Abstract
Encephalopathy consequent on perinatal hypoxia–ischemia occurs in 1–3 per 1,000 term births in the UK and frequently leads to serious and tragic consequences that devastate lives and families, with huge financial burdens for society. Although the recent introduction of cooling represents a significant advance, only 40 % survive with normal neurodevelopmental function. There is thus a significant unmet need for novel, safe, and effective therapies to optimize brain protection following brain injury around birth. The Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE) is a membrane protein present in many mammalian cell types. It is involved in regulating intracellular pH and cell volume. NHE1 is the most abundant isoform in the central nervous system and plays a role in cerebral damage after hypoxia–ischemia. Excessive NHE activation during hypoxia–ischemia leads to intracellular Na+ overload, which subsequently promotes Ca2+ entry via reversal of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Increased cytosolic Ca2+ then triggers the neurotoxic cascade. Activation of NHE also leads to rapid normalization of pHi and an alkaline shift in pHi. This rapid recovery of brain intracellular pH has been termed pH paradox as, rather than causing cells to recover, this rapid return to normal and overshoot to alkaline values is deleterious to cell survival. Brain pHi changes are closely involved in the control of cell death after injury: an alkalosis enhances excitability while a mild acidosis has the opposite effect. We have observed a brain alkalosis in 78 babies with neonatal encephalopathy serially studied using phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy during the first year after birth (151 studies throughout the year including 56 studies of 50 infants during the first 2 weeks after birth). An alkaline brain pHi was associated with severely impaired outcome; the degree of brain alkalosis was related to the severity of brain injury on MRI and brain lactate concentration; and a persistence of an alkaline brain pHi was associated with cerebral atrophy on MRI. Experimental animal models of hypoxia–ischemia show that NHE inhibitors are neuroprotective. Here, we review the published data on brain pHi in neonatal encephalopathy and the experimental studies of NHE inhibition and neuroprotection following hypoxia–ischemia.
Keywords: Brain pHi, NHE blockade, Neonatal encephalopathy, Brain alkalosis, Birth asphxyia, Neuroprotection, Hypoxia–ischemia
Introduction
Encephalopathy consequent on perinatal hypoxia–ischemia occurs in 1–3 per 1,000 term births in the UK and frequently leads to serious and tragic consequences that devastate lives and families, with huge financial burdens for society [1]. Although the recent introduction of cooling represents a significant advance, only around 40 % survive with normal neurodevelopmental function [2]. There is thus a significant unmet need for novel, safe, and effective therapies to optimize brain protection following brain injury around birth.
In this review, we discuss both preclinical and clinical research studies that have led to a better understanding of the pathophysiology and metabolic pathways following an acute hypoxic–ischemic perinatal event. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) has been an important tool to understand the evolution of energy failure and brain intracellular pH (pHi) after hypoxia–ischemia [3]. Phosphorus-31 (31P) MRS has demonstrated an alkaline shift in brain pHi [4]; those infants with worse cerebral injury on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have a more alkaline brain pHi on 31P MRS [5]. It is likely that the rapid shift in brain pHi to alkaline values following hypoxia–ischemia plays an important role in cell death.
The Na+/H+ exchangers (NHE) are a family of ion membrane transport proteins involved in maintaining a normal pHi and cell volume in many mammalian cell types, by extruding protons in exchange for sodium influx into cells in an electroneutral manner. Excessive activation of NHE is likely to lead to the alkaline shifts in pHi and increased cell death via Na+ overload, which promote intracellular Ca2+ entry. Here, we also review the role of NHE in hypoxia–ischemia, the evidence of neuroprotection with NHE blockade in animal models, and the important association of alkaline brain pHi and seizures.
Acute Hypoxic–Ischemic Perinatal Brain Injury in the Term Infant
Perinatal hypoxic–ischemic brain injury in the term baby is a significant problem throughout the world. Hypoxia–ischemia may occur acutely or chronically and is most commonly associated with maternal factors (hypotension, severe hypoxia), cord factors (prolapse, occlusion), placental factors (insufficiency and abruption), and uterine factors (rupture). Neonatal postnatal events such as shock, respiratory, or cardiac arrest can also lead to hypoxic–ischemic injury. Neonatal encephalopathy (NE) is the clinical manifestation of the ensuing disordered brain function and occurs in 1–3 per 1,000 live term births in the UK and other developed world countries [1]. The encephalopathy typically presents as respiratory difficulties, depression of tone and reflexes, subnormal level of consciousness, and often seizures. Serious consequences follow moderate to severe NE; these include death in 10–15 %, cerebral palsy in 15 %, and other significant cognitive, developmental, and behavioral problems in 40 % of survivors [6]. The financial and human costs to the family and society are thus very high.
Following two decades of laboratory studies [7, 8], clinical trials [2], and recent endorsement from regulatory bodies [9], therapeutic hypothermia is now the standard clinical care for moderate to severe NE in the UK and developed world. Meta-analysis [2, 10] of three large pragmatic trials [2, 11–13] show that therapeutic hypothermia reduces death or disability at 18 months with a risk ratio of 0.81 (95 % CI 0.71–0.93) and a number needed to treat of 6–7. Importantly, data are emerging, which confirm that the favorable outcome of cooled babies at age 18 months is associated with favorable outcome at age 7–8 years [14].
However, hypothermia is only partially effective after neonatal hypoxia–ischemia, and 40 % of all treated infants still suffer severe neurodevelopmental disability or death despite treatment. Additional neuroprotective agents are needed either to augment hypothermic neuroprotection [15] or to use alone in settings where hypothermia has not been established as standard care.
Pattern of Brain Injury on Conventional MRI
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms underlying brain injury in the newborn brain at term has rapidly advanced in recent years. Using MRI, the patterns of hypoxic–ischemic brain injury that have been described in pathology studies in the past can now be demonstrated in superb detail and resolution in vivo in human neonates [16, 17]. Using MRS, the timing of the evolution of energy failure and changes in brain pHi have been fundamental in suggesting new avenues for neuroprotection.
The two main patterns of injury on MRI have been clearly described in the 1950s–1970s in a primate model: the injury pattern associated with acute total asphyxia [18] and with chronic partial asphyxia [19, 20]. These two main patterns are described below and in Fig. 1. A normal neonatal MR image is shown in Fig. 1 (top row). The corresponding 1H MR spectra acquired from the left thalamus are shown for each set of MR images. The 1H MRS values from the white matter are also shown for the watershed predominant pattern of brain injury.
Fig. 1.
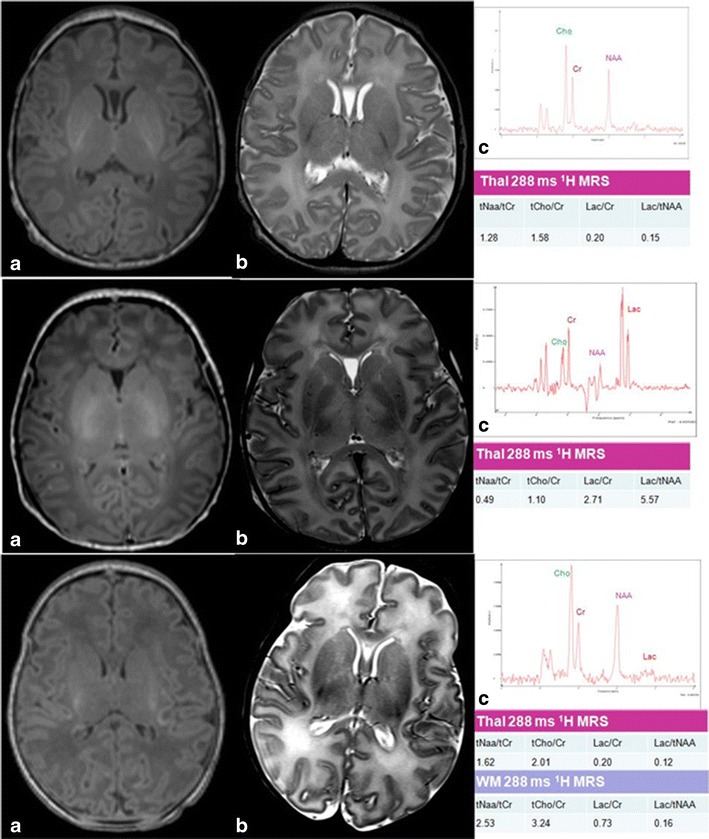
Patterns of brain injury on MRI. Top row (3 Tesla): a axial T1-weighted (w) MPRAGE and b T-2 w 2D 3 mm 3 T MRI of a term infant with normal intracranial appearances on day 5 after birth. This infant presented with stage 1 (mild) neonatal encephalopathy. A normal signal intensity is seen from the posterior limb of the internal capsule on a and b. A thalamic proton (1H) magnetic resonance (MR) spectrum TE 288 ms from the same infant is shown in c. The lactate peak at 1.3 ppm is just visible. Middle row (3 Tesla): a axial T1-w MPRAGE and b axial T2-w 2D 3 mm of an infant with a predominant BGT pattern of brain injury (involvement of basal ganglia, thalami, and perirolandic cortices). A thalamic 1H MR spectrum TE 288 ms from the same infant is shown in c. A high thalamic Lac/NAA ratio of 5.57 is observed. Bottom row (1.5 Tesla): a axial T1-w; b axial T2-w 2D 3 mm of an infant with neonatal encephalopathy with a predominant watershed injury pattern. Areas of cerebral cortical infarction affecting the insular cortices, frontal, and temporal occipital lobes in anterior and posterior arterial watershed territory is seen. A thalamic 1H MR spectrum TE 288 ms from the same infant is shown in c. The Lac/NAA is normal in the thalamus. The white matter spectrum (not shown) has a raised Lac/Cr peak area ratio
Predominant basal ganglia–thalamus pattern (BGT) is the most frequent pattern in “acute asphyxia,” affecting bilaterally the central grey nuclei (ventrolateral thalami and posterior putamina) and perirolandic cortex (Fig. 1 middle row). The hippocampus and brainstem can also be involved. This pattern of injury is most often seen following an acute sentinel event, e.g., uterine rupture, placental abruption, or prolapsed cord [21]. The basal ganglia and thalami are susceptible to acute perinatal hypoxic–ischemic injury due to their high metabolic rate and increased concentration of NMDA receptors [22]. Survivors face a range of functional impairments, which include cerebral palsy, feeding problems, speech and language problems, visual and hearing impairment, later seizures, behavioral difficulties, and cognitive impairment. Cerebral palsy affects three quarters of infants with NE with BGT lesions, and the severity of the BGT lesions is the best predictor of motor problems. A normal signal intensity of the posterior limb of the internal capsule within the neonatal period following neonatal encephalopathy is a good predictor of the ability to walk at 2 years [23].
Watershed predominant pattern of injury typically follows “prolonged partial asphyxia.” The areas involved are the vascular watershed zones (anterior–middle cerebral artery and posterior–middle cerebral artery), affecting white matter and in more severely affected infants the overlying cortex (Fig. 1, bottom row). The lesions can be uni- or bilateral, posterior and/or anterior. Conventional MRI can detect the loss of the cortical ribbon [24, 25]. These lesions may become cystic, atrophy, or develop gliosis [26]. Common associated etiological factors are hypotension, infection, and hypoglycemia [27]. Infants with a watershed pattern of injury have predominantly cognitive impairments often without functional motor deficits. Cognitive deficits include memory impairments, visual–motor or visual–perceptive dysfunction, or increased hyperactivity, sometimes in the absence of functional motor problems [28–32].
Cerebral Energy Metabolism Following Perinatal Hypoxia–Ischemia
MRS has been used to study brain energy metabolism noninvasively; over the last 30 years phosphorus-31 (31P) and proton (1H) MRS have provided unique information on cerebral energy metabolism during the evolution of brain injury following hypoxia–ischemia in the newborn infant [33], neonatal rat [34], and the newborn piglet [3, 35] (Fig 2). In human infants, shortly after intrapartum hypoxia–ischemia 31P MRS often reveals normal cerebral energetics [36]. However, in infants with adverse outcome, despite adequate oxygenation and circulation, phosphocreatine (PCr) and nucleotide triphosphate (NTP, mainly ATP) decline, and Pi increases, in the first days of life [33, 36–38]. Brain pHi has been observed to become alkaline during this phase [4, 5] (see next section). These metabolic changes were termed “secondary energy failure” (SEF) on the basis that they followed impaired intrapartum cerebral energy generation (resulting in transiently reduced PCr and NTP and increased Pi), which resolved following resuscitation [3] (Fig. 3). It was assumed that SEF was consequential to a pathological mechanism initiated by intrapartum hypoxia–ischemia or/and reperfusion/reoxygenation. 1H MRS provides complementary information to 31P MRS (in particular cerebral lactate, a marker of anaerobic metabolism and N-acetyl-aspartate (NAA), an abundant amino acid found mostly in neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) [39]). Because of the greater sensitivity of the 1H nucleus, data can be obtained from smaller regions of the brain. Cerebral lactate rises and NAA falls during transient hypoxia–ischemia; these metabolites return almost to baseline levels after successful resuscitation, only to be followed by a secondary increase in lactate and slower reduction in NAA in the hours that follow. These 1H MRS changes occur in parallel to the energy disruption (reduction in PCr/EPP and NTP/EPP) seen on 31P MRS. A recent meta-analysis of the prognostic accuracy of MR methods demonstrated that thalamic 1H MRS Lac/NAA peak area ratio acquired between days 5 and 14 after birth is a highly sensitive and specific biomarker of long-term neurodevelopmental outcome in infants with neonatal encephalopathy [40].
Fig. 2.
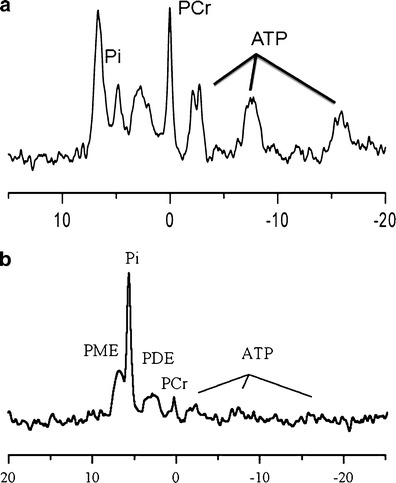
Representative 31P MRS spectra from a a normal baby and b a baby with severe neonatal encephalopathy. Seven main peaks can be assigned in a cerebral 31P MR spectrum: phosphomonoesters (PME), inorganic phosphate (Pi), phosphocreatine (PCr), phosphodiesters (PDE), and the three phosphate groups (α, β, and γ) in nucleotide triphosphate (NTP). The chemical shift difference between PCr and Pi forms the basis of intracellular pH measurement in the in vivo brain
Fig. 3.
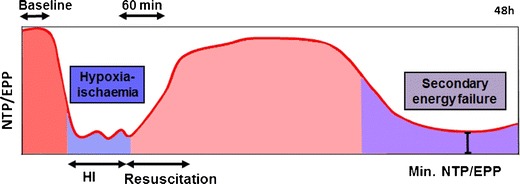
Schematic diagram illustrating the biphasic pattern of energy failure associated with a transient hypoxia–ischemic insult visualized using 31P MRS in the UCL piglet model. Nucleotide triphosphate (NTP)/exchangeable phosphate pool (EPP = Pi + PCr + NTP) is shown on the y-axis. The change in NTP/EPP during transient hypoxia–ischemia (HI), resuscitation, the latent phase (period between the recovery from acute HI and the evolution of secondary energy failure (SEF)), and SEF itself are shown. During the acute energy depletion, some cells undergo primary cell death, the magnitude of which will depend on the severity and duration of HI. Following perfusion, the initial hypoxia-induced cytotoxic edema and accumulation of excitatory amino acids typically resolve over 30–60 min with apparent recovery of cerebral oxidative metabolism (latent phase). It is thought that the neurotoxic cascade is largely inhibited during the latent phase and that this period provides a “therapeutic window” for therapies such as hypothermia and other agents. Cerebral oxidative metabolism may then secondarily deteriorate 6–15 h later (as SEF). This phase is marked by the onset of seizures, secondary cytotoxic edema, accumulation of cytokines, and mitochondrial failure
Brain pHi Changes in Babies with Neonatal Encephalopathy
31P MRS is the only noninvasive way to measure pHi apart from positron emission tomography, which requires injection of radioactive ligands and is not feasible in babies. Using 31P MRS, brain pHi can be measured using the chemical shift difference of Pi from PCr [41], or phosphoethanolamine from PCr [42, 43] or ATP from PCr [44]. The pHi value calculated from the chemical shift difference of Pi form PCr is thought to reflect the pHi in dead or injured cells, whereas that derived from other metabolites may reflect different cell populations. A summary of the studies of brain pHi using 31P MRS performed in normal neonates and infants is shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Studies in normal neonates and infants documenting brain pHi using 31P MRS (based on [36, 38, 151–156])
| Reference | n | GA at birth (weeks) | Age when studies | Mean brain pHi | Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hope et al. [36] | 6 | Median 40 (28–40) | Mean 76 h (16 h–97 days) | 7.14 ± 0.10 | Surface coil |
| Hamilton et al. [151] | 18 | Median 32 (28–42) | 5 (1–61) days GA + PNA median 35 weeks (28–42) | 6.98 ± 0.34 (28 weeks) | Surface coil |
| Boesch et al. [152] | 12 | ? | GA + PNA median 43 weeks (33 weeks–6 years) | 7.08 (SD 0.1) | Surface coil |
| 8 were studied at 40 weeks | |||||
| Azzopardi et al. [153] | 30 (data from 23) | Median 33 (24–42) | GA + PNA median 34 weeks (26–42) | 7.1—no change with maturation | Surface coil |
| AGA 28 weeks 7.14 (±0.28) | |||||
| 42 weeks 7.09 (±0.28) | |||||
| SGA 28 weeks 6.97 (±0.24) | |||||
| 42 weeks 7.19 (±0.24) | |||||
| Laptook et al. 1989 [154] | 7 | 40±1 | 10 examinations within the first 2 weeks after birth | 7.02 ± 0.08 | Surface coil |
| Van der Knapp et al. [155] | 41 | Term | Mean 71 months (1 months–16 years) | 7.04 (95 % CI 6.96–7.12) | Volume localized (ISIS) |
| No significant change | |||||
| Buchli et al. [156] | 16a | Term | 2–28 days GA + PNA mean 42 weeks (39–44) | 7.11 (±0.06) | Volume localized (ISIS) |
| Martin et al. [38] | 10a | Median 40 (36.3–42.1) | Median 4.3 days | 7.12 (±0.05) | Volume localized (ISIS) |
| Robertson et al., unpublished data | 3 | Median 39 (38–40) | GA + PNA median 44 weeks (41–64) | 7.02 (±0.03) | Volume localized (ISIS) |
GA gestational age, PNA postnatal age
aControls were healthy term newborn babies who had been hospitalised for non-neurologic reasons
Brain pH homeostasis in the cytosol and other cellular compartments is maintained by a dynamic, finely tuned balance between proton-extruding and proton-importing processes [45]. Under physiologic conditions, the extracellular pH is ∼7.4; however, the cytosolic pH is more acid (∼7.2). Other organelles possess their own specific pH (Fig. 4). Almost all proteins depend on pH to maintain their structure and function; pH plays an important part in many metabolic functions and the charge of biological surfaces affects many cellular reactions. There is a tendency for the cytosol to accumulate acid (from metabolic reactions—ATP production in the cytoplasm by glycolysis and in mitochondria by oxidative phosphorylation) (Fig. 5). Protons are actively extruded from the cytosol by proton pumping ATPases, coupling to other substrates through exchangers; the main transporter that protects cells against acidification is the Na+/H+ exchanger (see “Brain pHi and Seizures”).
Fig. 4.
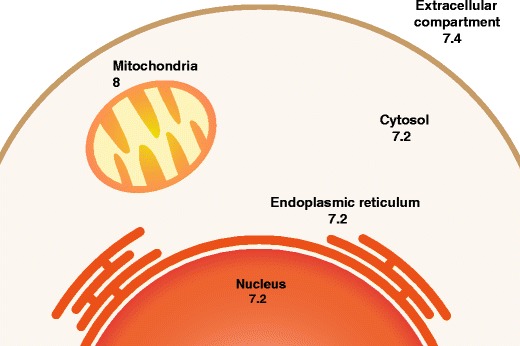
A schematic diagram showing the pH of the main cellular compartments in a typical mammalian cell (from Casey et al. [45]) The mitochondrial pH represents that in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Fig. 5.
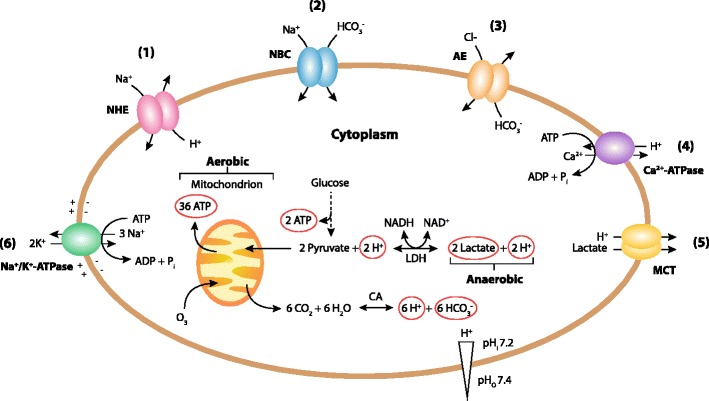
Ion transporters that regulate cytoplasmatic pHi. There is a tendency to acidification of the cytoplasm due to the activity of the anaerobic metabolism producing lactate from glucose and aerobic metabolism (oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria that produce CO2). The main transporters regulating cytosolic pH are the plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchangers (NHEs) (see (1) on the diagram) and the Na+/HCO3 − cotransporters (NBCs) (2). The plasma membrane Cl−/HCO3 − or anion exchangers (AE) (3) counterbalance these mechanisms by acidifying the cell, and plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPases (4) also acidify the cytosol by exchanging cytosolic Ca2+ for extracellular H+ when intracellular Ca2+ is elevated. Importantly in the brain after hypoxia–ischemia, the monocarboxylate-H+ co-transporters (MCTs) will alkalinize the cell (5). The Na+/K+-ATPase pumps (6) establish an inward electrochemical Na+ gradient. Adapted from (from Casey et al. [45]). CA carbonic anhydrase, LDH lactate dehydrogenase, pH i intracellular or cytosolic pH, pH o extracellular or outside pH
In 2002, we studied the chemical shift difference of Pi in whole-brain 31P MRS in relation to outcome in babies with neonatal encephalopathy [5]. In 78 babies with neonatal encephalopathy studied serially during the first year after birth (151 studies throughout the year including 56 studies of 50 infants during the first 2 weeks after birth), we demonstrated that: (1) alkaline brain pHi was associated with severely impaired outcome in babies; (2) the degree of brain alkalosis was related to the severity of brain injury on MRI and brain lactate concentration (Fig. 6); and (3) brain alkalosis persisted for several weeks in babies with a severely impaired outcome and persistence was associated with cerebral atrophy on MRI. A brain pHi of 7.15 and above measured in the first 2 weeks after birth had a sensitivity of 71 % and specificity of 92 % for predicting adverse outcome. Published studies that have measured brain pHi using 31P MRS in infants with birth asphyxia are listed in Table 2.
Fig. 6.
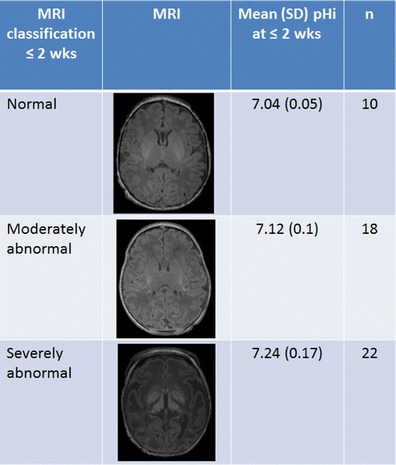
Association of the severity of brain injury in conventional MRI and mean brain pHi within the first 2 weeks of age in 50 infants with mild, moderate, and severe neonatal encephalopathy. Mean (SD) brain pHi at <2 weeks of age in infants with neonatal encephalopathy classified according to the brain MRI pattern (data from Robertson et al. [5]). There are significant differences between the brain pHi in the group with a normal brain MRI and the brain pHi in the group with a severely abnormal MRI
Table 2.
Studies in infants with birth asphyxia documenting brain pHi measured by 31P MRS (based on [4, 5, 33, 36, 38, 151, 154, 157])
| Reference | n | GA at birth (weeks) | Age when studies | Mean brain pHi | Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cady et al. [157] | 7 (3 birth asphyxia) | 33–40 | 42 h–26 days | 7.2 (SD 0.1)a | Surface coil |
| One infant studies on 5 occasions (on day 26: brain pHi = 7.4) | |||||
| Hope et al. 1984 [36] | 10 | 38–41 | 8 h–27 days (obtained in 3–6 times in each infant) | 7.17 ± 0.1 at time of lowest PCr/Pi (mean age 113 h: 16 h–9 days) | Surface coil |
| Hamilton et al. [151] | 27 Echodensities seen on USS (13 birth asphyxia) | Median 40 (27–42) | Median 3 days (8 h–23 days) | “Tended to be raised.” Values from 19 of the infants were above the regression line for normal infants; 6 were above the 95 % CI | Surface coil |
| Laptook et al. [154] | 1 | 36 | 1.5, 8, 15 days, 9 months | 7.3–7.4 | Surface coil |
| 5 | 38 ± 2 | Within first 2 weeks after birth | 7.14 (±0.12) Significantly different from the normal infants when other 31P metabolites showed no difference | ||
| Azzopardi et al. [33] | 61 (all infants) | 27–42 | 3 days (0–23) | 7.14 ± 0.27 (n = 61) | Surface coil |
| 40 infants with asphyxia | 40 (31–42) | 3 days (1–10) | 7.16 ± 0.19 (n = 36) | ||
| Martin et al. [38] | 23 | Median 40 (36.9–41.9) | Median 3 days (NNS 1—severe) | 7.21 (±0.16) | Volume localized (ISIS) |
| Median 5.5 days (NNS 2—moderate) | 7.09 (±0.04) | ||||
| Median 3 days (NNS 3—mild) | 7.10 (±0.08) | ||||
| Robertson et al. [4] | 43 | Median 39.5 (36–42) | 77 examinations: 25 within 2 weeks age 16 between 2 and 4 weeks | At time of lowest PCr/Pi (within first 2 weeks of age) | Volume localized (CSI) |
| 25 between 4 and 30 weeks | 7.23 (±0.07)—abnormal outcome group | ||||
| 11 when >30 weeks old | 7.08 (±0.04)—normal outcome group | ||||
| Robertson et al. [5] | 78 | 39.5 (SD 1.6) (36–42) | 151 examinations within the first year after birth. 50 infants studies within 2 weeks of age | At time of lowest PCr/Pi (within first 2 weeks of age) | Volume localized (ISIS) |
| 35 (+ 43 presented above) | 7.28 (±0.15)—23 infants with severe outcome or died | ||||
| 7.11 (±0.09)—normal outcome group |
NNS neonatal score, NNS1 severe NE, NNS 2 moderate NE, NNS 3 mild NE, GA gestational age, PNA postnatal age
aThe pHi was taken from a heterogeneous group of infants including infants with congenital muscular dystrophy and with meningitis. The author noted there was no evidence of intracellular acidosis in infants with birth asphyxia and stated that the pHi was similar in infants with birth asphyxia to those without. On close examination, however, infants with birth asphyxia tended to have a more alkaline pHi
In vivo data suggest that the return of pHi to normal or alkaline values may be deleterious to cells that have undergone hypoxia–ischemia. This rebound alkalosis has been termed pH paradox and has been described in several cell types [46–48]. Possible mechanisms leading to pH-dependent injury include activation of phospholipases and proteases, which have an alkaline pKa, onset of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, leading to uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation and aggravation of ATP depletion [49], and an exacerbation of excitotoxic neuronal injury due to an increased NMDA activation at alkaline pHi [50, 51]. An understanding of one of the main transporter groups leading to brain alkalosis after hypoxia–ischemia (the NHEs) is therefore important for future neuroprotection strategies.
Na+/H+ Exchangers
The NHEs are a family of ion integrate membrane transport proteins involved in maintaining pHi and cell volume in many mammalian cell types [52, 53], by extruding protons from, and taking up sodium ions into cells in an electroneutral manner (1:1 stoichiometry) (Fig. 5).
To date at least ten NHE isoforms (NHE1 to NHE10) have been identified in mammals [54]. NHE10 was recently described as an osteoclast-specific member of NHE family, regulating osteoclasts differentiation and survival [55]. NHE1–5 are expressed on the plasma membranes in various types. NHE6–9 reside on intracellular organellar membranes of the endosomal-trans Golgi network [56, 57]. NHE isoforms have similar membrane topologies, with an N-terminal membrane domain consisting of 12 predicted transmembrane segments and a more divergent C-terminal cytoplasmic domain [45, 57]. The NHE1 isoform has been studied closely and is present at the cell surface of most cells, especially plasma membranes. It is the most abundant isoform in the CNS [58, 59]. NHE1 plays a crucial role in protecting cells from internal acidification, acting together with bicarbonate-transporting systems and restoring cell volume to steady-state levels [60].
Intracellular acidosis is the major stimulus that regulates NHE1 activity. As the H+ concentration of the cytosol rises, a rapid increase in the activity of the transporter occurs. Near-maximal velocity is achieved in approximately one pH unit (Hill coefficient >1), thereby minimizing exposure of the cytoplasm to excess acidification [61, 62].
In addition to responding to intracellular acidification, various signals can alter the NHE1 internal pH sensitivity, such as hormones, mitogens, and physical stimuli (e.g., mechanical stretch and hyperosmolarity), modulating its state of phosphorylation [45, 53, 63–67]. The exchange activity is more active at alkaline pH values due to a shift of the set point by phosphorylation of the residues. It is also regulated at the transcriptional level, supporting the control at mRNA levels and at protein production level [68, 69]. An alkaline cytoplasmic pH (pHc) is thought to provide a permissive environment for the progression of diverse cellular processes, including changes in cell shape [70], adhesion [71], migration [72, 73], chemotaxis [74, 75], and proliferation [76–78].
Effect of Hypoxia–Ischemia on NHE
Reductions in blood flow with ischemia and reduction in oxygen supply with hypoxia decrease the supply of oxygen required to maintain tissue ATP levels, especially in excitable organs such as the heart and brain that have a high demand for energy. As ATP stores are depleted, lactate, pyruvate, and protons accumulate owing to anaerobic metabolism of glycogen stores. The accompanying cytoplasmic acidification causes hyperactivation of plasma membrane NHE1 and the consequent accumulation of intracellular Na+. The Na+ overload reverses the mode of operation of Na+/Ca2+ exchange, driving excess Ca2+ into the cell. The resulting elevation in intracellular Ca2+ concentration, and subsequent activation of proteases, phospholipases, and formation of oxygen- and nitrogen-free radicals, precipitates a cascade of deleterious effects, including altered membrane excitability and contractility, generation of toxic free radicals, cellular hypertrophy, apoptosis, and necrosis—events that result in cell death [79, 80]. Activation of NHE also leads to the rapid normalization of pHi during reperfusion after hypoxia ischemia [45, 54, 81, 82].
Removal of external Na+ or reducing the external pH attenuates the postanoxia alkalization [83]. When ATP levels fall to 35 % of control in isolated CA1 neurons during chemical anoxia, NHE activity is reduced by 44 %. Activation of NHE function, Na+ pump function and the Na+ driving for NHE are all dependent upon ATP energy levels, ATP being required for phosphorylation of the protein.
NH Exchanger Blockade and Neuroprotection in Neonatal Models
Although the NHE activation is essential for the restoration of physiological pHi, hyperactivation of NHE1 in neurons, in response to the metabolic acidification associated with an ischemic–hypoxic insult [46, 84–87], disrupts the intracellular ion balance, causing intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ overload [88], which eventually leads to cell death. Experimental in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated neuroprotection with NHE inhibitors; these are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3.
Preclinical studies—brain pH and NHE inhibitors in perinatal brain injury (based on [46, 84, 85, 88–90, 93, 101, 102, 107, 110, 111, 138, 145, 158–160])
| Paper | Species | Model, study design | NHE inhibitor | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro studies | ||||
| Vornov et al. [46] |
Ex vivo Rodent 17-day rat fetuses 10–12 cell culture |
–Neuronal tissue culture model of ischemia (18–19-day culture) from embryonic 17-day rat fetuses –20 min ischemia with metabolic inhibition (KCN + 2-DG) –Injury: LDH liberation |
–Group 1: ischemic conditions vs. prolonged ischemia (30 min) –Group 2: incubation with NHE inhibitors at normal pHe (dimethylamiloride and harmaline) slowed pHi recovery |
–Profound protective effects: ↓ pHe during 1st hour recovery. →suggesting protective effects due to intracellular acidosis –1st demonstration of protective effects of blocking NHE in cerebral ischemia model (during recovery); worst injury if pHi normalizes fast →acidosis protects: suppressing pH-sensitive mechanisms of injury or blocking Na entry (NHE) |
| Matsumoto et al. [88] |
Ex vivo rodent 1-day rats Culture of cortical neurons |
–Hypercapnia (5 % CO2) for 10–14 days, then cortical neurons cultured on glass-based dishes –Assess glutamate-induced neuronal death; neurons morphological change; Ca2+ i concentration and pHi |
–Some given SM-20220 20 min preglutamate exposure or MK-801 (NMDA receptor antagonist) |
–SM-20220: ↓ glutamate-induced neuronal death over 6 h, inhibited postglutamate exposure: acute cellular swelling, persistent ↑ [Ca2+]i and intracellular acidification →Neuroprotection: inhibit persistent ↑[Ca2+]i and acidification in excitotoxicity |
| Robertson et al. [89] |
Ex vivo rodent 14- and 7-day models of rat pups Brain slices |
–Progressive energy decline after HI insult in rat brain slice neonatal model; P31and H1 MRS 350 μm slice –7-day rat pups brain slices perfused in KHB: (1) at 37 °C; (2) at 32 °C, and 14-day slices perfused for 8 h in similar solutions and then NHE blocker |
–14-day pups brain slices perfused for 8 h: (1) at 37 °C in KHB (2) at 32 °C in KHB (3) at 37 °C in HEPES buffer, (4) amiloride at 37 °C in HEPES |
–No gestational age effect on energy decline between 7- and 14-day model –Brain slice model underwent secondary energy failure At 5 h: alkaline pHi, ↓ PCr/Pi and ↑ Lac/NAA, and ↓ NTP/PME, at 37°C –Changes delayed with hypothermia (32o C) or amiloride (pHi acidified and preserved NTP/PME, at baseline and at 5 h) |
| Kersh et al. [85] |
Ex vivo rodent 3–15-day rat both sex Brain slices |
–Hypercapnia (15 % CO2) –NH4Cl-induced acidification in brainstem neurons from chemosensitive regions of neonatal rats (brainstem slices from RTNn, NTSn, and LCn) |
–Control (DMSO-vehicle) –Amiloride –HOE 642 –S1611 –EIPA |
–pHi recovery mediated by different pH-regulating transporters in neurons from different chemosensitive regions (NHE1 in RTNn; NHE1 and 3 in NTSn; NBC in LCn) –Recovery suppressed by hypercapnia in all neurons (maintained acidic pH) |
| Liu et al. [90] |
Ex vivo rodent 1–3-day neonatal mice Glial cultures |
–Isolation of mixed primary glial cultures in mice –Activation of microglia after lipopolysaccharide or oxygen and glucose deprivation and reoxygenation |
–Group 1: untreated –Group 2: HOE 642 |
–HOE 642 abolished pHi regulation in microglia basal conditions –Activation of microglia accelerated pHi regulation (↑ pHi, ↑ Na+ i and Ca2+i, and production of superoxide anion (SOA) and cytokines (CK)) –HOE 642 abolished pHi regulation, ↓ production SOA, CK and iNOS –Hypothesis: NHE1 to maintain microglial pHi homeostasis (NADPH oxidase and “respiratory” burst) |
| In vivo studies | ||||
| Ferimer et al. [158] |
Rodent 13 Wistar rats |
Cardiac arrest (KCl) in rats followed by resuscitation 7 min later in untreated vs. MIA |
MIA Controls (untreated) |
–MIA delays normalization of brain pHi after cardiac arrest in rats –MIA: ↓ cardiac pH in rats postarrest +15 min reperfusion –MIA doesn’t change pHi from nonischemic value. |
| Phillis et al. [107] |
Rodent 21 Sprague–Dawley rats |
–Ischemia: 20 min occlusion CA (group 3 30 min), with EEG (flat). Then 40 min reperfusion –Cortical superfusate (bilaterally every 10 min): free fatty acids (FFA), lactate, and glucose levels |
–Group 1 (n = 9): aCSF (control) –Group 2 (n = 6): EIPA topical (cortex) 35 min pre- and during ischemia –Group 3 (n = 6): 30 min ischemia |
–NHE inhibition prevented activation phospholipases (suppress ↑ FFA during reperfusion) –EIPA: lactate levels significantly lower by end of experiment |
| Pilitsis et al. [110] |
Rodent 24 Sprague–Dawley rats |
–Cerebral ischaemia (20 min CA occlusion) –Measurement of phospholipase activation by efflux of FFA in the ischemic/reperfused rat cerebral cortex |
–Group 1: SM-20220 topical (cortex) pre- and during ischemia (n = 13) –Group 2: control (ischemia) (n = 11) |
–↓significantly ischemia-evoked efflux of FFAs: importance NHEs in eliciting FFA efflux –Inhibition may be essential for neuroprotection in ischemia–reperfusion injury |
| Kendall et al. [93] |
Rodent 47 mice 7-day (adult C57/Bl6 female and males bred in-house) |
–HI: 2 h left CA occlusion followed by moderate (30 min) or severe (1 h) hypoxia (8 % O2) –Outcome at 48 h: viable tissue in injured hemisphere (severe HI) or injury score and TUNEL stain (moderate) |
–Group 1: MIA intraperitoneal –Group 2: 0.9 % saline equivalent volume Given 8 hourly starting 30 min before HI |
–MIA neuroprotective when commenced before HI (no weight difference) –Severe insult: significant neuroprotective (↑forebrain tissue survival) –Moderate insult: ↓ damage hippocampus –MIA ↓ neutrophil count and hence brain swelling after HI |
| Rocha et al. [159] |
Rodent 3–4-month mice male Swiss-Webster |
–Metabolic stress and dopaminergic damage in mice caused by malonate (mitochondrial inhibitor) –Dialysate levels of DA and metabolites baseline (1 h prior to drug delivery) and afterwards, every 20 min |
–Group 1: HOE-642 dialized intracerebral (striatum) 20-min periods, separated by drug washout ≥1 h –Group 2: EIPA –Group 3: control (only malonate) |
–HOE-642 pretreatment: ↓malonate-induced DA overflow and ↓ striatal DA content, without ↓ intensity metabolic stress or subsequent DAergic axonal damage –Absence NHE1 on nigrostriatal DAergic neurons suggests HOE-642 effects on striatal DA overflow via NHE1 on other cell types or via multiple NHE isoforms |
| Hwang et al. [84] |
Rodent 6 m Mongolian gerbils |
–HI by 5 min bilateral occlusion common CA –Assess delayed neuronal death and immunohistochemistry for NHE1 (at 30 min, 3 h, 12 h and 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 days following surgery) –Locomotor activity monitored for 10 days post-HI |
–Group 1: normal (sham: same surgical procedure but NO ischemia) –Group 2: vehicle (saline given) –Group 3: EIPA OD for 3–9 days after ischemic sugery, starting 30 min postischemic surgery |
–↑NHE protein level in CA1 region from 2 days post-HI; activation NHE1 in CA1 glial cells from 2 to 3 days post-HI; in CA1 pyramidal neurons and glial cells(astrocytes) from 4 days –EIPA potently protected CA1 pyramidal neurons from ischemic injury, and ↓ activation of astrocytes and microglia in ischemic CA1 region –Hypothesis: role of NHE1 in delayed death NHE inhibitors protect neurons from ischemic damage |
| Shi et al. [101] |
Rodent 136 mice –NHE1+/− heterozygous mice –Wild-type mice SV129/Black Swiss –NHE1+/− and +/+ litter mate males |
–Transient focal cerebral ischaemia and reperfusion (I/R) by 60 min occlusion left MCA –Activated microglial cells identified by expression of 2 microglial marker proteins (CD11b and Iba1) and by transformation of morphology |
–Group 1: vehicle control (equivalent volume of saline intraperitoneal) –Group 2: HOE 642 intraperitoneal at 30 min prior to the onset of reperfusion, and then daily up to 1–7 days during reperfusion |
–Immediate ↑ microglial activation ipsilateral to ischemia in NHE1+/+ brains at 1 h I/1 h R (gradually ↓ during 6–24 h) Sharp ↑ microglial activation peri-infarct and ↑ proinflammatory CK 3 days after I/R –HOE 642 or NHE1+/− mice: less microglia activation, lNADPH oxidase activation, ↓ proinflammatory response at 3–7 days post-I/R Blocking NHE1 significantly ↓ microglial phagocytosis in vitro –↑↑ NHE1 protein expression in activated microglia and astrocytes NHE1 inhibition ↓ microglial proinflammatory activation following I/R |
| Ferrazzano et al. [160] |
Rodent 44 wild-type controls (NHE1+/−), NHE1 genetic knockdown mice (NHE1+/−) |
–Transient focal cerebral ischemia by 30–60 min occlusion of left MCA induced in wild-type controls (NHE1+/+), NHE1 genetic knockdown mice (NHE1+/−), and NHE1+/+ mice treated with HOE-642 –Brain MRI (diffusion DWI and T2 weighted) |
Randomised to: –Group 1: HOE 642 30 min pre- or 1 h postreperfusion intraperitoneally. Then at 24 and 48 h after reperfusion –Group 2: control (saline as vehicle) |
–Significant protection in NHE1+/− mice ↓injury in DWI 1 h postreperfusion in NHE1+/−; and smaller infarct in T2 at 72 h vs NHE1+/+mice –HOE642 prereperfusion or during early reperfusion: ↓ ischemic damage (remains protective given during early reperfusion!) →Therapeutic potential for inhibition NHE1 in cerebral ischemia |
| Cengiz et al. [102] |
Rodent 9 days 46 C57BL/6J mice |
–30 min unilateral ligation of the left common CA, plus exposure to hypoxia (8 % O2 for 55 min) –Assessment of morphology, neurodegenerationand motor and spatial learning abilities at 4–8 weeks of age after HI |
Randomised to: –Group 1 (n = 13): HOE 642 intraperitoneal: 5 min pre-HI, 24 and 48 h post –Group 2 (n = 10): control (saline) pre/posttreatment –Group 3 (n = 13): HOE-642 posttreatment (10 min, 24 and 48 h post-HI) –Group 4 (n = 10): control (saline) post |
Inhibition of NHE1: neuroprotective in neonatal HI brain injury –Control brains 72 h post-HI: neurodegeneration in several areas brain; NHE1 upregulated in specific astrocytes; and motor-learning deficit seen at 4 weeks age –HOE 642: better preserved morphologic hippocampal structures; less neurodegeneration in acute stage HI; and improved striatum-dependent motor and spatial learning at 8 weeks of age after HI →NHE1-mediated disruption of ionic homeostasis contributes to striatal and CA1 pyramidal neuronal injury after neonatal HI |
| Helmy et al. [138] |
Rodent 6 days 159 Male Wistar rat pups |
–60 min of asphyxia by hypoxia 9 %, or hypercapnia 20 %, or both combined. Then normal restoration of room air or graded re-establishment of normocapnia (half CO2 levels every 30 min) –Monitoring with EEG recording and pH-sensitive microelectrodes |
Some in each group: MIA intraperitoneally 30 min preasphyxia –Group 1 (60 min hypoxia 9 % then 21 %) –Group 2 (60 min hypercapnia 20 %) –Group 3 (asphyxia: CO2 20 % + O2 9 %) –Group 4 (asphyxia like group 2 and then graded re-establishment of normocapnia) –Group 5: controls (room air only) |
–Recovery from asphyxia followed by large seizure burden and ↑ brain pH –Graded restoration of normocapnia after asphyxia strongly suppresses alkaline shift in brain pH and seizure burden –MIA pre-insult: virtually blocked seizures |
| Helmy et al. [145] |
Rodent 6–7 days Male Wistar rat pups |
–60 min of asphyxia by hypoxia 9 % and hypercapnia 20 %. Then normal restoration or graded re-establishment of normocapnia (half CO2 levels every 30 min) –Monitoring with EEG recording, pH-sensitive microelectrodes and histology |
5 pups in each group: MIA intraperitoneally 30 min pre-HI A few: amiloride intraperitoneally 30 min preasphyxia –Group 1 (asphyxia CO2 20 % + O2 9 %, then room air) –Group 2 (asphyxia like group 1 and then graded restoration normocapnia) |
–Neocortical neurons in vivo: biphasic pH changes acid–alkaline response –Graded restoration normocapnia: strongly suppress alkaline overshoot –Parallel ↑ pHe and pHi post-HI: net loss acid equivalents from brain tissue not attributable to BBB disruption (lack of ↑Na fluorescein extravasation into brain and EEG characteristics of BBB) –MIA: abolition net efflux acid equivalents from brain, and suppression seizure (sz) activity –Post-asphyxia sz: due to brain alkalosis (NHE-dependent net extrusion acid across BBB) –BBB-mediated pH regulation: new approach prevention and therapy neonatal sz |
| Robertson et al. [111] |
Piglet 18 white male <24 h old |
–Transient global cerebral HI (bilateral occlusion common CA) 31P and 1H MRS before, during and up to 48 h after HI. Tissue injury at 48 h |
Randomized to: –Saline placebo –iv MIA 10 min post-HI and 8 hourly |
–MIA starting 10 min after severe HI: neuroprotection: ↓ brain Lac/NAA, cell death and microglial activation |
Abbreviations: NHE Na+/H+ exchanger, NHE1 isoform 1 of NHE, NCX1 Na+/Ca2+ exchanger-1, NBC Na- and HCO3-dependent transporter, KCN potassium cyanide, HI hypoxia-ischemia, CA carotid arteries, BBB blood–brain barrier, MIA N-methyl-isobutyl-amiloride (inhibitor of NHE), EIPA N-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)-amiloride (highly potent derivative of amiloride for the nonselective inhibition of the NHE system in various cell types), SM-20220 N-(aminoiminomethyl)-1-methyl-1H-indole-2-carboxamide methanesulfonate (a highly selective and specific NHE1 inhibitor, 50 times more potent than EIPA), HOE-642 cariporide mesilate or 4-isopropyl-3-methylsulfonylbenzoyl-guanidine methanesulfonate (a selective NHE1 inhibitor), S1611 (a selective NHE3 inhibitor), Harmaline (a non-amiloride NHE5 inhibitor), NTP/PME nucleotide triphosphate/phosphomonoester, Pi inorganic phosphate, PCr phosphocreatine, Lac/NAA lactate/NAA ratio, RTNn retrotrapezoid nucleus neurons, NTSn nucleus tractus solitarii neurons, LCn locus coeruleus neurons
There are two major classes of pharmacological NHE inhibitors. One class includes amiloride and its derivatives by double substitution of the nitrogen of the 5-amino group: dimethylamiloride (DMA), N-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)-amiloride (EIPA), N-methyl-isobutyl-amiloride (MIA), and 5-(N,N-hexamethylene)-amiloride. They are nonselective inhibitors of the NHE system in various cell types, and EIPA is highly potent. Another class of inhibitors includes the derivatives of the benzylguanidines such as HOE 694, HOE 642 (cariporide mesilate or 4-isopropyl-3-methylsulfonylbenzoyl-guanidine methanesulfonate), eniporide, and BIIB-513, which selectively inhibited NHE1. The replacement of the pyrazine ring of amiloride by a pyridine ring or by a phenyl increased the potency and the NHE selectivity. In the last two decades, several bicyclic guanidines were prepared: zoniporide, MS-31038, SM-20220, SM-20550, SMP-300, KBR9032, BMS-284640, T-162559, TY-12533, S-3226, or SL-591227 [52]. Of these, HOE 642 is extremely potent, being 105 times more specific for NHE1 vs. NHE3 [78], and zoniporide is very potent too and 150-fold selective for NHE1 vs. the other isoforms. S1611 and S3226 are two selective NHE3 inhibitors. Harmaline is a nonamiloride NHE5 inhibitor. The inhibitory potency of NHE inhibitors towards the different NHE isoforms is described in detail in a review by Masereel et al., [52].
During in vitro cerebral ischemia, NHE inhibitors (DMA, harmaline [46], SM-20220 [88], amiloride [89], and HOE-642 [85, 87, 90]) had a protective effect, in terms of delayed pHi normalization both in neuronal cells and in astrocytes [46, 89–92], inhibition of microglia [90], and less intracellular calcium accumulation [87, 88]. This anoxia-induced alkalization was also ameliorated in NHE1−/− CA1 neurons. In parallel, cell death was reduced in wild-type neurons treated with HOE 642 or in NHE1−/− neurons in cultured mouse cortical neurons undergoing 3 h oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) and 21 h reoxygenation (from ∼70 % to 40–50 %) [87].
Vornov et al. [46], described that pHi decreased by 0.2 pH units, but then recovered when inhibition was removed in rat cortical neuronal cultures undergoing metabolic inhibition for 20 min. NHE1 inhibitors, dimethylamiloride or harmaline, significantly reduced the postinhibition pHi recovery, showing less brain injury in these compared to those with a fast pHi normalization.
As mentioned above, NHE1 activity also affects cellular Na+ levels. A small but significant (∼2-fold) increase in neuronal intracellular concentration of Na+ ([Na+]i) results after 2 h OGD, reaching to ∼7-fold increase during 1 h reoxygenation. HOE 642 attenuated the rise in [Na+]i following OGD. NHE1−/− neurons did not exhibit significant increase in [Na+]i. This supports that NHE1 activity is elevated upon reoxygenation [83, 86]. Three hours of OGD and 21 h reoxygenation lead to cell death in ∼70 % of the NHE1+/+ neurons. However, cell death is significantly reduced in wild-type neurons treated with HOE 642 or in NHE1−/− neurons [87].
In vivo studies mainly in rodents have found that NHE1 inhibitors reduce brain injury in hypoxia–ischemia models [93] and decrease infarct size in a focal ischemia model [87]. In NHE1 heterozygous mice, there was a significant decrease in infarct size of around 30 % compared with normal NHE+/+ mice following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) [87], similar to those NHE+/+ mice treated with HOE 642. It implies that the disruption of Na+ and Ca2+ homeostasis contributes to ischemic neuronal damage. These studies firmly demonstrate the dominant role of NHE1 among other NHE isoforms in cerebral ischemic brain damage.
Other studies show neuroprotection in ischemic models. SM-20220 (N-(aminoiminomethyl)-1-methyl-1H-indole-2-carboxamide methanesulfonate), a highly selective NHE1 inhibitor, given intravenously 1 h after MCAO significantly reduced the extent of cerebral edema and Na+ content after 2 h ischemia and 4 h reperfusion and infarct volume after 22 h reperfusion [94]. SM-20220 decreased infarct size in both transient and permanent MCAO models. The reduction of infarct size improved when the treatment is delayed for 5, 30, or 60 min after the onset of ischemia [94]. SM-20220 led to ∼50 % decrease in infarct size at 72 h reperfusion. Other groups have shown similar reductions in infarct volume and edema with other NHE blockers [95–97].
Some NHE blockers, specifically SM-20220 [98] and MIA [93], have been found to reduce the number of neutrophils in the ischemic hemisphere. SM-20220 attenuates leukocyte adhesion and migration in the mesenteric artery [99] and improves endothelial dysfunction [100]. NHE1 blockers (EIPA and HOE 642) [84, 90, 101, 102] reduced microglial activation posthypoxia ischemia and hence the microglial phagocytosis and astrocytosis in CA1 region. Cengiz et al. [102] found that HOE 642 given either prehypoxia–ischemia or starting 10 min after the insult reduced neurodegeneration in the acute stage in hippocampus, striatum, and ipsitaleral thalamus, and improved the striatum-dependent motor and spatial learning skills at 8 weeks.
NHE1 inhibitors are neuroprotective in astrocytes in a similar way to neurons. The intracellular Na+ overload is substantially mediated through activation of the ERK1/2 pathways [92]. In a more severe model of in vitro ischemia, cultured astrocytes were superfused with a solution, which mimics the ionic composition of the ischemic extracellular space (a hypoxic, acidic, ion shifted ringers (HAIR) solutions at 37 °C) [103, 104]. Exposure to HAIR caused a rapid decline in astrocyte pHi. This is consistent with the finding that NHE1 activity is inhibited by low extracellular pH (pHe) [105]. When exposed to normal buffer again, astrocytes rapidly alkalized and a significant rebound of pHi over the baseline took place [104]. Bondarenko et al. [104] have reported that HAIR and reoxygenation leads to ∼40 % cell death in astrocytes, which is significantly reduced in the presence of NHE blockers such as EIPA or HOE 694 during HAIR and reoxygenation, or during reoxygenation alone.
NHE inhibitors have also been shown to preserve neurological function after ischemic injury. In a model of ischemia and hypothermia in piglets, Castella et al. [106] observe a rapid neurological recovery in subjects receiving HOE 642 just at the onset of cooling. Several studies [84, 107] demonstrate that EIPA not only protects gerbil hippocampal neurons from ischemic injury but also reduces the magnitude of the ischemia-induced locomotor hyperactivity at both 24 h and 6 days after reperfusion. Ischemic injury to the gerbil forebrain produces an increase in locomotor activity, which is related to the degree of pyramidal neuronal damage in the CA1 region of the hippocampus [84, 108]. In another Mongolian gerbil model, the recovery time of consciousness significantly improved (lower neurological scores at 2 h postreperfusion) following a 30 min transient global cerebral ischemia in those treated with SM-20220, compared to the vehicle group [109]. This improvement in neurological deficit persisted until 24 h postreperfusion.
In summary, NHE inhibitors (or genetically modified NHE1−/−) are neuroprotective in animal models. They reduce the alkalinization of the cell (inhibition of phospholipases and kinases [107, 110] and delayed secondary energy failure [89]), and decrease the calcium and sodium intracellular overload, reducing cell edema and cell damage. They suppress microglial activation, especially in hippocampal regions (pyramidal neurons of the CA1 area in rodents) [84] and in striatum and ipsilateral thalamus in a focal ischemia model [102]. Improved functional outcome also follows NHE inhibition [102].
NHE Inhibition Following Transient Hypoxia–Ischemia in the Piglet Model of Perinatal Asphyxia
Robertson et al. [111] used the piglet model of perinatal asphyxia to study the effect of NHE1 inhibition with MIA given 10 min after the end of hypoxia–ischemia and eight hourly thereafter. MIA improved cerebral energy metabolism in the thalamic area in the 48 h after hypoxia–ischemia on MRS biomarkers and reduced cell death and microglial activation in some brain areas. The use of clinically relevant MRS biomarkers and reduced cell death in a large animal model of perinatal asphyxia is an important step towards the clinical translation of NHE inhibitors. It is important to assess whether NHE blockade would augment hypothermic neuroprotection in this devastating disease.
Brain pHi and Seizures
Relation Between Brain pHi and Seizures
Neonatal seizures are the most common manifestation of a neurological disorder in the newborn period. Neonatal encephalopathy is the most frequent cause of seizures at term. In some studies, the duration of electrographic seizures in newborn babies is associated with worse MRI appearances [112] and poor neurodevelopmental outcome [113]. Newborn babies with neonatal encephalopathy as a cause of seizures tend to have a higher seizure burden than those with a stroke [113]. Increased morbidity and mortality, brain injury, and poor neurodevelopmental outcome have been associated with a higher seizure burden [113–120]. Therefore, addressing neonatal seizures is a priority, but current drugs are largely ineffective and are not free of serious side effects on the neonatal brain [121–123].
Therapeutic hypothermia not only improves outcomes of babies with neonatal encephalopathy by reducing the rate of death and disability at 18 months of age, but it also appears to reduce seizure burden [124]. Cooling appears either to act directly to reduce seizure burden or to augment the action of conventional anticonvulsants. Xenon gas, which is currently being used in clinical phase II trials to augment hypothermic neuroprotection in babies, appears to reduce seizure burden when administered with cooling [125]. The data are consistent with those from preclinical models [124].
There is however still an unresolved controversy whether seizures worsen outcome by themselves or whether they are associated to those with a more severe degree of encephalopathy, hence the higher mortality and morbidity [126, 127]. The molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying birth-asphyxia seizures are unknown, but understanding the seizure-triggering mechanisms plays a key role in the design of novel therapeutic strategies.
A profound acidosis (blood pH 7.00 or lower) at the time of birth is an essential criterion in the diagnosis of perinatal asphyxia [128, 129]. However, postasphyxia seizures do not coincide with the maximal blood acidosis but are typically first observed during the recovery period after a delay that usually ranges in human babies from 2 to 16 h [130]. A wide range of observations have shown that changes in extra- and intracellular pH exert a strong modulatory effect on brain excitability under normal and pathophysiological conditions, whereby an alkalosis enhances excitability while an acidosis has an opposite effect [131–138]. The immature brain appears to be particularly sensitive to changes in pHi. Recent experiments have shown that changes of 0.05 pH units on neonatal hippocampal slices have a profound effect on endogenous network activity [137].
In a rat pup model of neonatal asphyxia, brain alkalosis after recovery from asphyxia played a key role in the triggering of seizures [138]. Brain pH was measured with intracortical ion sensitive microelectrodes, and EEG was recorded from parietal cortex in freely moving rat pups with simultaneous video recording [138]. There was a robust correlation between postasphyxic brain pH changes and seizure burden; that is, the more alkaline the brain pH after asphyxia, the higher the seizure burden. The alkaline brain pH overshoot after asphyxia reached values of up to 0.40 pH units above normal brain pH; these are similar finding to previous studies in rats [93], piglet [3, 111], and human newborn [4, 5]. Some pups received MIA (the NHE inhibitor) intraperitoneally 30 min before asphyxia; in those rat pups pretreated with MIA, seizure burden was reduced. These data add weight to the evidence that acidosis suppresses neuronal excitability, whereas alkalosis does the opposite [133, 139–141]. Taking this further, there is accumulating evidence that brain pHi plays a key role in modulating neuronal survival after injury [131, 142, 143].
In another study in neonatal rat pups by the same group, a rise in brain pH was accompanied by seizure activity following injection of sodium bicarbonate [144]. The authors suggested that a “graded restoration of normacapnia” should be recommended for resuscitation of neonatal encephalopathy as this may reduce seizures and improve outcome [144].
The same group explored mechanisms of postasphyxia brain alkalosis [145] in the rat pup exposed to one hour of asphyxia (simultaneous hypoxia and hypercapnia). They observed that the postasphyxia brain alkalosis was generated in the absence of a rise of blood pH. The increase in both extracellular and intracellular pH recorded in the brain implied an enhanced net loss of acid equivalents from brain tissue across the BBB. BBB disruption itself was excluded by the absence of increased sodium fluorescein extravasation into the brain and by electrophysiological characteristics of the BBB [145]. The net efflux of acid equivalents from the brain across the BBB was abolished by MIA, suppressing the postasphyxia rebound alkalosis of the brain extracellular pH without having any significant effect on the weight of the pups. Remarkably, MIA also abolished postasphyxia seizures (reduced seizure burden by 88 %) when applied preinsult in rat pups [138, 145] and ameliorated brain injury when applied before hypoxia–ischemia in neonatal mice [93]. These findings support the conclusion that activation of NHE in the BBB leads to brain alkalosis and consequent seizures.
Therapeutic hypothermia is now standard care for infants in the developed world with moderate to severe neonatal encephalopathy [146]. It is unknown if NHE inhibition combined with therapeutic hypothermia might augment hypothermic neuroprotection after perinatal asphyxia. Some in vitro studies suggest that moderate hypothermia (reducing temperature from 37 to 20 °C) itself increases NHE activity [147, 148], while others suggest that hypothermia produces a partial inhibition of NHE activity [149]. The combined effects of an NHE inhibitor with hypothermia could significantly augment hypothermic neuroprotection especially as they act on separate pathways. Importantly, studies suggest that the potency of NHE inhibition under hypothermic conditions is not influenced by a change in temperature [149] and NHE inhibition was beneficial in a perfused heart model even after hypothermic ischemia [150]. Preclinical large animal studies of combined therapy with cooling are high priority.
Summary
Perinatal hypoxic–ischemic brain injury in term babies is still a significant problem throughout the world. Therapeutic hypothermia has improved outcome, especially of those with a moderate insult. Unfortunately, around 40 % of infants treated with therapeutic hypothermia still have adverse outcomes. Experimental data suggest that the addition of another agent to cooling may enhance overall protection either additively or synergistically. Experimental models have demonstrated the central role of NHE in maintaining brain pHi and ion homeostasis, and in microglial activation in some areas of the brain. NHE inhibitors are a promising neuroprotective agent in animal models, improving brain energy metabolism in in vivo MRS, reducing cell death, seizure burden, and brain injury with improvement of functional outcome. Preclinical studies are urgently needed to assess possible augmentation of hypothermic neuroprotection with NHE inhibition.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
This work was undertaken at UCH/UCL who received a proportion of funding from the UK Department of Health's NIHR Biomedical Research Centres funding scheme.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- 1.Kurinczuk JJ, White-Koning M, Badawi N. Epidemiology of neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic–ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86(6):329–338. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2010.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Edwards AD, Brocklehurst P, Gunn AJ, Halliday H, Juszczak E, Levene M, et al. Neurological outcomes at 18 months of age after moderate hypothermia for perinatal hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: synthesis and meta-analysis of trial data. BMJ. 2010;340:c363. doi: 10.1136/bmj.c363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lorek A, Takei Y, Cady EB, Wyatt JS, Penrice J, Edwards AD, et al. Delayed (“secondary”) cerebral energy failure after acute hypoxia–ischemia in the newborn piglet: continuous 48-hour studies by phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr Res. 1994;36(6):699–706. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199412000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Robertson NJ, Cox IJ, Cowan FM, Counsell SJ, Azzopardi D, Edwards AD. Cerebral intracellular lactic alkalosis persisting months after neonatal encephalopathy measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr Res. 1999;46(3):287–296. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199909000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Robertson NJ, Cowan FM, Cox IJ, Edwards AD. Brain alkaline intracellular pH after neonatal encephalopathy. Ann Neurol. 2002;52(6):732–742. doi: 10.1002/ana.10365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Robertson CM, Perlman M. Follow-up of the term infant after hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy. Paediatr child Health. 2006;11(5):278–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bona E, Hagberg H, Loberg EM, Bagenholm R, Thoresen M. Protective effects of moderate hypothermia after neonatal hypoxia–ischemia: short- and long-term outcome. Pediatr Res. 1998;43(6):738–745. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199806000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thoresen M, Penrice J, Lorek A, Cady EB, Wylezinska M, Kirkbride V, et al. Mild hypothermia after severe transient hypoxia–ischemia ameliorates delayed cerebral energy failure in the newborn piglet. Pediatr Res. 1995;37(5):667–670. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199505000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Therapeutic hypothermia with intracorporeal temperature monitoring for hypoxic perinatal brain injury. 2010. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/IPG347/Guidance/pdf/English. Accessed 26 May 2010.
- 10.Jacobs SE, Berg M, Hunt R, Tarnow-Mordi WO, Inder TE, Davis PG. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;1:CD003311. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003311.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gluckman PD, Wyatt JS, Azzopardi D, Ballard R, Edwards AD, Ferriero DM, et al. Selective head cooling with mild systemic hypothermia after neonatal encephalopathy: multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9460):663–670. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17946-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, et al. Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(15):1574–1584. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcps050929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Azzopardi DV, Strohm B, Edwards AD, Dyet L, Halliday HL, Juszczak E, et al. Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(14):1349–1358. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0900854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Guillet R, Edwards AD, Thoresen M, Ferriero DM, Gluckman PD, Whitelaw A, et al. Seven- to eight-year follow-up of the CoolCap trial of head cooling for neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatr Res. 2012;71(2):205–209. doi: 10.1038/pr.2011.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kelen D, Robertson NJ. Experimental treatments for hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86(6):369–377. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2010.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Barkovich AJ, Miller SP, Bartha A, Newton N, Hamrick SE, Mukherjee P, et al. MR imaging, MR spectroscopy, and diffusion tensor imaging of sequential studies in neonates with encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(3):533–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cowan F, Rutherford M, Groenendaal F, Eken P, Mercuri E, Bydder GM, et al. Origin and timing of brain lesions in term infants with neonatal encephalopathy. Lancet. 2003;361(9359):736–742. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12658-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ranck JB, Jr, Windle WF. Brain damage in the monkey, Macaca mulatta, by asphyxia neonatorum. Exp Neurol. 1959;1(2):130–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brann AW, Jr, Myers RE. Central nervous system findings in the newborn monkey following severe in utero partial asphyxia. Neurology. 1975;25(4):327–338. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.4.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Myers RE. Two patterns of perinatal brain damage and their conditions of occurrence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972;112(2):246–276. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Okereafor A, Allsop J, Counsell SJ, Fitzpatrick J, Azzopardi D, Rutherford MA, et al. Patterns of brain injury in neonates exposed to perinatal sentinel events. Pediatrics. 2008;121(5):906–914. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-0770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Johnson M, Hanson GR, Gibb JW, Adair J, Filloux F. Effect of neonatal hypoxia–ischemia on nigro-striatal dopamine receptors and on striatal neuropeptide Y, dynorphin A and substance P concentrations in rats. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1994;83(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(94)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Martinez-Biarge M, Diez-Sebastian J, Rutherford MA, Cowan FM. Outcomes after central grey matter injury in term perinatal hypoxic–ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86(11):675–682. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2010.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Groenendaal F, de Vries LS. Watershed infarcts in the full term neonatal brain. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005;90(6):F488. doi: 10.1136/adc.2005.073544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chau V, Poskitt KJ, Sargent MA, Lupton BA, Hill A, Roland E, et al. Comparison of computer tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scans on the third day of life in term newborns with neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2009;123(1):319–326. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-0283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rutherford M, Pennock J, Schwieso J, Cowan F, Dubowitz L. Hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy: early and late magnetic resonance imaging findings in relation to outcome. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1996;75(3):F145–F151. doi: 10.1136/fn.75.3.f145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Burns CM, Rutherford MA, Boardman JP, Cowan FM. Patterns of cerebral injury and neurodevelopmental outcomes after symptomatic neonatal hypoglycemia. Pediatrics. 2008;122(1):65–74. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-2822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Miller SP, Newton N, Ferriero DM, Partridge JC, Glidden DV, Barnwell A, et al. Predictors of 30-month outcome after perinatal depression: role of proton MRS and socioeconomic factors. Pediatr Res. 2002;52(1):71–77. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200207000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Marlow N, Rose AS, Rands CE, Draper ES. Neuropsychological and educational problems at school age associated with neonatal encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005;90(5):F380–F387. doi: 10.1136/adc.2004.067520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Barnett A, Mercuri E, Rutherford M, Haataja L, Frisone MF, Henderson S, et al. Neurological and perceptual-motor outcome at 5–6 years of age in children with neonatal encephalopathy: relationship with neonatal brain MRI. Neuropediatrics. 2002;33(5):242–248. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-36737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gonzalez FF, Miller SP. Does perinatal asphyxia impair cognitive function without cerebral palsy? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006;91(6):F454–F459. doi: 10.1136/adc.2005.092445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gadian DG, Aicardi J, Watkins KE, Porter DA, Mishkin M, Vargha-Khadem F. Developmental amnesia associated with early hypoxic–ischaemic injury. Brain. 2000;123(Pt 3):499–507. doi: 10.1093/brain/123.3.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Azzopardi D, Wyatt JS, Cady EB, Delpy DT, Baudin J, Stewart AL, et al. Prognosis of newborn infants with hypoxic–ischemic brain injury assessed by phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr Res. 1989;25(5):445–451. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198905000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Blumberg RM, Cady EB, Wigglesworth JS, McKenzie JE, Edwards AD. Relation between delayed impairment of cerebral energy metabolism and infarction following transient focal hypoxia–ischaemia in the developing brain. Exp Brain Res Exp Hirnforsch Exp Cereb. 1997;113(1):130–137. doi: 10.1007/BF02454148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Iwata O, Iwata S, Thornton JS, De Vita E, Bainbridge A, Herbert L, et al. “Therapeutic time window” duration decreases with increasing severity of cerebral hypoxia–ischaemia under normothermia and delayed hypothermia in newborn piglets. Brain Res. 2007;1154:173–180. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.03.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hope PL, Costello AM, Cady EB, Delpy DT, Tofts PS, Chu A, et al. Cerebral energy metabolism studied with phosphorus NMR spectroscopy in normal and birth-asphyxiated infants. Lancet. 1984;2(8399):366–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cady EB, Amess P, Penrice J, Wylezinska M, Sams V, Wyatt JS. Early cerebral-metabolite quantification in perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy by proton and phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging. 1997;15(5):605–611. doi: 10.1016/s0730-725x(97)00017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Martin E, Buchli R, Ritter S, Schmid R, Largo RH, Boltshauser E, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of cerebral 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Pediatr Res. 1996;40(5):749–758. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199611000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Urenjak J, Williams SR, Gadian DG, Noble M. Specific expression of N-acetylaspartate in neurons, oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocyte progenitors, and immature oligodendrocytes in vitro. J Neurochem. 1992;59(1):55–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Thayyil S, Chandrasekaran M, Taylor A, Bainbridge A, Cady EB, Chong WK, et al. Cerebral magnetic resonance biomarkers in neonatal encephalopathy: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2010;125(2):e382–e395. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Moon RB, Richards JH. Determination of intracellular pH by 31P magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1973;248(20):7276–7278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Petroff OA, Prichard JW, Behar KL, Alger JR, den Hollander JA, Shulman RG. Cerebral intracellular pH by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurology. 1985;35(6):781–8. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Corbett RJ, Laptook AR, Nunnally RL. The use of the chemical shift of the phosphomonoester P-31 magnetic resonance peak for the determination of intracellular pH in the brains of neonates. Neurology. 1987;37(11):1771–9. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 44.Williams GD, Smith MB. Application of the accurate assessment of intracellular magnesium and pH from the 31P shifts of ATP to cerebral hypoxia–ischemia in neonatal rat. Magn Reson Med: off J Soc Magn Reson Med/Soc Magn Reson Med. 1995;33(6):853–857. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910330618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Casey JR, Grinstein S, Orlowski J. Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(1):50–61. doi: 10.1038/nrm2820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Vornov JJ, Thomas AG, Jo D. Protective effects of extracellular acidosis and blockade of sodium/hydrogen ion exchange during recovery from metabolic inhibition in neuronal tissue culture. J Neurochem. 1996;67(6):2379–2389. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.67062379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bond JM, Herman B, Lemasters JJ. Protection by acidotic pH against anoxia/reoxygenation injury to rat neonatal cardiac myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;179(2):798–803. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91887-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bond JM, Chacon E, Herman B, Lemasters JJ. Intracellular pH and Ca2+ homeostasis in the pH paradox of reperfusion injury to neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1993;265(1 Pt 1):C129–C137. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.1.C129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lemasters JJ, Nieminen AL, Qian T, Trost LC, Herman B. The mitochondrial permeability transition in toxic, hypoxic and reperfusion injury. Mol Cell Biochem. 1997;174(1–2):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Traynelis SF, Cull-Candy SG. Proton inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1990;345(6273):347–350. doi: 10.1038/345347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Giffard RG, Weiss JH, Choi DW. Extracellular alkalinity exacerbates injury of cultured cortical neurons. Stroke: J Cereb Circ. 1992;23(12):1817–1821. doi: 10.1161/01.str.23.12.1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Masereel B, Pochet L, Laeckmann D. An overview of inhibitors of Na(+)/H(+) exchanger. Eur J Med Chem. 2003;38(6):547–554. doi: 10.1016/s0223-5234(03)00100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Slepkov ER, Rainey JK, Sykes BD, Fliegel L. Structural and functional analysis of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Biochem J. 2007;401(3):623–633. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kintner DB, Wang Y, Sun D. Role of membrane ion transport proteins in cerebral ischemic damage. Front Biosci: J Virtual Libr. 2007;12:762–770. doi: 10.2741/2099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lee SH, Kim T, Park ES, Yang S, Jeong D, Choi Y, et al. NHE10, an osteoclast-specific member of the Na+/H+ exchanger family, regulates osteoclast differentiation and survival [corrected] Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;369(2):320–326. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Brett CL, Wei Y, Donowitz M, Rao R. Human Na(+)/H(+) exchanger isoform 6 is found in recycling endosomes of cells, not in mitochondria. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;282(5):C1031–C1041. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00420.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Orlowski J, Grinstein S. Diversity of the mammalian sodium/proton exchanger SLC9 gene family. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447(5):549–565. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ma E, Haddad GG. Expression and localization of Na+/H+ exchangers in rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1997;79(2):591–603. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(96)00674-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Douglas RM, Schmitt BM, Xia Y, Bevensee MO, Biemesderfer D, Boron WF, et al. Sodium-hydrogen exchangers and sodium-bicarbonate co-transporters: ontogeny of protein expression in the rat brain. Neuroscience. 2001;102(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Rotin D, Grinstein S. Impaired cell volume regulation in Na+–H+ exchange-deficient mutants. Am J Physiol. 1989;257(6 Pt 1):C1158–65. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 61.Aronson PS. Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+–H+ exchanger. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:545–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Paris S, Pouyssegur J. Growth factors activate the Na+/H+ antiporter in quiescent fibroblasts by increasing its affinity for intracellular H+ J Biol Chem. 1984;259(17):10989–10994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Haworth RS, Roberts NA, Cuello F, Avkiran M. Regulation of protein kinase D activity in adult myocardium: novel counter-regulatory roles for protein kinase Cepsilon and protein kinase A. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;43(6):686–695. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Khaled AR, Moor AN, Li A, Kim K, Ferris DK, Muegge K, et al. Trophic factor withdrawal: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activates NHE1, which induces intracellular alkalinization. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21(22):7545–7557. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.22.7545-7557.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Malo ME, Li L, Fliegel L. Mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger is mediated through phosphorylation of amino acids Ser770 and Ser771. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(9):6292–6299. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611073200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Tominaga T, Ishizaki T, Narumiya S, Barber DL. p160ROCK mediates RhoA activation of Na–H exchange. EMBO J. 1998;17(16):4712–4722. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.16.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Yan W, Nehrke K, Choi J, Barber DL. The Nck-interacting kinase (NIK) phosphorylates the Na+–H+ exchanger NHE1 and regulates NHE1 activation by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(33):31349–31356. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102679200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Fernandez-Rachubinski F, Fliegel L. COUP-TFI and COUP-TFII regulate expression of the NHE through a nuclear hormone responsive element with enhancer activity. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268(3):620–634. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2001.01915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Slepkov E, Fliegel L. Regulation of expression of the Na+/H+ exchanger by thyroid hormone. Vitam Horm. 2004;69:249–269. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(04)69009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Denker SP, Huang DC, Orlowski J, Furthmayr H, Barber DL. Direct binding of the Na–H exchanger NHE1 to ERM proteins regulates the cortical cytoskeleton and cell shape independently of H(+) translocation. Mol Cell. 2000;6(6):1425–1436. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Meima ME, Mackley JR, Barber DL. Beyond ion translocation: structural functions of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger isoform-1. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2007;16(4):365–372. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e3281bd888d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Denker SP, Barber DL. Cell migration requires both ion translocation and cytoskeletal anchoring by the Na–H exchanger NHE1. J Cell Biol. 2002;159(6):1087–1096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200208050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Stock C, Schwab A. Role of the Na/H exchanger NHE1 in cell migration. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2006;187(1–2):149–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2006.01543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Hayashi H, Aharonovitz O, Alexander RT, Touret N, Furuya W, Orlowski J, et al. Na+/H+ exchange and pH regulation in the control of neutrophil chemokinesis and chemotaxis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008;294(2):C526–C534. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00219.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Patel H, Barber DL. A developmentally regulated Na–H exchanger in Dictyostelium discoideum is necessary for cell polarity during chemotaxis. J Cell Biol. 2005;169(2):321–329. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200412145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kapus A, Grinstein S, Wasan S, Kandasamy R, Orlowski J. Functional characterization of three isoforms of the Na+/H+ exchanger stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. ATP dependence, osmotic sensitivity, and role in cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(38):23544–23552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Pouyssegur J, Seuwen K. Transmembrane receptors and intracellular pathways that control cell proliferation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:195–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Putney LK, Barber DL. Na-H exchange-dependent increase in intracellular pH times G2/M entry and transition. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(45):44645–44649. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308099200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Cheung JY, Bonventre JV, Malis CD, Leaf A. Calcium and ischemic injury. N Engl J Med. 1986;314(26):1670–1676. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606263142604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Siesjo BK. Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia. Part I: Pathophysiology. J Neurosurg. 1992;77(2):169–184. doi: 10.3171/jns.1992.77.2.0169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Wakabayashi S, Fafournoux P, Sardet C, Pouyssegur J. The Na+/H+ antiporter cytoplasmic domain mediates growth factor signals and controls “H(+)-sensing”. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(6):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Obara M, Szeliga M, Albrecht J. Regulation of pH in the mammalian central nervous system under normal and pathological conditions: facts and hypotheses. Neurochem Int. 2008;52(6):905–919. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Sheldon C, Church J. Intracellular pH response to anoxia in acutely dissociated adult rat hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Neurophys. 2002;87(5):2209–2224. doi: 10.1152/jn.2002.87.5.2209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hwang IK, Yoo KY, An SJ, Li H, Lee CH, Choi JH, et al. Late expression of Na+/H+ exchanger 1 (NHE1) and neuroprotective effects of NHE inhibitor in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region induced by transient ischemia. Exp Neurol. 2008;212(2):314–323. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kersh AE, Hartzler LK, Havlin K, Hubbell BB, Nanagas V, Kalra A, et al. pH regulating transporters in neurons from various chemosensitive brainstem regions in neonatal rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009;297(5):R1409–R1420. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.91038.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Jorgensen EO, Holm S. The course of circulatory and cerebral recovery after circulatory arrest: influence of pre-arrest, arrest and post-arrest factors. Resuscitation. 1999;42(3):173–182. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9572(99)00116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Luo J, Chen H, Kintner DB, Shull GE, Sun D. Decreased neuronal death in Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1-null mice after in vitro and in vivo ischemia. J Neurosci. 2005;25(49):11256–11268. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3271-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Matsumoto Y, Yamamoto S, Suzuki Y, Tsuboi T, Terakawa S, Ohashi N, et al. Na+/H+ exchanger inhibitor, SM-20220, is protective against excitotoxicity in cultured cortical neurons. Stroke: J Cereb Circ. 2004;35(1):185–190. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000106910.42815.C2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Robertson NJ, Bhakoo K, Puri BK, Edwards AD, Cox IJ. Hypothermia and amiloride preserve energetics in a neonatal brain slice model. Pediatr Res. 2005;58(2):288–296. doi: 10.1203/01.PDR.0000170899.90479.1E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Liu Y, Kintner DB, Chanana V, Algharabli J, Chen X, Gao Y, et al. Activation of microglia depends on Na+/H+ exchange-mediated H+ homeostasis. J Neurosci. 2010;30(45):15210–15220. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3950-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Yao H, Gu XQ, Douglas RM, Haddad GG. Role of Na(+)/H(+) exchanger during O(2) deprivation in mouse CA1 neurons. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;281(4):C1205–C1210. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.281.4.C1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Kintner DB, Look A, Shull GE, Sun D. Stimulation of astrocyte Na+/H+ exchange activity in response to in vitro ischemia depends in part on activation of ERK1/2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;289(4):C934–C945. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00092.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Kendall GS, Robertson NJ, Iwata O, Peebles D, Raivich G. N-methyl-isobutyl-amiloride ameliorates brain injury when commenced before hypoxia ischemia in neonatal mice. Pediatr Res. 2006;59(2):227–231. doi: 10.1203/01.pdr.0000196805.68082.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Kuribayashi Y, Itoh N, Kitano M, Ohashi N. Cerebroprotective properties of SM-20220, a potent Na(+)/H(+) exchange inhibitor, in transient cerebral ischemia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;383(2):163–168. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00645-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Kitayama J, Kitazono T, Yao H, Ooboshi H, Takaba H, Ago T, et al. Inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger reduces infarct volume of focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2001;922(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)03175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Touret N, Tanneur V, Godart H, Seidler R, Taki N, Burger E, et al. Characterization of sabiporide, a new specific NHE-1 inhibitor exhibiting slow dissociation kinetics and cardioprotective effects. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;459(2–3):151–158. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(02)02824-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Park HS, Lee BK, Park S, Kim SU, Lee SH, Baik EJ, et al. Effects of sabiporide, a specific Na+/H+ exchanger inhibitor, on neuronal cell death and brain ischemia. Brain Res. 2005;1061(1):67–71. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Suzuki Y, Matsumoto Y, Ikeda Y, Kondo K, Ohashi N, Umemura K. SM-20220, a Na(+)/H(+) exchanger inhibitor: effects on ischemic brain damage through edema and neutrophil accumulation in a rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Brain Res. 2002;945(2):242–248. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)02806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Horikawa N, Nishioka M, Itoh N, Kuribayashi Y, Matsui K, Ohashi N. The Na(+)/H(+) exchanger SM-20220 attenuates ischemic injury in in vitro and in vivo models. Pharmacology. 2001;63(2):76–81. doi: 10.1159/000056116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Horikawa N, Kuribayashi Y, Itoh N, Nishioka M, Matsui K, Kawamura N, et al. Na+/H+ exchange inhibitor SM-20220 improves endothelial dysfunction induced by ischemia-reperfusion. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2001;85(3):271–277. doi: 10.1254/jjp.85.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Shi Y, Chanana V, Watters JJ, Ferrazzano P, Sun D. Role of sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 1 in microglial activation and proinflammatory responses in ischemic brains. J Neurochem. 2011;119(1):124–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07403.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Cengiz P, Kleman N, Uluc K, Kendigelen P, Hagemann T, Akture E, et al. Inhibition of Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 is neuroprotective in neonatal hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14(10):1803–1813. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Bondarenko A, Chesler M. Rapid astrocyte death induced by transient hypoxia, acidosis, and extracellular ion shifts. Glia. 2001;34(2):134–142. doi: 10.1002/glia.1048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Bondarenko A, Svichar N, Chesler M. Role of Na+–H+and Na+–Ca2+ exchange in hypoxia-related acute astrocyte death. Glia. 2005;49(1):143–152. doi: 10.1002/glia.20107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Mellergard PE, Ouyang YB, Siesjo BK. The regulation of intracellular pH in cultured astrocytes and neuroblastoma cells, and its dependence on extracellular pH in a HCO3-free solution. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992;70(Suppl):S293–S300. doi: 10.1139/y92-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Castella M, Buckberg GD, Tan Z. Neurologic preservation by Na+–H+ exchange inhibition prior to 90 minutes of hypothermic circulatory arrest. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79(2):646–654. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Phillis JW, Ren J, O’Regan MH. Inhibition of Na(+)/H(+) exchange by 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)-amiloride reduces free fatty acid efflux from the ischemic reperfused rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 2000;884(1–2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02938-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Gerhardt SC, Boast CA. Motor activity changes following cerebral ischemia in gerbils are correlated with the degree of neuronal degeneration in hippocampus. Behav Neurosci. 1988;102(2):301–303. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.102.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kuribayashi Y, Itoh N, Horikawa N, Ohashi N. SM-20220, a potent Na+/H+ exchange inhibitor, improves consciousness recovery and neurological outcome following transient cerebral ischaemia in gerbils. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2000;52(4):441–444. doi: 10.1211/0022357001774057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Pilitsis JG, Diaz FG, O’Regan MH, Phillis JW. Inhibition of Na(+)/H(+) exchange by SM-20220 attenuates free fatty acid efflux in rat cerebral cortex during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Res. 2001;913(2):156–158. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)02760-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Robertson NJ, Kato T, Bainbridge A, Chandrasekaran M, Iwata O, Kapetanakis A, et al. Methyl-isobutyl amiloride reduces brain Lac/NAA, cell death and microglial activation in a perinatal asphyxia model. J Neurochem. 2013;124(5):645–657. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.van Rooij LG, Toet MC, van Huffelen AC, Groenendaal F, Laan W, Zecic A, et al. Effect of treatment of subclinical neonatal seizures detected with aEEG: randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2010;125(2):e358–e366. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-0136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.McBride MC, Laroia N, Guillet R. Electrographic seizures in neonates correlate with poor neurodevelopmental outcome. Neurology. 2000;55(4):506–513. doi: 10.1212/wnl.55.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Lingwood BE, Dunster KR, Healy GN, Ward LC, Colditz PB. Cerebral impedance and neurological outcome following a mild or severe hypoxic/ischemic episode in neonatal piglets. Brain Res. 2003;969(1–2):160–167. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(03)02295-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Haynes RL, Baud O, Li J, Kinney HC, Volpe JJ, Folkerth DR. Oxidative and nitrative injury in periventricular leukomalacia: a review. Brain Pathol. 2005;15(3):225–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2005.tb00525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Silverstein FS, Jensen FE. Neonatal seizures. Ann Neurol. 2007;62(2):112–120. doi: 10.1002/ana.21167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Lindstrom K, Hallberg B, Blennow M, Wolff K, Fernell E, Westgren M. Moderate neonatal encephalopathy: pre- and perinatal risk factors and long-term outcome. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2008;87(5):503–509. doi: 10.1080/00016340801996622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Bjorkman ST, Miller SM, Rose SE, Burke C, Colditz PB. Seizures are associated with brain injury severity in a neonatal model of hypoxia–ischemia. Neuroscience. 2010;166(1):157–167. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.11.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Stolp H, Neuhaus A, Sundramoorthi R, Molnar Z. The long and the short of it: gene and environment interactions during early cortical development and consequences for long-term neurological disease. Front Psychiatry. 2012;3:50. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2012.00050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Uria-Avellanal C, Marlow N, Rennie JM. Outcome following neonatal seizures. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013;18(4):224–232. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2013.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Rennie JM, Boylan GB. Neonatal seizures and their treatment. Curr Opin Neurol. 2003;16(2):177–181. doi: 10.1097/01.wco.0000063768.15877.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Evans DJ, Levene MI, Tsakmakis M. Anticonvulsants for preventing mortality and morbidity in full term newborns with perinatal asphyxia. Cochrane database Syst Rev. 2007;3:CD001240. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001240.pub2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Rennie J, Boylan G. Treatment of neonatal seizures. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007;92(2):F148–F150. doi: 10.1136/adc.2004.068551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Low E, Boylan GB, Mathieson SR, Murray DM, Korotchikova I, Stevenson NJ, et al. Cooling and seizure burden in term neonates: an observational study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012;97(4):F267–F272. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2011-300716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Azzopardi D, Robertson NJ, Kapetanakis A, Griffiths J, Rennie JM, Mathieson SR, et al. Anticonvulsant effect of xenon on neonatal asphyxial seizures. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2013;98(5):F437–F439. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-303786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Glass HC, Glidden D, Jeremy RJ, Barkovich AJ, Ferriero DM, Miller SP. Clinical neonatal seizures are independently associated with outcome in infants at risk for hypoxic–ischemic brain injury. J Pediatr. 2009;155(3):318–323. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.03.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Kwon JM, Guillet R, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, McDonald SA, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Clinical seizures in neonatal hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy have no independent impact on neurodevelopmental outcome: secondary analyses of data from the neonatal research network hypothermia trial. J Child Neurol. 2011;26(3):322–328. doi: 10.1177/0883073810380915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Poland R, Freeman R, American Academy of Pediatrics. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists . Relationship between perinatal factors and neurologic outcome. In: Poland R, Freeman R, editors. Guidelines for perinatal care. Elk Grove Village: American Academy of Pediatrics; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 129.Salhab WA, Wyckoff MH, Laptook AR, Perlman JM. Initial hypoglycemia and neonatal brain injury in term infants with severe fetal acidemia. Pediatrics. 2004;114(2):361–366. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.2.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Shalak L, Perlman JM. Hypoxic–ischemic brain injury in the term infant—current concepts. Early Hum Dev. 2004;80(2):125–141. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2004.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Siesjo BK. Cell damage in the brain: a speculative synthesis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(2):155–185. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Chesler M. The regulation and modulation of pH in the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;34(5):401–427. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90034-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Kaila K. Ionic basis of GABAA receptor channel function in the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1994;42(4):489–537. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(94)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Tombaugh GC, Somjen GG. Effects of extracellular pH on voltage-gated Na+, K+ and Ca2+ currents in isolated rat CA1 neurons. J Physiol. 1996;493(Pt 3):719–732. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Erecinska M, Deas J, Silver IA. The effect of pH on glycolysis and phosphofructokinase activity in cultured cells and synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1995;65(6):2765–2772. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65062765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Rehncrona S, Rosen I, Siesjo BK. Excessive cellular acidosis: an important mechanism of neuronal damage in the brain? Acta Physiol Scand. 1980;110(4):435–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Ruusuvuori E, Kirilkin I, Pandya N, Kaila K. Spontaneous network events driven by depolarizing GABA action in neonatal hippocampal slices are not attributable to deficient mitochondrial energy metabolism. J Neurosci. 2010;30(46):15638–15642. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3355-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Helmy MM, Tolner EA, Vanhatalo S, Voipio J, Kaila K. Brain alkalosis causes birth asphyxia seizures, suggesting therapeutic strategy. Ann Neurol. 2011;69(3):493–500. doi: 10.1002/ana.22223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Tang CM, Dichter M, Morad M. Modulation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate channel by extracellular H+ Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(16):6445–6449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Tombaugh GC, Somjen GG. Differential sensitivity to intracellular pH among high- and low-threshold Ca2+ currents in isolated rat CA1 neurons. J Neurophys. 1997;77(2):639–653. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.77.2.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Towfighi J, Mauger D, Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ. Influence of age on the cerebral lesions in an immature rat model of cerebral hypoxia–ischemia: a light microscopic study. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1997;100(2):149–160. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(97)00036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Simon RP, Niro M, Gwinn R. Brain acidosis induced by hypercarbic ventilation attenuates focal ischemic injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;267(3):1428–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Vannucci RC, Towfighi J, Brucklacher RM, Vannucci SJ. Effect of extreme hypercapnia on hypoxic–ischemic brain damage in the immature rat. Pediatr Res. 2001;49(6):799–803. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200106000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Schuchmann S, Schmitz D, Rivera C, Vanhatalo S, Salmen B, Mackie K, et al. Experimental febrile seizures are precipitated by a hyperthermia-induced respiratory alkalosis. Nat Med. 2006;12(7):817–823. doi: 10.1038/nm1422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Helmy MM, Ruusuvuori E, Watkins PV, Voipio J, Kanold PO, Kaila K. Acid extrusion via blood–brain barrier causes brain alkalosis and seizures after neonatal asphyxia. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Higgins RD, Raju T, Edwards AD, Azzopardi DV, Bose CL, Clark RH, et al. Hypothermia and other treatment options for neonatal encephalopathy: an executive summary of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver NICHD workshop. J Pediatr. 2011;159(5):851.e1–858.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Zhou ZQ, Willis JS. Differential effects of cooling in hibernator and nonhibernator cells: Na permeation. Am J Physiol. 1989;256(1 Pt 2):R49–R55. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.256.1.R49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Plesnila N, Muller E, Guretzki S, Ringel F, Staub F, Baethmann A. Effect of hypothermia on the volume of rat glial cells. J Physiol. 2000;523(Pt 1):155–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Hoshino K, Avkiran M. Effects of moderate hypothermia on sarcolemmal Na(+)/H(+) exchanger activity and its inhibition by cariporide in cardiac ventricular myocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 2001;134(7):1587–1595. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Yamauchi T, Ichikawa H, Sawa Y, Fukushima N, Kagisaki K, Maeda K, et al. The contribution of Na+/H+ exchange to ischemia–reperfusion injury after hypothermic cardioplegic arrest. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997;63(4):1107–1112. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(96)01390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Hamilton PA, Hope PL, Cady EB, Delpy DT, Wyatt JS, Reynolds EO. Impaired energy metabolism in brains of newborn infants with increased cerebral echodensities. Lancet. 1986;1(8492):1242–1246. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Boesch C, Gruetter R, Martin E, Duc G, Wuthrich K. Variations in the in vivo P-31 MR spectra of the developing human brain during postnatal life. Work in progress. Radiology. 1989;172(1):197–199. doi: 10.1148/radiology.172.1.2740503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Azzopardi D, Wyatt JS, Hamilton PA, Cady EB, Delpy DT, Hope PL, et al. Phosphorus metabolites and intracellular pH in the brains of normal and small for gestational age infants investigated by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr Res. 1989;25(5):440–444. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198905000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Laptook AR, Corbett RJ, Uauy R, Mize C, Mendelsohn D, Nunnally RL. Use of 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy to characterize evolving brain damage after perinatal asphyxia. Neurology. 1989;39(5):709–712. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.5.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.van der Knaap MS, van der Grond J, van Rijen PC, Faber JA, Valk J, Willemse K. Age-dependent changes in localized proton and phosphorus MR spectroscopy of the brain. Radiology. 1990;176(2):509–515. doi: 10.1148/radiology.176.2.2164237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Buchli R, Martin E, Boesiger P, Rumpel H. Developmental changes of phosphorus metabolite concentrations in the human brain: a 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy study in vivo. Pediatr Res. 1994;35(4 Pt 1):431–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Cady EB, Costello AM, Dawson MJ, Delpy DT, Hope PL, Reynolds EO, et al. Non-invasive investigation of cerebral metabolism in newborn infants by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet. 1983;1(8333):1059–1062. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91906-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Ferimer HN, Kutina KL, LaManna JC. Methyl isobutyl amiloride delays normalization of brain intracellular pH after cardiac arrest in rats. Crit Care Med. 1995;23(6):1106–1111. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199506000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Rocha MA, Crockett DP, Wong LY, Richardson JR, Sonsalla PK. Na(+)/H(+) exchanger inhibition modifies dopamine neurotransmission during normal and metabolic stress conditions. J Neurochem. 2008;106(1):231–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05355.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Ferrazzano P, Shi Y, Manhas N, Wang Y, Hutchinson B, Chen X, et al. Inhibiting the Na+/H+ exchanger reduces reperfusion injury: a small animal MRI study. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2011;3:81–88. doi: 10.2741/e222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


