Abstract
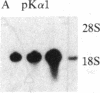
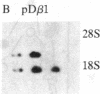
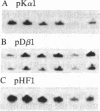
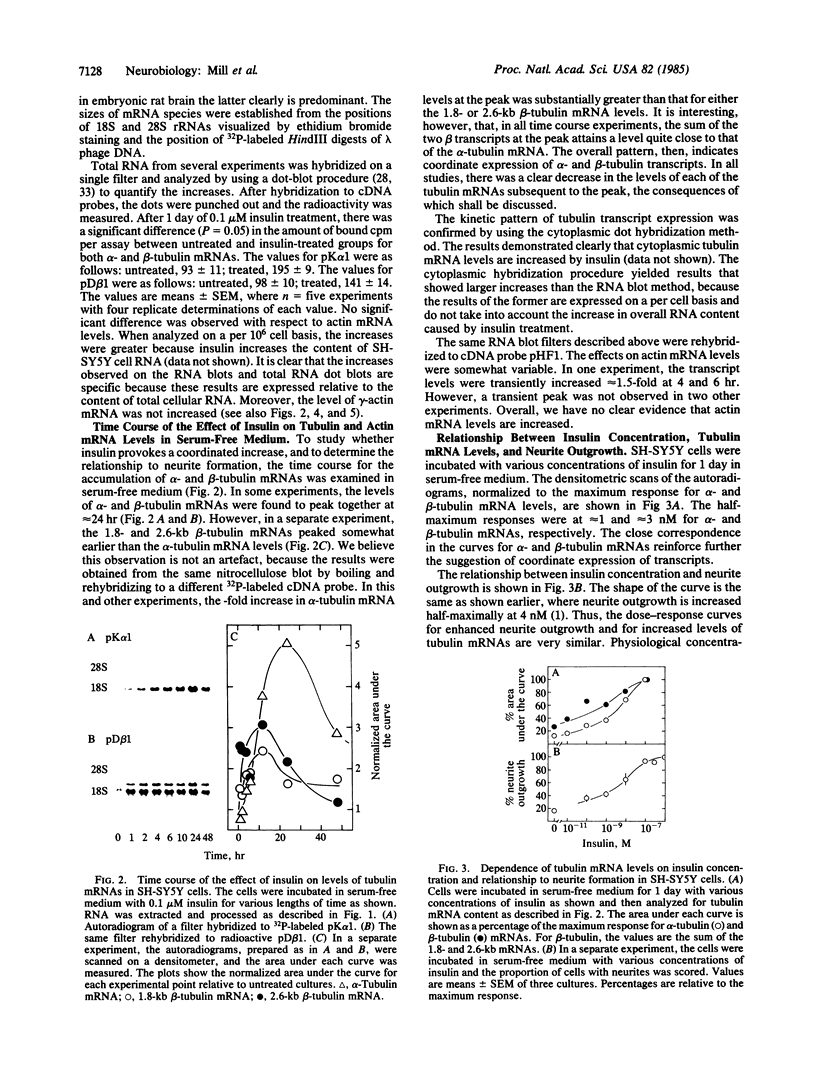
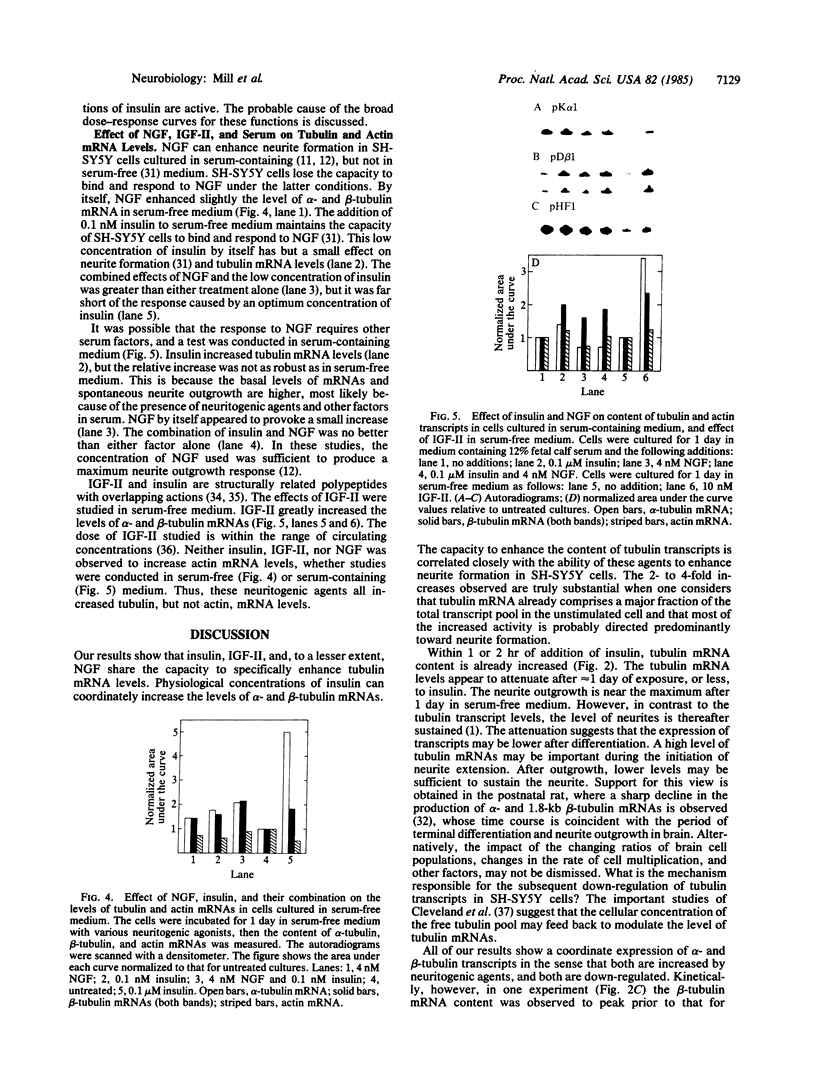
We have previously shown that insulin and the insulin-like growth factors share some important neurotrophic properties with nerve growth factor (NGF), including the capacity to enhance neurite formation. In this study, we have examined the effects of these neuritogenic agents on the expression of genes coding for important cytoskeletal proteins of axons and dendrites. Insulin specifically and coordinately increased the levels of alpha- and beta-tubulin mRNAs in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. The dose-response curves for these increases were very similar to that for enhancement of neurite formation. Tubulin transcripts reached a transient maximum in approximately 1 day, suggesting that higher levels are important during initiation of neurites and that high levels are not required to sustain neurites once formed. Insulin-like growth factor II shared with insulin the capacity to substantially increase tubulin mRNA levels. NGF had but a small effect. Complementary mechanisms for these neurotrophic agents are suggested, because other studies show NGF and insulin can synergistically potentiate neurite formation. None of the factors altered the levels of actin mRNA. Thus, neurite formation does not seem to require a coordinate increase in actin and tubulin transcripts in SH-SY5Y cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acquaviva A. M., Bruni C. B., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Cell-free synthesis of rat insulin-like growth factor II. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):656–658. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedler J. L., Roffler-Tarlov S., Schachner M., Freedman L. S. Multiple neurotransmitter synthesis by human neuroblastoma cell lines and clones. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 1):3751–3757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M. M., Greene L. A. Changes in the colchicine susceptibility of microtubules associated with neurite outgrowth: studies with nerve growth factor-responsive PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):379–386. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. F., Farmer S. R. Regulation of tubulin and actin mRNA production in rat brain: expression of a new beta-tubulin mRNA with development. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1333–1342. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Gilbert D. Cytoskeletal elements in neurons. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:505–523. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton L. E., Wilson W. H., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor in mouse saliva. Rapid isolation procedures for and characterization of 7 S nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7807–7812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Kirschner M. W., Cowan N. J. Isolation of separate mRNAs for alpha- and beta-tubulin and characterization of the corresponding in vitro translation products. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1021–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., Sherline P., Kirschner M. W. Unpolymerized tubulin modulates the level of tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan N. J., Dobner P. R., Fuchs E. V., Cleveland D. W. Expression of human alpha-tubulin genes: interspecies conservation of 3' untranslated regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1738–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodyer C. G., De Stéphano L., Lai W. H., Guyda H. J., Posner B. I. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor receptors in rat anterior pituitary, hypothalamus, and brain. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1187–1195. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. L., Dudley L., Dobner P. R., Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. Identification of two human beta-tubulin isotypes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):854–862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havrankova J., Roth J., Brownstein M. Insulin receptors are widely distributed in the central nervous system of the rat. Nature. 1978 Apr 27;272(5656):827–829. doi: 10.1038/272827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N., Shooter E. M. Regulation of nerve growth factor synthesis in mouse submaxillary glands by testosterone. J Neurochem. 1975 Dec;25(6):843–851. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb04416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Server A. C., Ishii D. N., Riopelle R. J., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 24;297(21):1149–1158. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711242972105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M. Immunological cross-reactivity of multiplication-stimulating activity polypeptides. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):401–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Scherson T., Ginzburg I., Littauer U. Z., Schwartz M. Regulation of mRNA levels for microtubule proteins during nerve regeneration. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 17;162(2):270–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80770-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacold S. T., Blackard W. G. Central nervous system insulin receptors in normal and diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 1979 Dec;105(6):1452–1457. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-6-1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Polo J. R., Werbach-Perez K., Tiffany-Castiglioni E. A human clonal cell line model of differentiating neurons. Dev Biol. 1979 Aug;71(2):341–355. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Ishii D. N. Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II and nerve growth factor on neurite outgrowth in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 8;302(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Lang F. F., Ishii D. N. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor II permit nerve growth factor binding and the neurite formation response in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2562–2566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Polypeptides with nonsuppressible insulin-like and cell-growth promoting activities in human serum: isolation, chemical characterization, and some biological properties of forms I and II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2365–2369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. H. Axonal transport: components, mechanisms, and specificity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:467–504. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Ishii D. N., Efstratiadis A. Developmental and tissue-specific expression of a family of transcripts related to rat insulin-like growth factor II mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1119–1134. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld K. H., Ishii D. N. Fast and slow nerve growth factor binding sites in human neuroblastoma and rat pheochromocytoma cell lines: relationship of sites to each other and to neurite formation. J Neurosci. 1985 Jul;5(7):1717–1728. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-07-01717.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld K. H., Ishii D. N. Nerve growth factor effects and receptors in cultured human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):375–391. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinelli W., Sonnenfeld K. H., Ishii D. N. Effects of phorbol ester tumor promoters and nerve growth factor on neurite outgrowth in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):5067–5073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinores S., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor: mechanism of action. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:223–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Froesch E. R., Humbel R. E. The insulin-like growth factors (IGF) of human serum: chemical and biological characterization and aspects of their possible physiological role. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;19:257–309. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152819-5.50024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]