Abstract
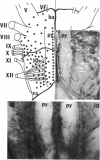
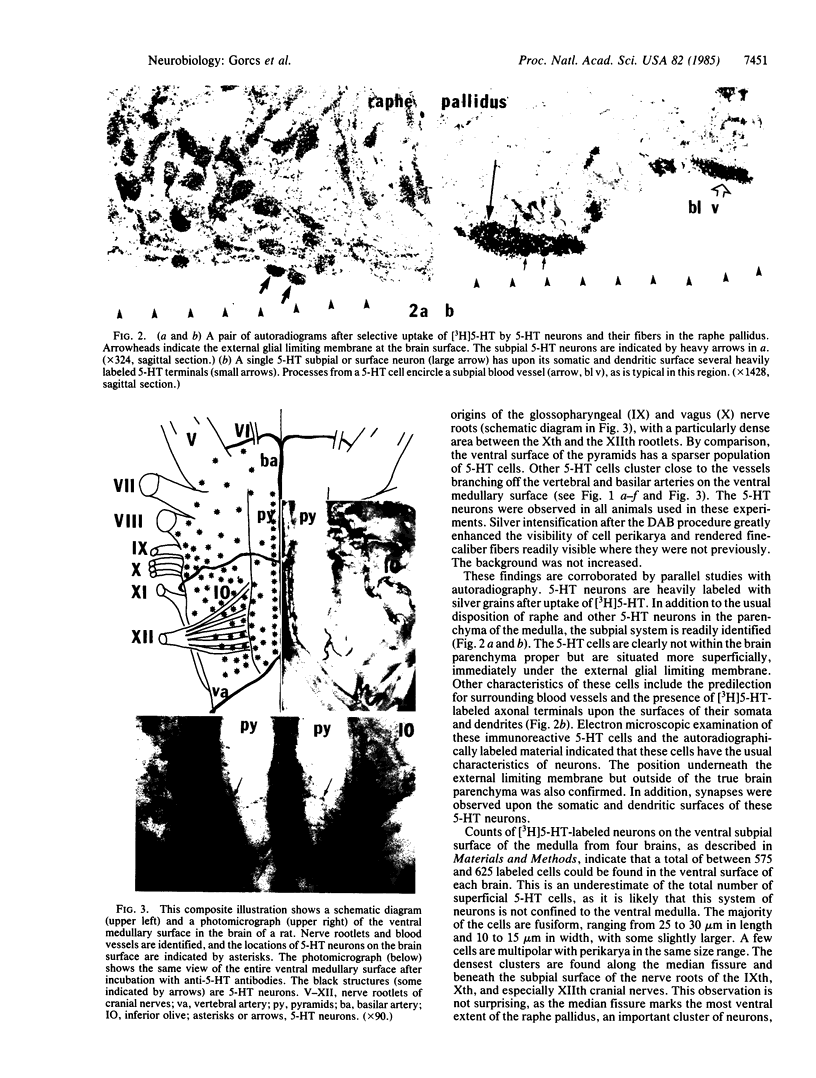
Serotonin neurons and fibers on the subpial surface of the ventral medulla oblongata in the rat are described by immunohistochemistry and autoradiography. The neurons are concentrated in the area encompassed by the origins of the abducens, hypoglossal, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves. The highest number of serotonin surface neurons appears along the median medullary fissure or basilar sulcus, where they may represent the most ventral extensions of the raphe pallidus group. As these cells lie on the surface of the brain, they could be directly affected by alterations in the chemical composition of the cerebrospinal fluid and, depending on their connections, could influence important medullary functions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aghajanian G. K., Gallager D. W. Raphe origin of serotonergic nerves terminating in the cerebral ventricles. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Fine structure of labelled axons in the cerebellar cortex and nuclei of rodents and primates after intraventricular infusions with tritiated serotonin. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1975 Dec 31;148(3):235–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00319846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Indoleamine neurons and their processes in the normal rat brain and in chronic diet-induced thiamine deficiency demonstrated by uptake of 3H-serotonin. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Dec 15;176(4):467–493. doi: 10.1002/cne.901760402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Jonsson G., Palay S. L. Serotonin and substance P coexist i, neurons of the rat's central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1582–1586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Serotonin axons in the supra- and subependymal plexuses and in the leptomeninges; their roles in local alterations of cerebrospinal fluid and vasomotor activity. Brain Res. 1976 Jan 30;102(1):103–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Degueurce A., Duverger D., MacKenzie E. T., Scatton B. Central serotonergic nerves project to the pial vessels of the brain. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):55–57. doi: 10.1038/306055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grota L. J., Brown G. M. Antibodies to indolealkylamines: serotonin and melatonin. Can J Biochem. 1974 Mar;52(3):196–202. doi: 10.1139/o74-032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorez H. P., Richards J. G. Distribution of indolealkylamine nerve terminals in the ventricles of the rat brain. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Nov 15;144(4):511–522. doi: 10.1007/BF00307377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Takeuchi Y., Yamada H., Ueda S., Goto M. Immunohistochemical studies on the serotonergic innervation of the pia mater. Histochemistry. 1982;76(2):277–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00501930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbusch H. W. Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat-cell bodies and terminals. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):557–618. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]