Abstract
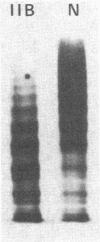
Von Willebrand factor (vWF) was purified from the plasma of a patient with type IIB von Willebrand disease (vWF from such a patient, IIB vWF) who had a normal platelet count and showed no evidence of spontaneous platelet aggregation. Large multimers of IIB vWF were absent from purified preparations and from plasma. Ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation was enhanced by purified IIB vWF. The aggregation of washed normal platelets mixed with IIB vWF (0.4 microgram/ml) required lower amounts of ristocetin than the aggregation of normal platelets mixed with the same concentrations of normal vWF. Moreover, purified IIB vWF alone induced aggregation of platelet-rich plasma at concentrations as low as 10 micrograms of IIB vWF/ml in the absence of any other agonist. Aggregation was blocked by a monoclonal antibody against the platelet membrane glycoprotein, GPIb, as well as by an anti-GPIIb/IIIa antibody. Washed platelet suspensions were promptly aggregated by IIB vWF only when fibrinogen and CaCl2 were added to the mixture. Purified IIB vWF induces the binding of fibrinogen to platelets. Such binding was blocked by the anti-GPIb monoclonal antibody as well as by the anti-GPIIb/IIIa monoclonal antibody that inhibited aggregation. A second anti-GPIIb/IIIa antibody, which has the property of blocking vWF but not fibrinogen binding to platelets, blocked neither aggregation nor fibrinogen binding induced by IIB vWF. These studies demonstrate that platelet aggregation is triggered by the initial interaction of IIB vWF with GPIb which is followed by exposure of fibrinogen binding sites on GPIIb/IIIa. Fibrinogen binds to these sites and acts as a necessary cofactor for the aggregation response.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruck C., Portetelle D., Glineur C., Bollen A. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluid by DEAE Affi-Gel blue chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Girolami A., Russell S., Ruggeri Z. M. Interaction of asialo von Willebrand factor with glycoprotein Ib induces fibrinogen binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex and mediates platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1198–1203. doi: 10.1172/JCI111816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto T., Ohara S., Hawiger J. Thrombin-induced exposure and prostacyclin inhibition of the receptor for factor VIII/von Willebrand factor on human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1212–1222. doi: 10.1172/JCI110560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Isoelectric focusing of human von Willebrand factor in urea-agarose gels. Blood. 1983 Feb;61(2):304–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainick H. R., Williams S. B., Coller B. S. Asialo von Willebrand factor interactions with platelets. Interdependence of glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa for binding and aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):19–25. doi: 10.1172/JCI111673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Nilsson I. M., Borge L., Gunnarsson M., Sjörin E. Platelet aggregation induced by 1-desamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (DDAVP) in Type IIB von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 6;309(14):816–821. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310063091402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAZAL L. A., AMSEL S., MILLER O. P., TOCANTINS L. M. THE PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF FIBRINOGEN PRECIPITATED FROM HUMAN PLASMA BY GLYCINE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:989–994. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Pidard D., Rosa J. P., Nurden A. T. The formation of Ca++-dependent complexes of platelet membrane glycoproteins IIb and IIIa in solution as determined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):268–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Bohn J. W., Ferry E. L., Yamamoto H., Molinaro C. A., Sherman L. A., Klinman N. R., Katz D. H. Monoclonal dinitrophenyl-specific murine IgE antibody: preparation, isolation, and characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2728–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Castella A. Platelet-type von Willebrand's disease: characterization of a new bleeding disorder. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):790–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Kupinski J. M., Castella A., Ruggeri Z. M. von Willebrand factor binds to platelets and induces aggregation in platelet-type but not type IIB von Willebrand disease. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1532–1542. doi: 10.1172/JCI111112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., DIXON D. J. EVIDENCE FOR LINKAGE OF UNIVALENT FRAGMENTS OR HALF-MOLECULES OF RABBIT GAMMA-GLOBULIN BY THE SAME DISULFIDE BOND. Biochemistry. 1964 Sep;3:1338–1342. doi: 10.1021/bi00897a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J., Johnson A. J., Karpatkin M. H., Puszkin S. Methods for the production of clinically effective intermediate- and high-purity factor-VIII concentrates. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jul;21(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., De Marco L., Gatti L., Bader R., Montgomery R. R. Platelets have more than one binding site for von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Mannucci P. M., Bader R., Barbui T. Factor VIII-related properties in platelets from patients with von Willebrand's disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jan;91(1):132–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Mannucci P. M., Lombardi R., Federici A. B., Zimmerman T. S. Multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor following administration of DDAVP: implications for pathophysiology and therapy of von Willebrand's disease subtypes. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1272–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Pareti F. I., Mannucci P. M., Ciavarella N., Zimmerman T. S. Heightened interaction between platelets and factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in a new subtype of von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1047–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. The complex multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1140–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Variant von Willebrand's disease: characterization of two subtypes by analysis of multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in plasma and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1318–1325. doi: 10.1172/JCI109795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Studies on human antihemophilic factor. Evidence for a covalently linked subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):925–937. doi: 10.1172/JCI108369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Kloczewiak M., Hawiger J. ADP-dependent common receptor mechanism for binding of von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen to human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4935–4939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N., Mills D. C., White J. G. Metabolism and function of human platelets washed by albumin density gradient separation. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jun;36(2):287–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Meyer D., Rabinowitz R., Pietu G., Girma J. P., Vicic W. J., Rogers J. Pseudo-von Willebrand's disease. An intrinsic platelet defect with aggregation by unmodified human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor and enhanced adsorption of its high-molecular-weight multimers. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 11;306(6):326–333. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202113060603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]