Abstract
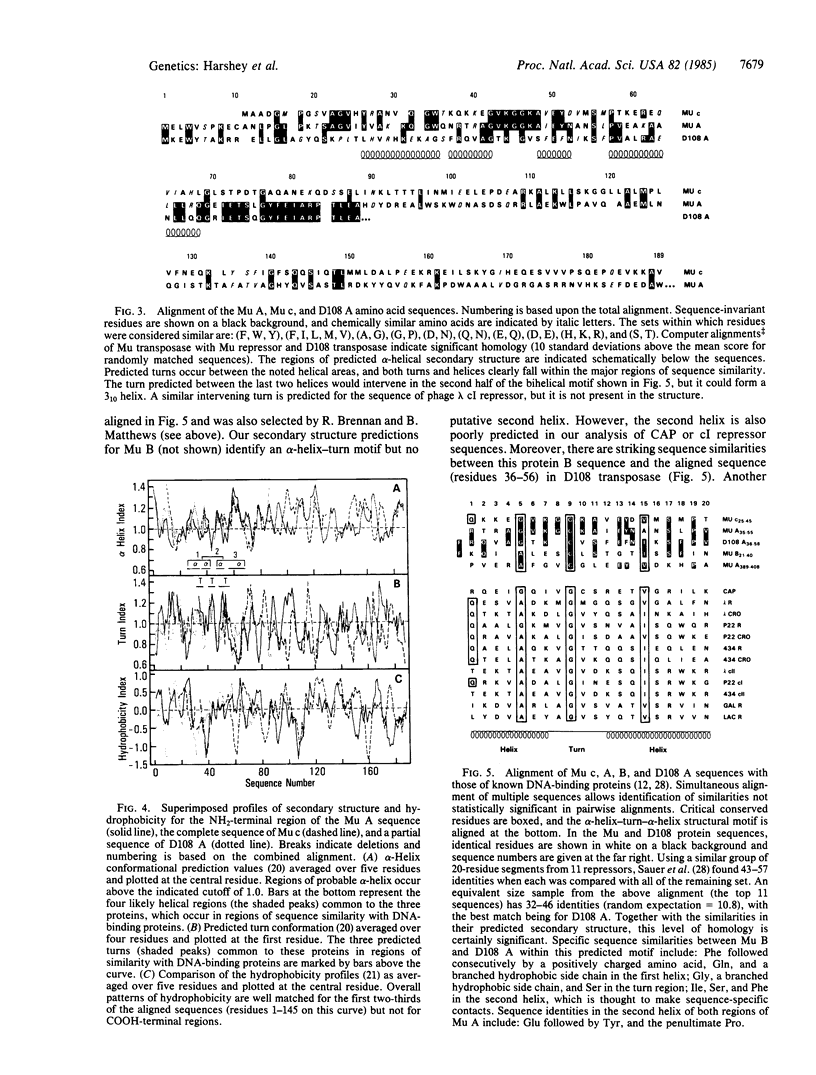
The phage Mu transposase is essential for integration, replication-transposition, and excision of Mu DNA. We present the complete nucleotide and derived amino acid sequence of the transposase and analyze implications for transposase/DNA interaction. The NH2 terminus of the Mu transposase has considerable sequence homology with the Mu repressor and with the NH2 terminus of the transposase of the Mu-like phage D108. These three proteins are known to share binding sites on DNA. The protein sequence and predicted secondary structural similarities at the NH2 termini of the three proteins suggest a common DNA-binding region similar to the regions found in proteins of known structure. An internal sequence in the Mu A protein also shares these features. We anticipate that these regions will be involved in DNA recognition during transposition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. F., Ohlendorf D. H., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Structure of the cro repressor from bacteriophage lambda and its interaction with DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):754–758. doi: 10.1038/290754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I. Bacteriophage mu as a transposition element. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:389–412. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., Gloor G., Miller J. L. Amplification and purification of the bacteriophage Mu encoded B transposition protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., de Bruijn F. J., Casadaban M. J., Lupski J. R., Kwoh T. J., Harshey R. M., DuBow M. S., Bukhari A. I. In vitro and in vivo manipulations of bacteriophage Mu DNA: cloning of Mu ends and construction of mini-Mu's carrying selectable markers. Gene. 1981 Jan-Feb;13(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. E. coli integration host factor binds to specific sites in DNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. Cloning of the A gene of bacteriophage Mu and purification of its product, the Mu transposase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1832–1835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi M., Mizuuchi K. Site-specific recognition of the bacteriophage Mu ends by the Mu A protein. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. S., Hull R. C., Curtiss R., 3rd Mutator bacteriophage D108 and its DNA: an electron microscopic characterization. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):420–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.420-430.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giphart-Gassler M., Reeve J., van de Putte P. Polypeptides encoded by the early region of bacteriophage Mu synthesized in minicells of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):165–191. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goosen N., van Heuvel M., Moolenaar G. F., van de Putte P. Regulation of Mu transposition. II. The escherichia coli HimD protein positively controls two repressor promoters and the early promoter of bacteriophage Mu. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groenen M. A., Timmers E., van de Putte P. DNA sequences at the ends of the genome of bacteriophage Mu essential for transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2087–2091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshey R. M. Switch in the transposition products of Mu DNA mediated by proteins: Cointegrates versus simple insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2012–2016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Kamp D. Nucleotide sequences of the attachment sites of bacteriophage Mu DNA. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):247–250. doi: 10.1038/280247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9-A resolution. Incorporation of amino acid sequence and interactions with cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9518–9524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Friedman D. I. An E. coli gene product required for lambda site-specific recombination. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90317-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Anderson S. K., Fujita D. J., Chaconas G., Baldwin D. L., Harshey R. M. The nucleotide sequence of the B gene of bacteriophage Mu. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8627–8638. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. Many gene-regulatory proteins appear to have a similar alpha-helical fold that binds DNA and evolved from a common precursor. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(2):109–114. doi: 10.1007/BF02300748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priess H., Kamp D., Kahmann R., Bräuer B., Delius H. Nucleotide sequence of the immunity region of bacteriophage Mu. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):315–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00729448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Yocum R. R., Doolittle R. F., Lewis M., Pabo C. O. Homology among DNA-binding proteins suggests use of a conserved super-secondary structure. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):447–451. doi: 10.1038/298447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Ohlendorf D. H., McKay D. B., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. Structural similarity in the DNA-binding domains of catabolite gene activator and cro repressor proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3097–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint A., Faelen M., Desmet L., Allet B. The products of gene A of the related phages Mu and D108 differ in their specificities. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(1):70–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00330326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Howard A., Xuong N. H., Salemme F. R. Crystallographic structure of Rhodospirillum molischianum ferricytochrome c' at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):399–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90286-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]