Abstract
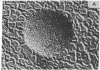
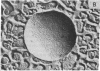
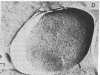
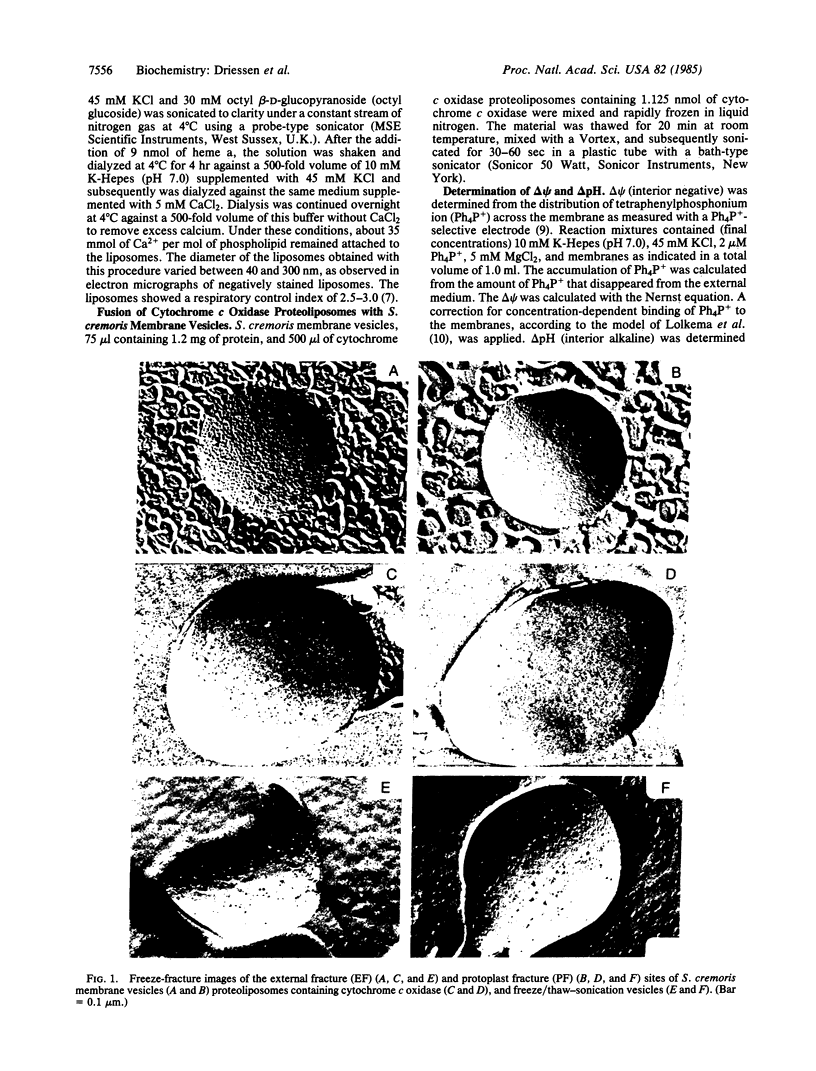
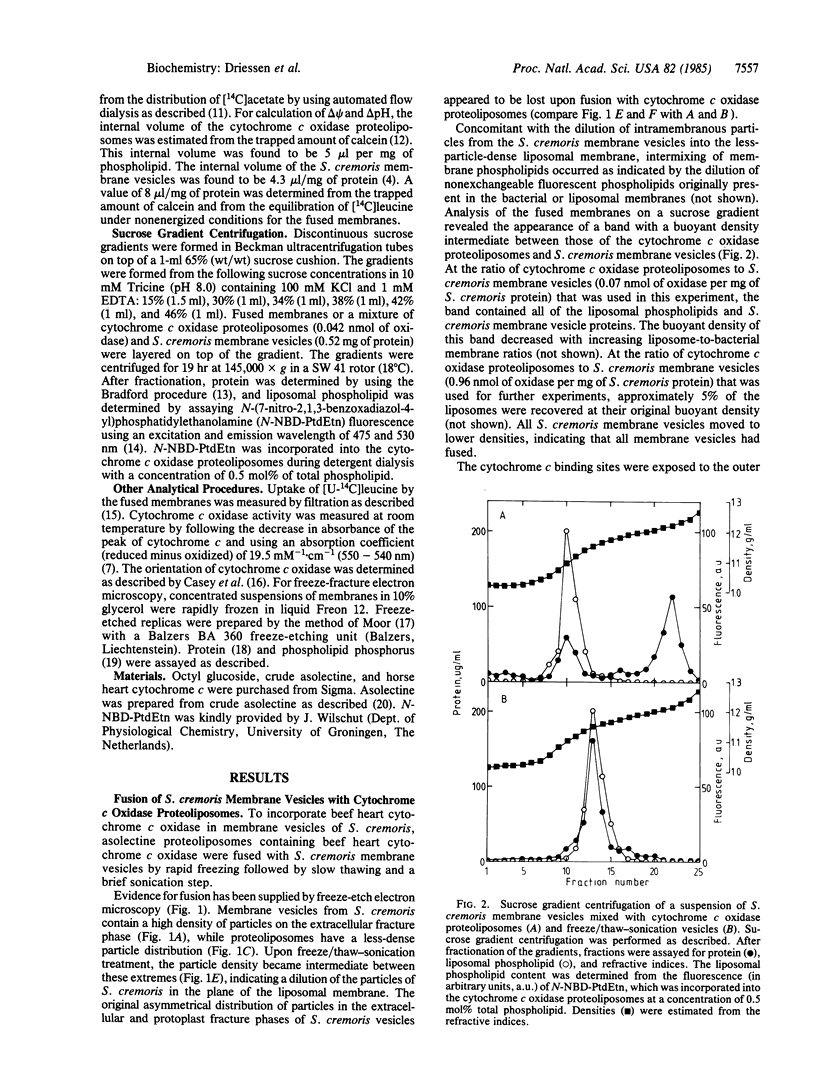
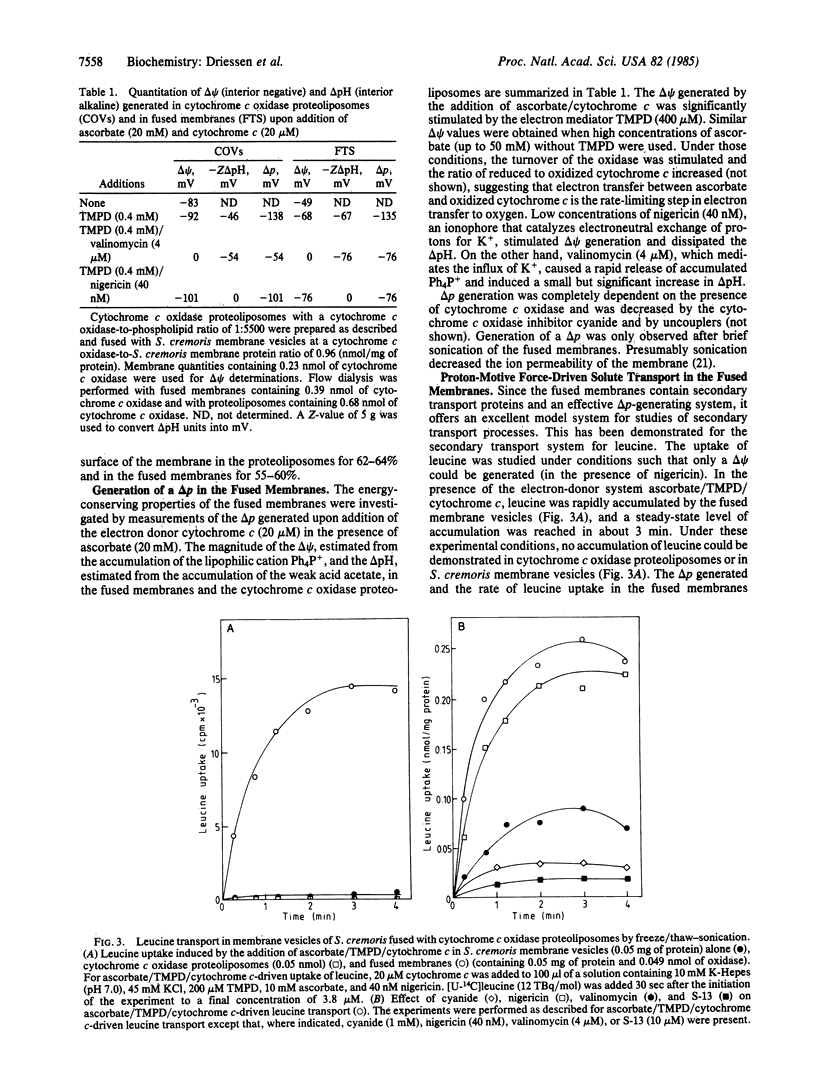
Membrane vesicles derived from the strictly fermentative lactic acid bacterium Streptococcus cremoris have been fused with proteoliposomes containing the beef heart mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase by means of a freeze/thaw-sonication technique. Evidence that fusion has taken place was obtained by freeze-etch electron microscopy, showing a less-dense intramembranous particle distribution in the fused membranes than in the bacterial membranes, and by sucrose gradient centrifugation, indicating a buoyant density of the majority of the membranes after fusion that was between the buoyant densities of the starting membrane preparations. In the fused membranes, 55-60% of the cytochrome c oxidase molecules are oriented with the cytochrome c binding site at the outer surface of the membrane. With the electron-donor system ascorbate/N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine/cytochrome c, a high proton-motive force (greater than 130 mV), inside negative and alkaline, can be generated in the fused membrane, and this proton-motive force can drive secondary transport of several amino acids. The procedure described can be used for incorporating a proton-motive force-generating system in isolated membrane vesicles from bacterial or eukaryotic origin that lack a suitable primary proton pump.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R. P., Ariano B. H., Azzi A. Studies on the transmembrane orientation of cytochrome c oxidase in phospholipid vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(2):313–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. Kinetic and steady-state investigations of solute accumulation in bacterial membranes by continuously monitoring the radioactivity in the effluent of flow-dialysis experiments. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. C., Kim J. J., Racker E. Ion transport and respiratory control in vesicles formed from cytochrome oxidase and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1338–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Sone N., Yoshida M., Kagawa Y. Isolation of the alanine carrier from the membranes of a thermophilic bacterium and its reconstitution into vesicles capable of transport. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(1):77–84. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:698–709. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster J. R., Jr, Hinkle P. C. Studies of the beta-galactoside transporter in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. I. Symmetrical facilitated diffusion and proton gradient-coupled transport. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7657–7661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOOR H. DIE GEFRIER-FIXATION LEBENDER ZELLEN UND IHRE ANWENDUNG IN DER ELEKTRONENMIKROSKOPIE. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1964 Apr 28;62:546–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita K., Patel L., Gennis R. B., Kaback H. R. Reconstitution of active transport in proteoliposomes containing cytochrome o oxidase and lac carrier protein purified from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Lageveen R. G., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Lactate efflux-induced electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.733-738.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U. Liposomes with a large trapping capacity prepared by freezing and thawing of sonicated phospholipid mixtures. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):186–194. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinbo T., Kamo N., Kurihara K., Kobatake Y. A PVC-based electrode sensitive to DDA+ as a device for monitoring the membrane potential in biological systems. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Apr 30;187(2):414–422. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Hoekstra D., Pagano R. E. Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4093–4099. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONETANI T. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. III. Improved preparation and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1680–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C., Yu L., King T. E. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. Interactions of the cytochrome oxidase protein with phospholipids and cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1383–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]