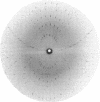
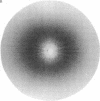
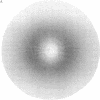
Abstract
By using ultra-high-flux synchrotron x-radiation from a wiggler source, good Laue diffraction data have been obtained from protein microcrystals of size 30 X 35 X 10 microns3, mounted wet in glass capillaries. At the flux level of 10(13)-10(14) photons per sec/mm2, the radiation damage is still low enough to allow a large survey of reciprocal space for a microcrystal and a complete survey for a normal-sized protein crystal. The development of sources for ultra-high-intensity synchrotron radiation is thus an important improvement in the technique for determination of structure through protein crystallography as well as in other cases where crystal size is often a limiting factor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Greenhough T. J., Helliwell J. R. The uses of synchrotron X-radiation in the crystallography of molecular biology. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1983;41(2):67–123. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(83)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Hodgson K. O., Stryer L. Helical channels in crystals of gramicidin A and of a cesium--gramicidin A complex: an x-ray diffraction study. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 5;121(1):41–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat K., Szebenyi D., Bilderback D. X-ray Laue Diffraction from Protein Crystals. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1423–1425. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4643.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. C., Wlodawer A., Yevitz M. M., Hodgson K. O. Applications of synchrotron radiation to protein crystallography: preliminary results. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):128–132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]