Abstract
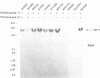
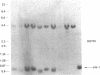
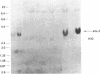
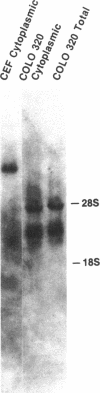
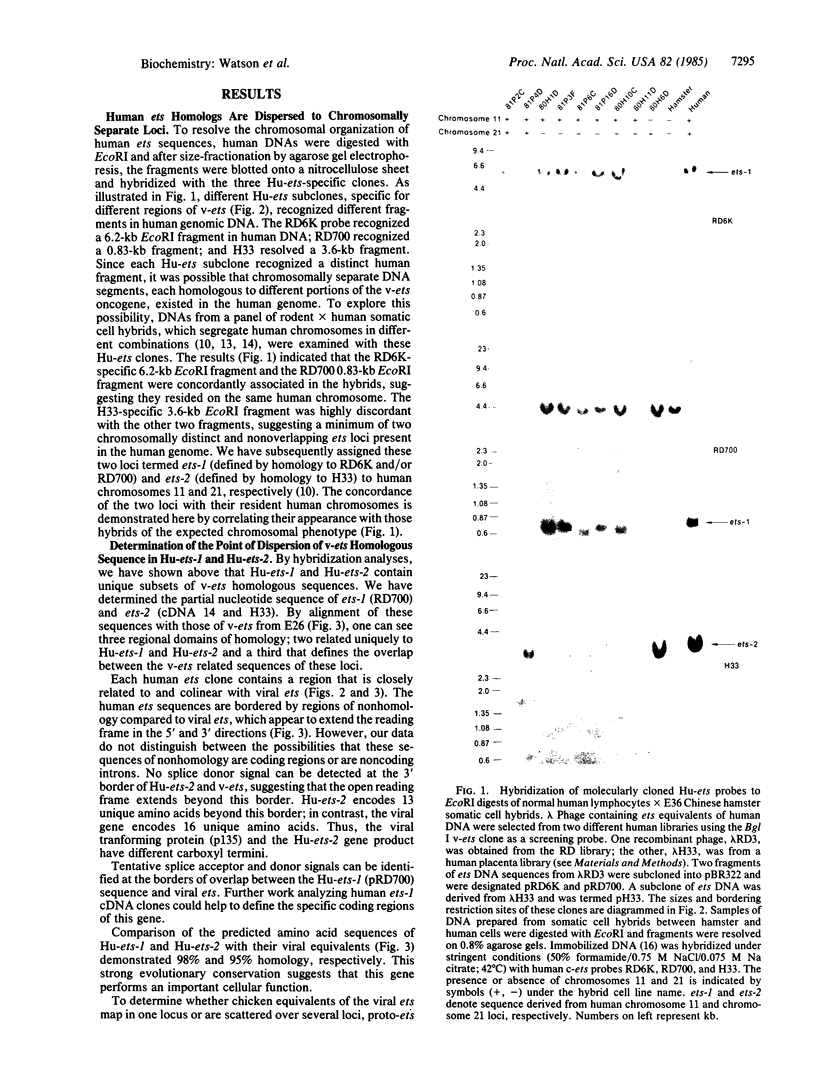
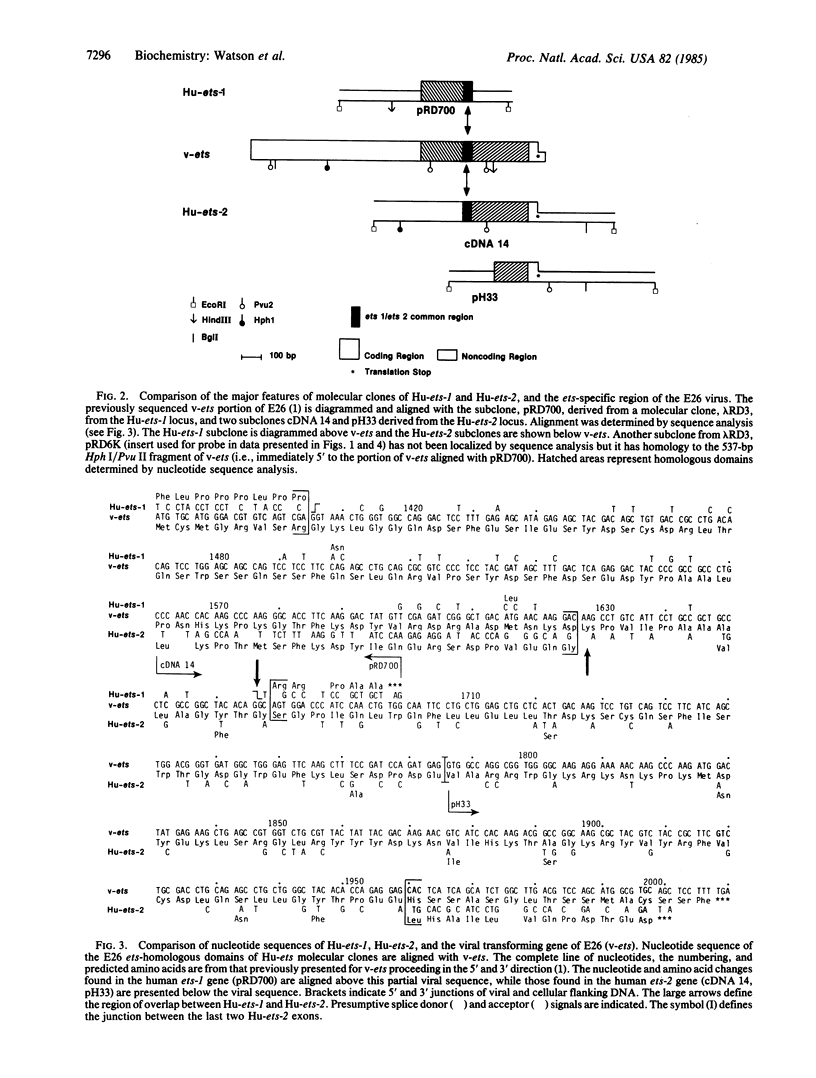
Human DNA segments homologous to the ets region from the transforming gene of avian erythroblastosis virus, E26, were molecularly cloned and shown to be closely related to the viral equivalent by hybridization and partial sequence analysis. The transforming gene of E26 has a tripartite origin with the structure delta gag [1.2 kilobases (kb) from the viral gag gene]-myb(0.9 kb from the chicken myb gene)-ets (1.6 kb from the chicken ets gene). Human ets DNA is located on two distinct human chromosomes. The human ets-1 locus on chromosome 11 encodes a single mRNA of 6.8 kb; the second locus, ets-2 on chromosome 21, encodes three mRNAs of 4.7, 3.2, and 2.7 kb. The ets-related sequences of human DNA on chromosomes 11 and 21 are discontiguous, except for a small overlap region encoding 14 amino acids, where 12 are conserved between these two loci. By contrast, the chicken homolog has contiguous ets-1 and ets-2 sequences and is primarily expressed in normal chicken cells as a single 7.5-kb mRNA. We conclude that the ets sequence shared by the virus, the chicken, and humans is likely to contain at least two dissociable functional domains, ets-1 and ets-2. Thus, the tripartite transforming gene of E26 includes four distinct domains that may be functionally relevant for the transforming function of the virus (delta gag, myb, ets-1, and ets-2).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Nunn M., Kan N., Watson D., Seeburg P. H., Papas T. Are activated proto-onc genes cancer genes? Haematol Blood Transfus. 1985;29:9–27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70385-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Retroviral transforming genes in normal cells? Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):219–226. doi: 10.1038/304219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flordellis C. S., Kan N. C., Lautenberger J. A., Samuel K. P., Garon C. F., Papas T. S. Analysis of the cellular proto-oncogene mht/raf: relationship to the 5' sequences of v-mht in avian carcinoma virus MH2 and v-raf in murine sarcoma virus 3611. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90257-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Gegonne A., Coll J., de Taisne C., Schneeberger A., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):395–397. doi: 10.1038/306395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash W. G., O'Brien S. J. Conserved regions of homologous G-banded chromosomes between orders in mammalian evolution: carnivores and primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6631–6635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M., Weiher H., Bullock P., Duesberg P. Avian erythroblastosis virus E26: nucleotide sequence of the tripartite onc gene and of the LTR, and analysis of the cellular prototype of the viral ets sequence. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):330–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90378-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S. J., Bonner T. I., Cohen M., O'Connell C., Nash W. G. Mapping of an endogenous retroviral sequence to human chromosome 18. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):74–77. doi: 10.1038/303074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]