Abstract
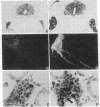
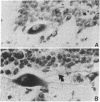
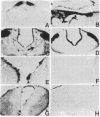
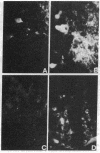
The present investigation was directed toward exploration of the spectrum of action of murine nerve growth factor (m-NGF) in peripheral cells and neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) of Xenopus laevis tadpoles. It was found that systemic m-NGF injections elicit growth and differentiative effects not only on sensory and sympathetic nerve cells but also on several populations in the CNS. The finding that aminergic and peptidergic neurons in brain centers are highly receptive to m-NGF activity provides evidence for the broad spectrum of action of this molecule in lower vertebrates and calls for a systematic search for these and other putative target cells in the CNS of higher vertebrates.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloe L., Levi-Montalcini R. Nerve growth factor-induced transformation of immature chromaffin cells in vivo into sympathetic neurons: effect of antiserum to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1246–1250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloe L., Mugnaini E., Levi-Montalcini R. Light and electron microscopic studies on the excessive growth of sympathetic ganglia in rats injected daily from birth with 6-OHDA and NGF. Arch Ital Biol. 1975 Dec;113(4):326–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer-Lelievre C. S., Ebendal T., Olson L., Seiger A. Localization of nerve growth factor-like immunoreactivity in rat nervous tissue. Med Biol. 1983;61(6):296–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benowitz L. I., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor in the goldfish brain: biological assay studies using pheochromocytoma cells. Brain Res. 1979 Feb 16;162(1):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni J. E., Clattenburg R. E., Millar E. Tanycyte ependymal cells in the third ventricle of young and adult rats: a Golgi study. Anat Anz. 1983;153(1):53–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody methods. Gen Cytochem Methods. 1958;1:399–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnahn H., Hefti F., Heumann R., Schwab M. E., Thoenen H. NGF-mediated increase of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) in the neonatal rat forebrain: evidence for a physiological role of NGF in the brain? Brain Res. 1983 Jul;285(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry I. A., Stöckel K., Thoenen H., Iversen L. L. The retrograde axonal transport of nerve growth factor. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 15;68(1):103–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., ANGELETTI P. U. Essential role of the nerve growth factor in the survival and maintenance of dissociated sensory and sympathetic embryonic nerve cells in vitro. Dev Biol. 1963 Mar;6:653–659. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R. Effects of mouse tumor transplantation on the nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1952 Aug 8;55(2):330–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1952.tb26548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Booker B. EXCESSIVE GROWTH OF THE SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA EVOKED BY A PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM MOUSE SALIVARY GLANDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):373–384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu C., Duprat A. M., Zalta J. P., Beetschen J. C. Action du facteur de croissance nerveuse (nerve growth factor) sur la différenciation de cellules embryonnaires d'amphibien. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Sep;68(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90582-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niall H. D. The evolution of peptide hormones. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:615–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raivich G., Zimmermann A., Sutter A. The spatial and temporal pattern of beta NGF receptor expression in the developing chick embryo. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):637–644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03677.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler M., Schwab M. E. Specific retrograde transport of nerve growth factor (NGF) from neocortex to nucleus basalis in the rat. Brain Res. 1984 May 21;300(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. L., Reichardt L. F. Expression of the beta-nerve growth factor gene correlates with the density of sympathetic innervation in effector organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7951–7955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. E., Delaney R. K. Retinal ganglion cell response to axotomy and nerve growth factor in the regenerating visual system of the newt (Notophthalmus viridescens): an ultrastructural morphometric analysis. Brain Res. 1979 Aug 3;171(2):197–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel D. L., Model P. G. Development of the sympathetic system in the Mexican axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum. Dev Biol. 1977 Mar;56(1):76–96. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip H. K., Johnson E. M., Jr Developing dorsal root ganglion neurons require trophic support from their central processes: evidence for a role of retrogradely transported nerve growth factor from the central nervous system to the periphery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6245–6249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]