Abstract
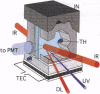
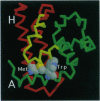
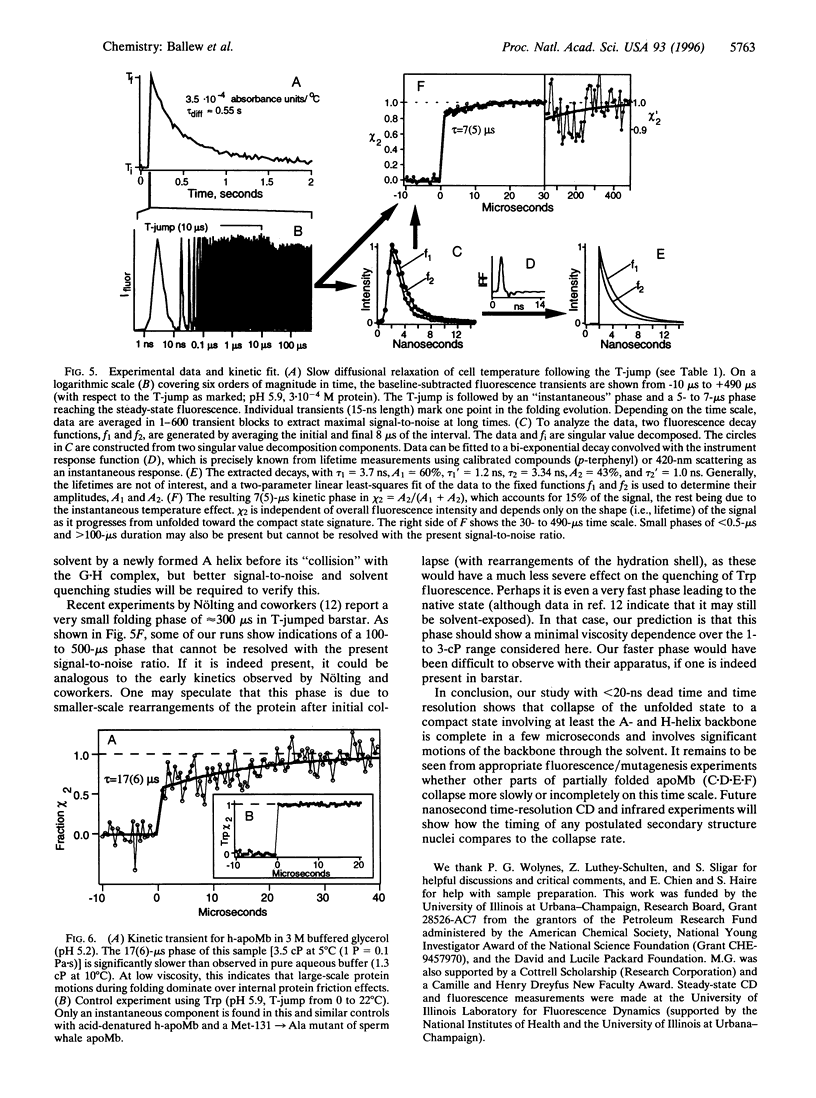
The rapid refolding dynamics of apomyoglobin are followed by a new temperature-jump fluorescence technique on a 15-ns to 0.5-ms time scale in vitro. The apparatus measures the protein-folding history in a single sweep in standard aqueous buffers. The earliest steps during folding to a compact state are observed and are complete in under 20 micros. Experiments on mutants and consideration of steady-state CD and fluorescence spectra indicate that the observed microsecond phase monitors assembly of an A x (H x G) helix subunit. Measurements at different viscosities indicate diffusive behavior even at low viscosities, in agreement with motions of a solvent-exposed protein during the initial collapse.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansari A., Jones C. M., Henry E. R., Hofrichter J., Eaton W. A. The role of solvent viscosity in the dynamics of protein conformational changes. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1796–1798. doi: 10.1126/science.1615323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismuto E., Gratton E., Irace G. Effect of unfolding on the tryptophanyl fluorescence lifetime distribution in apomyoglobin. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2132–2136. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryngelson J. D., Onuchic J. N., Socci N. D., Wolynes P. G. Funnels, pathways, and the energy landscape of protein folding: a synthesis. Proteins. 1995 Mar;21(3):167–195. doi: 10.1002/prot.340210302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill K. A., Bromberg S., Yue K., Fiebig K. M., Yee D. P., Thomas P. D., Chan H. S. Principles of protein folding--a perspective from simple exact models. Protein Sci. 1995 Apr;4(4):561–602. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeberg K. D., Springer B. A., Martinis S. A., Sligar S. G., Morikis D., Champion P. M. Alteration of sperm whale myoglobin heme axial ligation by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 23;29(42):9783–9791. doi: 10.1021/bi00494a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. V., Brayer G. D. High-resolution study of the three-dimensional structure of horse heart metmyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):885–897. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. A., Luthey-Schulten Z. A., Wolynes P. G. Protein tertiary structure recognition using optimized Hamiltonians with local interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9029–9033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang G. S., Oas T. G. Submillisecond folding of monomeric lambda repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6878–6882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings P. A., Wright P. E. Formation of a molten globule intermediate early in the kinetic folding pathway of apomyoglobin. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):892–896. doi: 10.1126/science.8235610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. M., Henry E. R., Hu Y., Chan C. K., Luck S. D., Bhuyan A., Roder H., Hofrichter J., Eaton W. A. Fast events in protein folding initiated by nanosecond laser photolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11860–11864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefhaber T. Kinetic traps in lysozyme folding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9029–9033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh S. N., Kay M. S., Baldwin R. L. Structure and stability of a second molten globule intermediate in the apomyoglobin folding pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5446–5450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishii I., Kataoka M., Goto Y. Thermodynamic stability of the molten globule states of apomyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jul 7;250(2):223–238. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nölting B., Golbik R., Fersht A. R. Submillisecond events in protein folding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10668–10672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panchenko A. R., Luthey-Schulten Z., Wolynes P. G. Foldons, protein structural modules, and exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 5;93(5):2008–2013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.5.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascher T., Chesick J. P., Winkler J. R., Gray H. B. Protein folding triggered by electron transfer. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1558–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips C. M., Mizutani Y., Hochstrasser R. M. Ultrafast thermally induced unfolding of RNase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 1;92(16):7292–7296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L., Griko YuV, Venyaminov SYu, Kutyshenko V. P. Cold denaturation of myoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sali A., Shakhnovich E., Karplus M. Kinetics of protein folding. A lattice model study of the requirements for folding to the native state. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 4;235(5):1614–1636. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler T., Herrler M., Marahiel M. A., Schmid F. X. Extremely rapid protein folding in the absence of intermediates. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Aug;2(8):663–673. doi: 10.1038/nsb0895-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Nicholls A., Friedman R., Honig B. Extracting hydrophobic free energies from experimental data: relationship to protein folding and theoretical models. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9686–9697. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner R. F., Kirby E. P. The interaction of the ground and excited states of indole derivatives with electron scavengers. J Phys Chem. 1969 Dec;73(12):4130–4135. doi: 10.1021/j100846a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEALE F. W. Cleavage of the haem-protein link by acid methylethylketone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Oct;35:543–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90407-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang G., Ma H. K. Menopausal osteoporosis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1994 Aug;46(2):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0020-7292(94)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timasheff S. N. The control of protein stability and association by weak interactions with water: how do solvents affect these processes? Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:67–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S., Causgrove T. P., Gilmanshin R., Fang K. S., Callender R. H., Woodruff W. H., Dyer R. B. Fast events in protein folding: helix melting and formation in a small peptide. Biochemistry. 1996 Jan 23;35(3):691–697. doi: 10.1021/bi952217p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]