Abstract
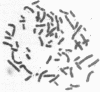
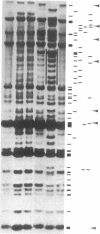
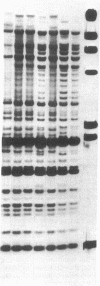
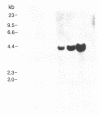
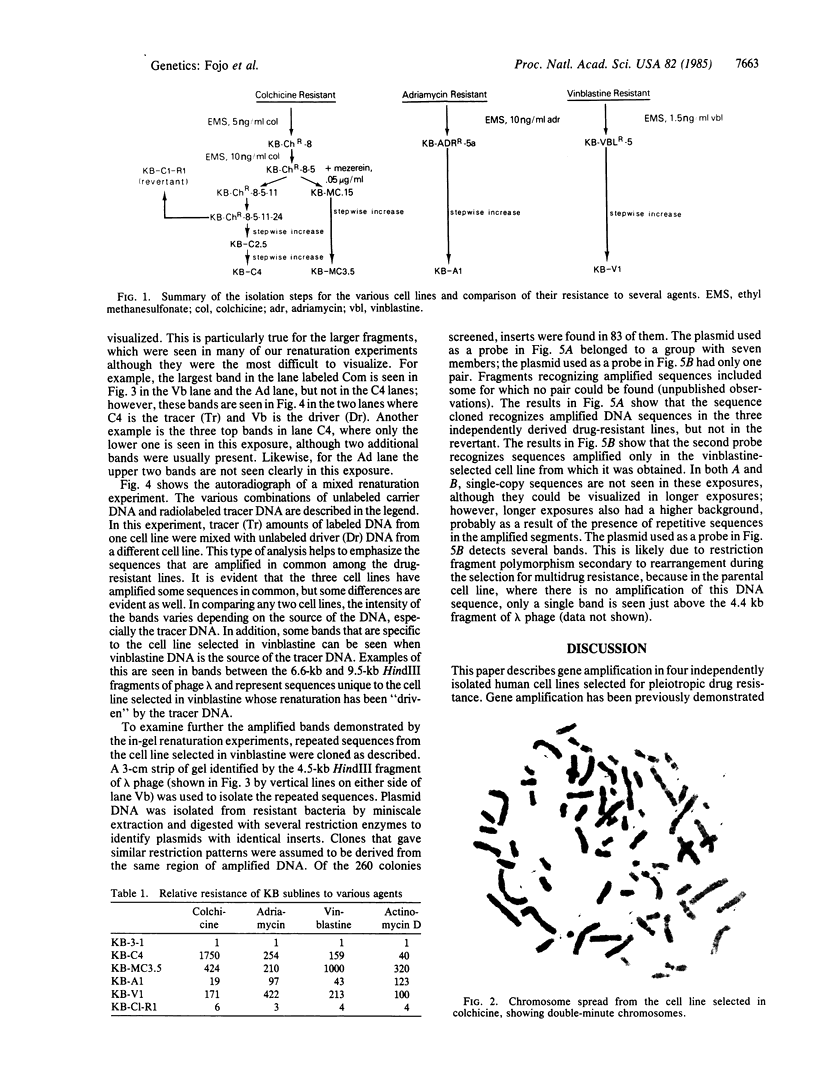
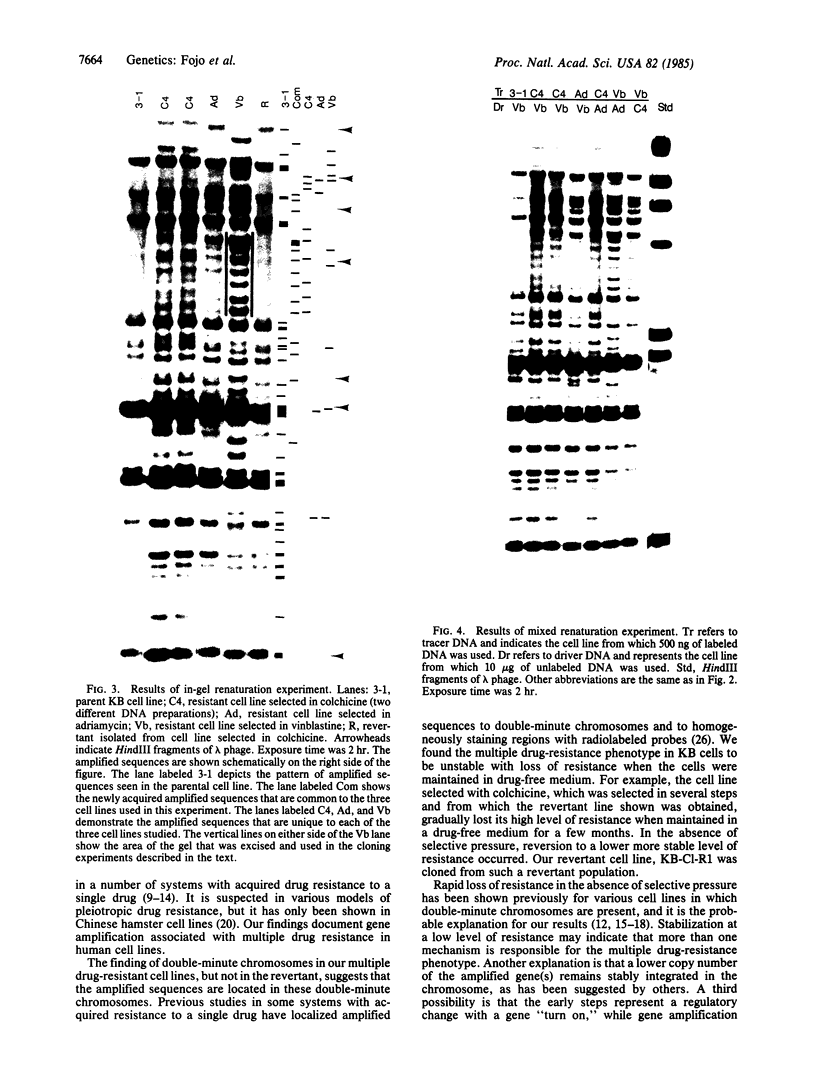
Four KB carcinoma cell lines selected independently for resistance to either colchicine, adriamycin, or vinblastine were studied. All cell lines showed high levels of resistance to the selecting drug and cross-resistance to the other drugs and to actinomycin D. Double-minute chromosomes could be identified on chromosomal spreads of these multidrug-resistant KB cell lines. Amplification of specific DNA sequences was demonstrated by using the technique of in-gel renaturation. All the cell lines share common amplified sequences. There are also amplified sequences that are specific for each cell line. A revertant cell line that has reacquired drug sensitivity has lost its amplified sequences. Specific probes obtained by cloning amplified sequences from the cell line selected in vinblastine recognize amplified sequences in all the resistant lines. The presence of common amplified sequences in these cell lines is strong evidence for the importance of these regions in multiple drug resistance.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama S., Fojo A., Hanover J. A., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Isolation and genetic characterization of human KB cell lines resistant to multiple drugs. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Mar;11(2):117–126. doi: 10.1007/BF01534700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Schimke R. T. Synthesis and degradation of folate reductase in sensitive and methotrexate-resistant lines of S-180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3063–3074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck W. T., Mueller T. J., Tanzer L. R. Altered surface membrane glycoproteins in Vinca alkaloid-resistant human leukemic lymphoblasts. Cancer Res. 1979 Jun;39(6 Pt 1):2070–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck W. T. Vinca alkaloid-resistant phenotype in cultured human leukemic lymphoblasts. Cancer Treat Rep. 1983 Oct;67(10):875–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedler J. L., Chang T. D., Meyers M. B., Peterson R. H., Spengler B. A. Drug resistance in Chinese hamster lung and mouse tumor cells. Cancer Treat Rep. 1983 Oct;67(10):859–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedler J. L., Riehm H. Cellular resistance to actinomycin D in Chinese hamster cells in vitro: cross-resistance, radioautographic, and cytogenetic studies. Cancer Res. 1970 Apr;30(4):1174–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen S. A., Till J. E., Ling V. Modulation of membrane drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):900–912. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. H., Goldsmith M. E., Levine R. M., Aitken S. C., Douglass E., Clendeninn N., Nienhuis A. W., Lippman M. E. Dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification and possible rearrangement in estrogen-responsive methotrexate-resistant human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15079–15086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curt G. A., Carney D. N., Cowan K. H., Jolivet J., Bailey B. D., Drake J. C., Chien Song K. S., Minna J. D., Chabner B. A. Unstable methotrexate resistance in human small-cell carcinoma associated with double minute chromosomes. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 27;308(4):199–202. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301273080406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federspiel N. A., Beverley S. M., Schilling J. W., Schimke R. T. Novel DNA rearrangements are associated with dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9127–9140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fojo A., Akiyama S., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Reduced drug accumulation in multiply drug-resistant human KB carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1985 Jul;45(7):3002–3007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Hamlin J. L. An amplified chromosomal sequence that includes the gene for dihydrofolate reductase initiates replication within specific restriction fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4083–4087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., Belli T. A., Zaczkiewicz L. T., Belli J. A. High-level, unstable adriamycin resistance in a Chinese hamster mutant cell line with double minute chromosomes. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):4023–4029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Brown P. C., Schimke R. T. Loss and stabilization of amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes in mouse sarcoma S-180 cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1084–1093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Lin C. C., Kan Y. W. Amplification and expression of human alpha-globin genes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1469–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling V., Thompson L. H. Reduced permeability in CHO cells as a mechanism of resistance to colchicine. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Feb;83(1):103–116. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. D., Azizkhan J. C., Hamlin J. L. Amplification of a cloned Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene after transfer into a dihydrofolate reductase-deficient cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1274–1282. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riehm H., Biedler J. L. Cellular resistance to daunomycin in Chinese hamster cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1971 Apr;31(4):409–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Buck L. B., Axel R. A structure for amplified DNA. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Ling V., Stanners C. P. Co-amplification of double minute chromosomes, multiple drug resistance, and cell surface P-glycoprotein in DNA-mediated transformants of mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):500–506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roninson I. B., Abelson H. T., Housman D. E., Howell N., Varshavsky A. Amplification of specific DNA sequences correlates with multi-drug resistance in Chinese hamster cells. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):626–628. doi: 10.1038/309626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roninson I. B. Detection and mapping of homologous, repeated and amplified DNA sequences by DNA renaturation in agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5413–5431. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- See Y. P., Carlsen S. A., Till J. E., Ling V. Increased drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cells in the presence of cyanide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 10;373(2):242–252. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90148-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegfried J. M., Tritton T. R., Sartorelli A. C. Comparison of anthracycline concentrations in S180 cell lines of varying sensitivity. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1983 Aug;19(8):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(83)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TJIO J. H., WHANG J. Chromosome preparations of bone marrow cells without prior in vitro culture or in vivo colchicine administration. Stain Technol. 1962 Jan;37:17–20. doi: 10.3109/10520296209114563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Vitto L., Rubnitz J. Co-amplification of rRNA genes with CAD genes in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant Syrian hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2066–2075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]