Abstract
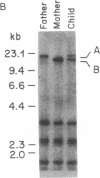
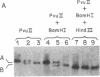
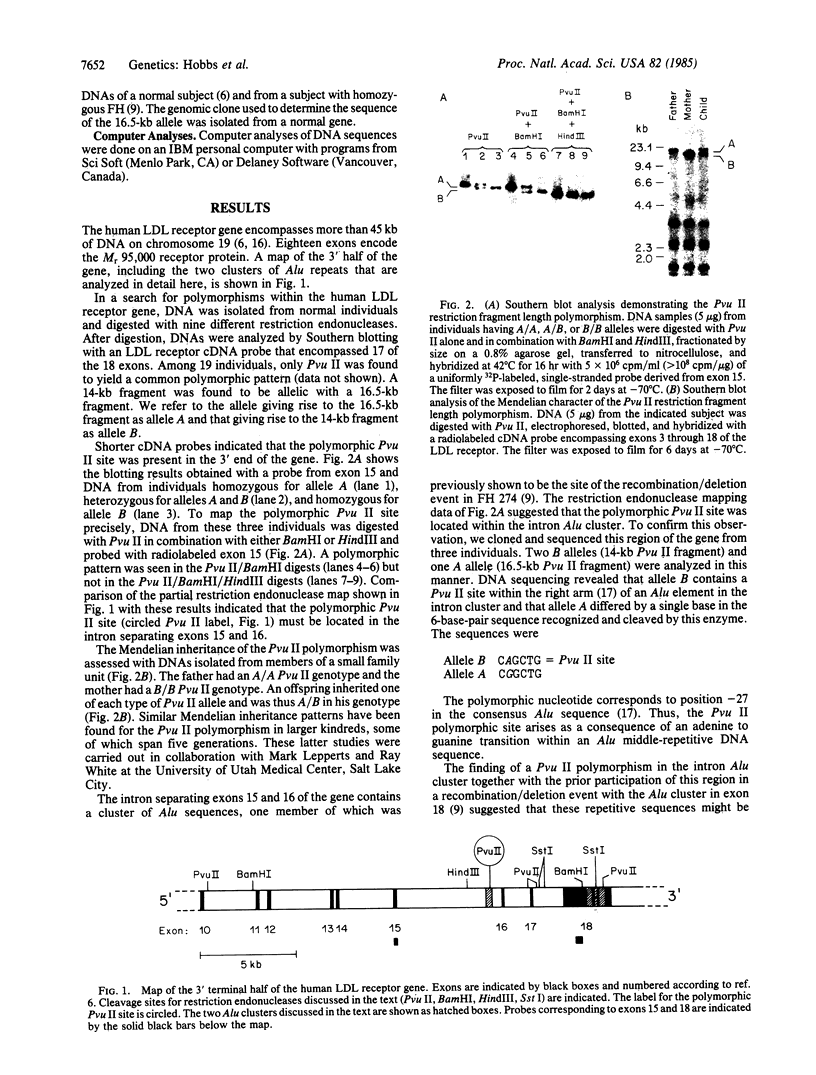
Two clusters of Alu sequences in the human low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene have been analyzed in detail. One Alu cluster is present within the intron separating exons 15 and 16 of the gene and contains a polymorphic Pvu II site. The presence or absence of this site gives rise to two allelic fragments of 14 and 16.5 kilobases, respectively, in genomic Southern blots using cloned cDNA probes. This DNA polymorphic site is caused by a single adenine to guanine transition within an Alu repetitive element. The second cluster of Alu sequences is located in exon 18 of the LDL receptor gene. Southern blotting of primate DNAs suggests that this cluster became associated with the gene about 30 million years ago. Comparison of bovine DNA sequences, which lack this Alu cluster, with those of the human indicates that the Alu sequences inserted in exon 18 in two independent events.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. How LDL receptors influence cholesterol and atherosclerosis. Sci Am. 1984 Nov;251(5):58–66. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1184-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Assignment of the human gene for the low density lipoprotein receptor to chromosome 19: synteny of a receptor, a ligand, and a genetic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2826–2830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Wood W. I., Tuddenham E. G., Shuman M. A., Goralka T. M., Chen E. Y., Lawn R. M. Detection and sequence of mutations in the factor VIII gene of haemophiliacs. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):427–430. doi: 10.1038/315427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries S. E., Kessling A. M., Horsthemke B., Donald J. A., Seed M., Jowett N., Holm M., Galton D. J., Wynn V., Williamson R. A common DNA polymorphism of the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene and its use in diagnosis. Lancet. 1985 May 4;1(8436):1003–1005. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91611-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Short interspersed repetitive DNA elements in eucaryotes: transposable DNA elements generated by reverse transcription of RNA pol III transcripts? Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Dozy A. M., Trecartin R., Todd D. Identification of a nondeletion defect in alpha-thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 17;297(20):1081–1084. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711172972002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):140–146. doi: 10.1126/science.3155573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Bliska J. B., Smithies O. Recombination and balanced chromosome polymorphism suggested by DNA sequences 5' to the human delta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5012–5016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilbeam D. The descent of hominoids and hominids. Sci Am. 1984 Mar;250(3):84–96. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0384-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Schneider W. J., Yamamoto T., Luskey K. L., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Domain map of the LDL receptor: sequence homology with the epidermal growth factor precursor. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90388-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Yamamoto T., Schneider W. J., Slaughter C. J., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. cDNA cloning of the bovine low density lipoprotein receptor: feedback regulation of a receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7501–7505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler L. A., Weber J. L., Gorski J. Polymorphism near the rat prolactin gene caused by insertion of an Alu-like element. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):159–160. doi: 10.1038/305159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley C. G., Ahlquist J. E. The phylogeny of the hominoid primates, as indicated by DNA-DNA hybridization. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(1):2–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02101980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):815–822. doi: 10.1126/science.2988123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabarovsky E. R., Chumakov I. M., Prassolov V. S., Kisselev L. L. The coding region of the human c-mos pseudogene contains Alu repeat insertions. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]