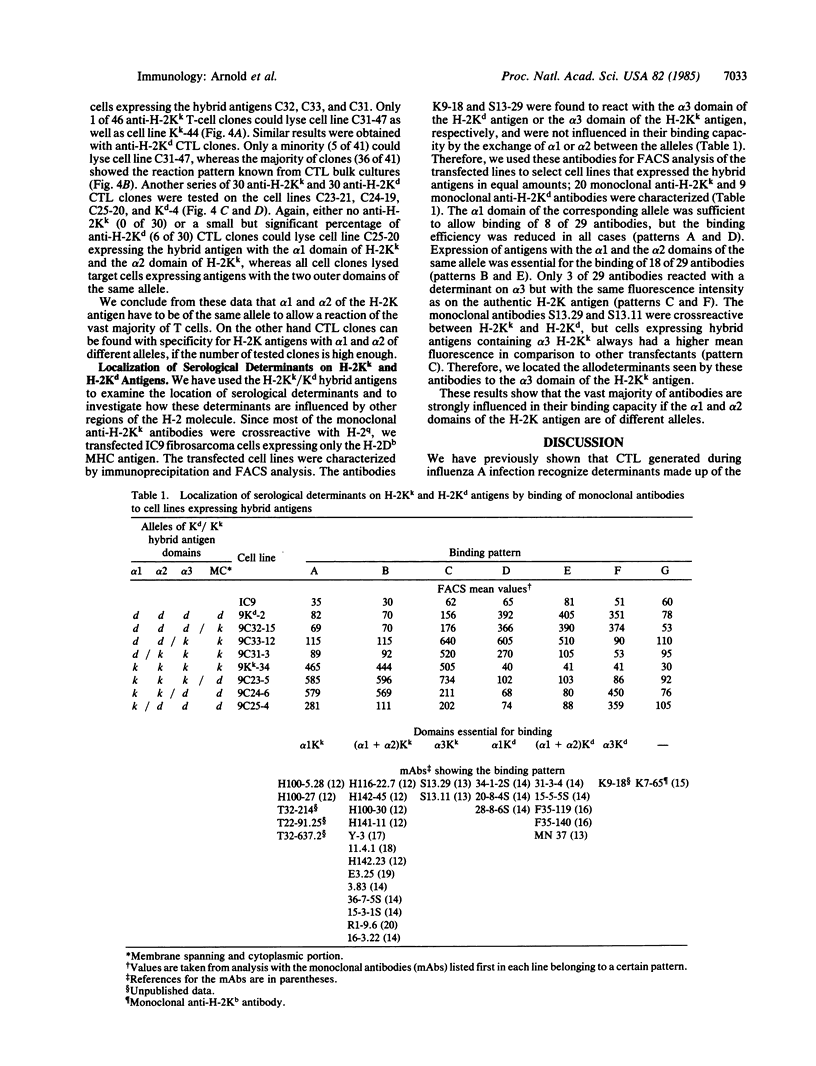
Hybrid genes were constructed for the localization of allodeterminants on murine class I antigens recognized by antibodies and cytolytic T lymphocytes. By using deletion subclones of the H-2Kd and H-2Kk genes, homologous regions were exchanged between the two alleles. The altered genes were introduced and expressed in mouse fibroblast and fibrosarcoma cells. Cells expressing hybrid antigens were analyzed with 29 monoclonal anti-H-2Kd and anti-H-2Kk antibodies and with 150 short-term alloreactive cytolytic T-cell clones. When only the first or only the second amino-terminal domain was exchanged, most T cells and 60% of the antibodies lost their reactivity to the H-2K antigen. No T-cell clone was directed against the third extracellular domain, whereas three antibodies could bind to this domain. This implies that nearly all determinants essential for a cytolytic T-cell response or for antibody binding lie on the two external domains and are conformational structures generated by the interaction of these two domains.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen H., Wraith D., Pala P., Askonas B., Flavell R. A. Domain interactions of H-2 class I antigens alter cytotoxic T-cell recognition sites. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):279–281. doi: 10.1038/309279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B., Burgert H. G., Archibald A. L., Kvist S. Complete nucleotide sequence of the murine H-2Kk gene. Comparison of three H-2K locus alleles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9473–9487. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B., Burgert H. G., Hamann U., Hämmerling G., Kees U., Kvist S. Cytolytic T cells recognize the two amino-terminal domains of H-2 K antigens in tandem in influenza A infected cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90528-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lennox E. S., Alderson T., Croft L. A monoclonal anti-HLA antibody recognizes a mouse tumor-associated antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Feb;13(2):160–166. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G. J., Rüsch E., Tada N., Kimura S., Hämmerling U. Localization of allodeterminants on H-2Kb antigens determined with monoclonal antibodies and H-2 mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4737–4741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Cooperative interaction of B lymphocytes with antigen-specific helper T lymphocytes is MHC restricted. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):547–549. doi: 10.1038/292547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch S., Koch N., Robinson P., Hämmerling G. Comparison of allogeneic and xenogeneic determinants on the H-2Kk molecule. Transplantation. 1983 Aug;36(2):177–180. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198308000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Roberts L., Dobberstein B. Mouse histocompatibility genes: structure and organisation of a Kd gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):245–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Choi E., Weis J., Seidman J. G., Ozato K., Liu L., Burakoff S. J., Reiss C. S. Dissection of serological and cytolytic T lymphocyte epitopes on murine major histocompatibility antigens by a recombinant H-2 gene separating the first two external domains. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):167–178. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Evans G. A., Shykind B., Margulies D. H., Seidman J. G. Hybrid H-2 histocompatibility gene products assign domains recognized by alloreactive T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2040–2043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewarson S., Figueroa F., Klein J. Monoclonal antibodies specific for class I and class II molecules controlled by the mouse H-2 complex. Immunogenetics. 1982;16(4):373–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00372310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonkonogy S. L., Amos D. B. Paired H-2-specific monoclonal antibodies react differently to red cells and lymphocytes. Immunogenetics. 1981 Dec;14(6):497–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00350121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Bulbuc N., Hämmerling G. J., Katzav S., Segal S., Feldman M. Abrogation of metastatic properties of tumour cells by de novo expression of H-2K antigens following H-2 gene transfection. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):301–305. doi: 10.1038/315301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C., Goronzy J., Hämmerling G. J. Recognition of polymorphic H-2 domains by T lymphocytes. I. Functional role of different H-2 domains for the generation of alloreactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes and determination of precursor frequencies. J Exp Med. 1981 Dec 1;154(6):1717–1731. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.6.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]