Abstract
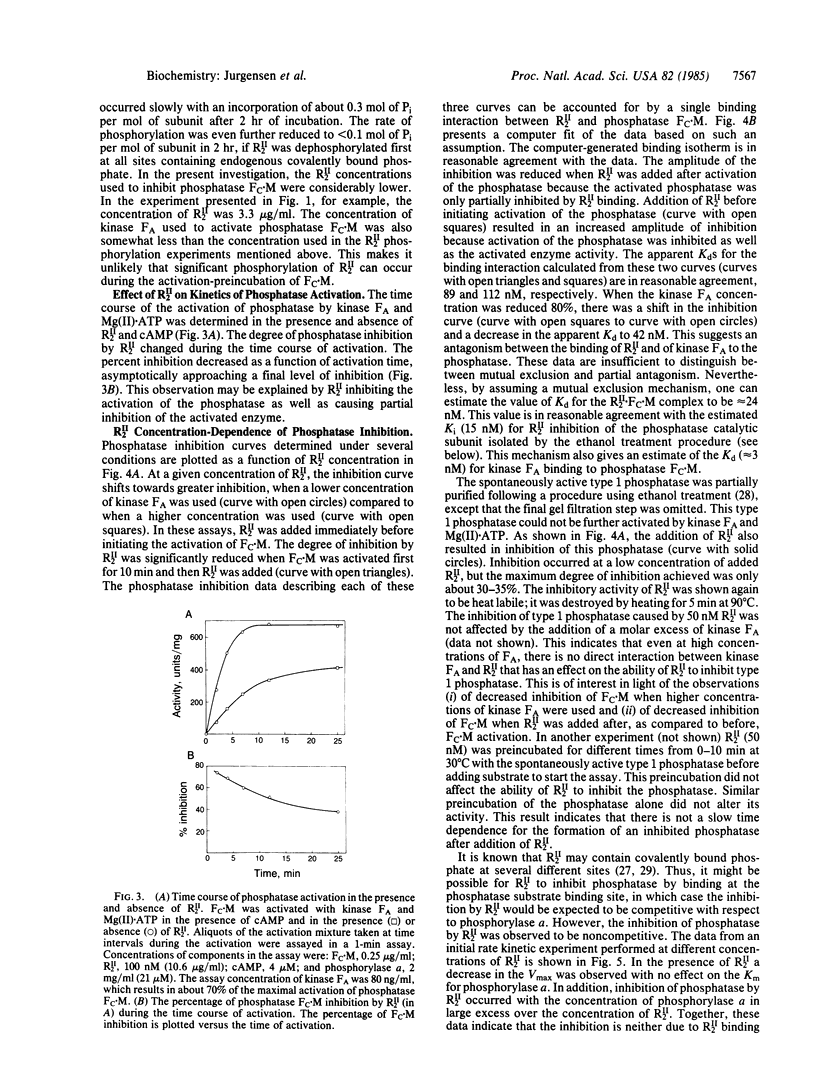
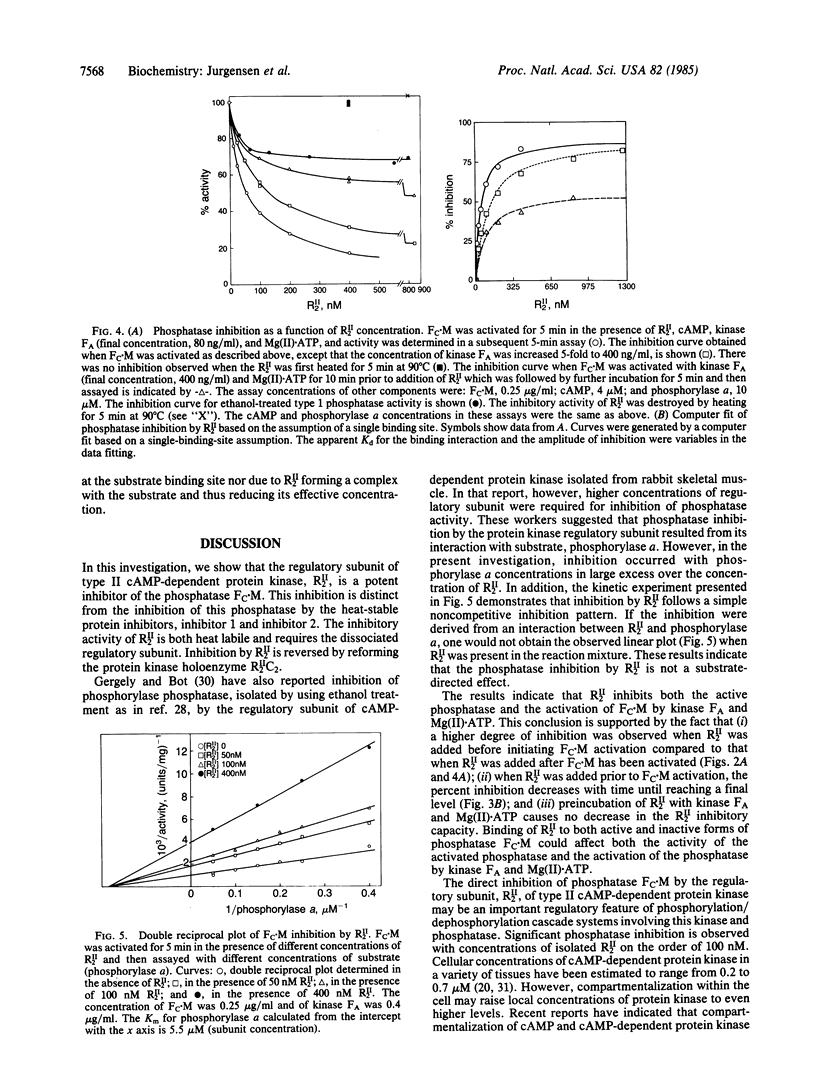
We report potent inhibition of the Mg(II).ATP-dependent protein phosphatase, Fc.M, by the regulatory subunit dimer of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase, RII2. The protein kinase catalytic subunit has no effect on phosphatase activity and is unable to substitute for kinase FA in the kinase FA- and Mg(II).ATP-mediated phosphatase activation reaction. Phosphatase inhibition was investigated as a function of RII2 concentration. The results suggest that RII2 both inhibits the active phosphatase and inhibits phosphatase activation. The inhibition is shown to be noncompetitive with respect to substrate (phosphorylase a). The potential physiological significance of this inhibition is discussed in terms of phosphorylation/dephosphorylation cascade systems involving this kinase and phosphatase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniw J. F., Nimmo H. G., Yeaman S. J., Cohen P. Comparison of the substrate specificities of protein phosphatases involved in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):423–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1620423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Brautigan D. L., Fischer E. H. Subunit structure and activation of inactive phosphorylase phosphatase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 5;22(14):3393–3399. doi: 10.1021/bi00283a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt H., Capulong Z. L., Lee E. Y. Purification and properties of rabbit liver phosphorylase phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8038–8044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt H., Lee E. Y., Killilea S. D. A protein inhibitor of rabbit liver phosphorylase phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):950–956. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90661-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Compartments of cyclic AMP and protein kinase in mammalian cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10233–10239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chock P. B., Rhee S. G., Stadtman E. R. Interconvertible enzyme cascades in cellular regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:813–843. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Duewer T., Fischer E. H. Phosphorylase from dogfish skeletal muscle. Purification and a comparison of its physical properties to those of rabbit muscle phosphorylase. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 6;10(14):2683–2694. doi: 10.1021/bi00790a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;14:117–196. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152814-0.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. The isolation and crystallization of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase b. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockhart D. A., Corbin J. D. Regulatory mechanisms in the control of protein kinases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982 Feb;12(2):133–186. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. The regulation of glycogen metabolism. Purification and properties of protein phosphatase inhibitor-2 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):195–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergely P., Bot G. The control of phosphorylase phosphatase by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80600-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Aitken A., Cohen P., Rymond M., Hofmann F. Phosphorylation of the type-II regulatory subunit of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase by glycogen synthase kinase 3 and glycogen synthase kinase 5. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(3):473–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Resink T. J., Cohen P. Reconstitution of a Mg-ATP-dependent protein phosphatase and its activation through a phosphorylation mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80760-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Yellowlees D., Kernohan J. C., Cohen P. Purification of glycogen synthase kinase 3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Copurification with the activating factor (FA) of the (Mg-ATP) dependent protein phosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(3):443–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Concentrations of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in various tissues. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1441–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. L., Glinsmann W. H. Separation and characterization of two phosphorylase phosphatase inhibitors from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):419–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. Protein phosphatases: properties and role in cellular regulation. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):331–338. doi: 10.1126/science.6306765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 1. Classification and substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurgensen S., Shacter E., Huang C. Y., Chock P. B., Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Merlevede W. On the mechanism of activation of the ATP X Mg(II)-dependent phosphoprotein phosphatase by kinase FA. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5864–5870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resink T. J., Hemmings B. A., Tung H. Y., Cohen P. Characterisation of a reconstituted Mg-ATP-dependent protein phosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):455–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Erlichman J., Rosen O. M. Molecular forms and subunit composition of a cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase purified from bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):36–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shacter E., Chock P. B., Stadtman E. R. Energy consumption in a cyclic phosphorylation/dephosphorylation cascade. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12260–12264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shacter E. Organic extraction of Pi with isobutanol/toluene. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):416–420. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Hemmings B. A., Cohen P., Goris J., Merlevede W. The MgATP-dependent protein phosphatase and protein phosphatase 1 have identical substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):197–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Yang S. D., Goris J., Merlevede W. ATP x Mg-dependent protein phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle. II. Purification of the activating factor and its characterization as a bifunctional protein also displaying synthase kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11768–11774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Yang S. D., Merlevede W. Rabbit skeletal muscle protein phosphatase(s). Identity of phosphorylase and synthase phosphatase and interconversion to the ATP-Mg-dependent enzyme form. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5894–5900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Moruzzi E., Ballou L. M., Fischer E. H. Phosphorylase phosphatase. Interconversion of active and inactive forms. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5857–5863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Merlevede W. ATP x Mg-dependent protein phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle. I. Purification of the enzyme and its regulation by the interaction with an activating protein factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11759–11767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Merlevede W. Identification of inhibitor-2 as the ATP-mg-dependent protein phosphatase modulator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10231–10234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Kerlavage A. R., Taylor S. S. Structural comparisons of cAMP-dependent protein kinases I and II from porcine skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2408–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



