Abstract
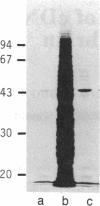
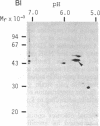
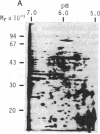
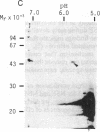
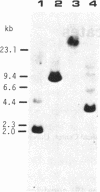
The cDNAs to mRNA for rat gamma gamma enolase (neuron-specific enolase; NSE; EC 4.2.1.11) were isolated from a cDNA library by using differential colony hybridization and a hybrid-selected translation assay. By overlapping of the nucleotide sequences of several cDNA inserts, it was found that they spanned 2232 base pairs (bp) which included 1299 bp of the complete coding region, 68 bp of the 5' noncoding region, and 848 bp of the 3' noncoding region, including a polyadenylylation signal. In addition, the poly(A) tail was also found. The amino acid sequence deduced from the nucleotide sequence was composed of 433 amino acids. Southern blot analysis with a cDNA insert detected one hybridizing fragment in rat genomic DNA digested with several different restriction enzymes. Dot-blot and transfer hybridization analyses of poly(A)+ RNA from developing rat brains showed an increase of NSE mRNA 10-30 days after birth.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan Y. L., Gutell R., Noller H. F., Wool I. G. The nucleotide sequence of a rat 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene and a proposal for the secondary structure of 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):224–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Araki K., Kushiya E., Takahashi Y. Partial purification and characterization of messenger RNA coding 14-3-2 protein from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1982 Aug;39(2):366–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb03957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Yoshida Y., Nabeshima Y., Takahashi Y. Biosynthesis of the brain-specific 14-3-2 protein in a cell-free system from wheat germ extract directed with poly(A)-containing RNA from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):687–693. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi K., Ishikawa K. Purification of messenger RNA coding for rat liver aldolase B subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):407–412. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Oobayashi A., Tanabe O., Ichishima E. Action of crystalline acid carboxypeptidase from Penicillium janthinellum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 26;397(2):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Sakimura K., Masuda T., Kushiya E., Takahashi Y. Changes in levels of translatable mRNA for neuron-specific enolase and non-neuronal enolase during development of rat brain and liver. J Biochem. 1983 Nov;94(5):1443–1450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]