Abstract
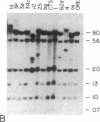
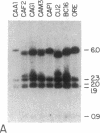
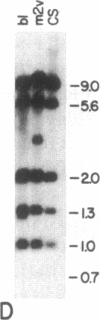
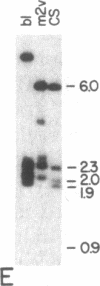
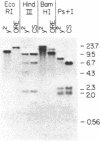
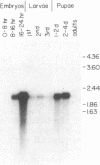
The yellow gene (y) is involved in pattern-specific melanin pigmentation of the cuticle of the adult fly and of larval mouth parts of Drosophila melanogaster. I have isolated some 70 kilobases (kb) of contiguous DNA from the y region. Chromosomal aberrations of y1-type alleles (null alleles) and y2-type alleles that give rise to characteristic pattern mosaicism of pigmentation were mapped by Southern blot analysis. The y2 allele is associated with the insertion of a "gypsy" transposable element 0.9 kb distal to the putative y coding region. A 3.1-kb region to which breakpoints of all y1-type alleles could be mapped is homologous to a 2.0-kb polyadenylylated mRNA, the expression of which is specifically regulated in development. This putative y gene transcript is present at high levels in pupae when melanization of the adult cuticle occurs, but its steady-state levels change dramatically during development, being highest in late embryos prior to hatching. This suggests that, in addition to melanin synthesis and/or deposition, the y gene product may have a role in other possibly neural functions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehme K. S. The Effect of Adult Body Color Mutations upon the Larva of Drosophila Melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1941 Jun 15;27(6):254–261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.27.6.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnet B., Wilson R. Pattern mosaicism for behavior controlled by the yellow locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1980 Dec;36(3):235–247. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300019868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Carramolino L., Cabrera C. V., Ruíz-Gómez M., Villares R., Boronat A., Modolell J. Molecular genetics of the achaete-scute gene complex of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carramolino L., Ruiz-Gomez M., Guerrero M. del C., Campuzano S., Modolell J. DNA map of mutations at the scute locus of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1185–1191. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csukás-Szatlóczky I., Parádi E. Phenoloxidase system in wild and mutant adults of drosophila melanogaster. I. Activation and activity of mono- and diphenoloxidases. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung. 1972;23(2):107–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dräger U. C., Olsen J. F. Origins of crossed and uncrossed retinal projections in pigmented and albino mice. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Jun;191(3):383–412. doi: 10.1002/cne.901910306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M. M. Back mutation in Drosophila melanogaster. I. X-ray induced back mutations at the yellow, scute and white loci. Genetics. 1961 Jun;46:671–682. doi: 10.1093/genetics/46.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M. M. Complementation at the yellow locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1961 Nov;46:1385–1388. doi: 10.1093/genetics/46.11.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Bellido A. Genetic Analysis of the Achaete-Scute System of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1979 Mar;91(3):491–520. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Bellido A., Santamaria P. Developmental Analysis of the Achaete-Scute System of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1978 Mar;88(3):469–486. doi: 10.1093/genetics/88.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. M. Genetic instability in Drosophila melanogaster: deletion induction by insertion sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5367–5369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillery R. W., Oberdorfer M. D., Murphy E. H. Abnormal retino-geniculate and geniculo-cortical pathways in several genetically distinct color phases of the mink (Mustela vison). J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jun 15;185(4):623–655. doi: 10.1002/cne.901850404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B., Delius H. Intervening sequences in chloroplast genomes. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVail J. H., Nixon R. A., Sidman R. L. Genetic control of retinal ganglion cell projections. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Dec 1;182(3):399–421. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Collins M., Rubin G. M. FB elements are the common basis for the instability of the wDZL and wC Drosophila mutations. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):551–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90252-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell H. K., Weber U. M., Schaar G. Phenol oxidase characteristics in mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1967 Oct;57(2):357–368. doi: 10.1093/genetics/57.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Bender W., Meselson M. Drosophila melanogaster mutations suppressible by the suppressor of Hairy-wing are insertions of a 7.3-kilobase mobile element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1678–1682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash W. G. Patterns of pigmentation color states regulated by the y locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1976 Feb;48(2):336–343. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash W. G., Yarkin R. J. Genetic regulation and pattern formation: a study of the yellow locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1974 Aug;24(1):19–26. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300015044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalenghe F., Turco E., Edström J. E., Pirrotta V., Melli M. Microdissection and cloning of DNA from a specific region of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00286105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strongin A. C., Guillery R. W. The distribution of melanin in the developing optic cup and stalk and its relation to cellular degeneration. J Neurosci. 1981 Nov;1(11):1193–1204. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-11-01193.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Burnet B., Eastwood L., Connolly K. Behavioural pleiotropy of the yellow gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1976 Aug;28(1):75–88. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300016748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Bingham P. M. Regulation of white locus expression: the structure of mutant alleles at the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]