Abstract
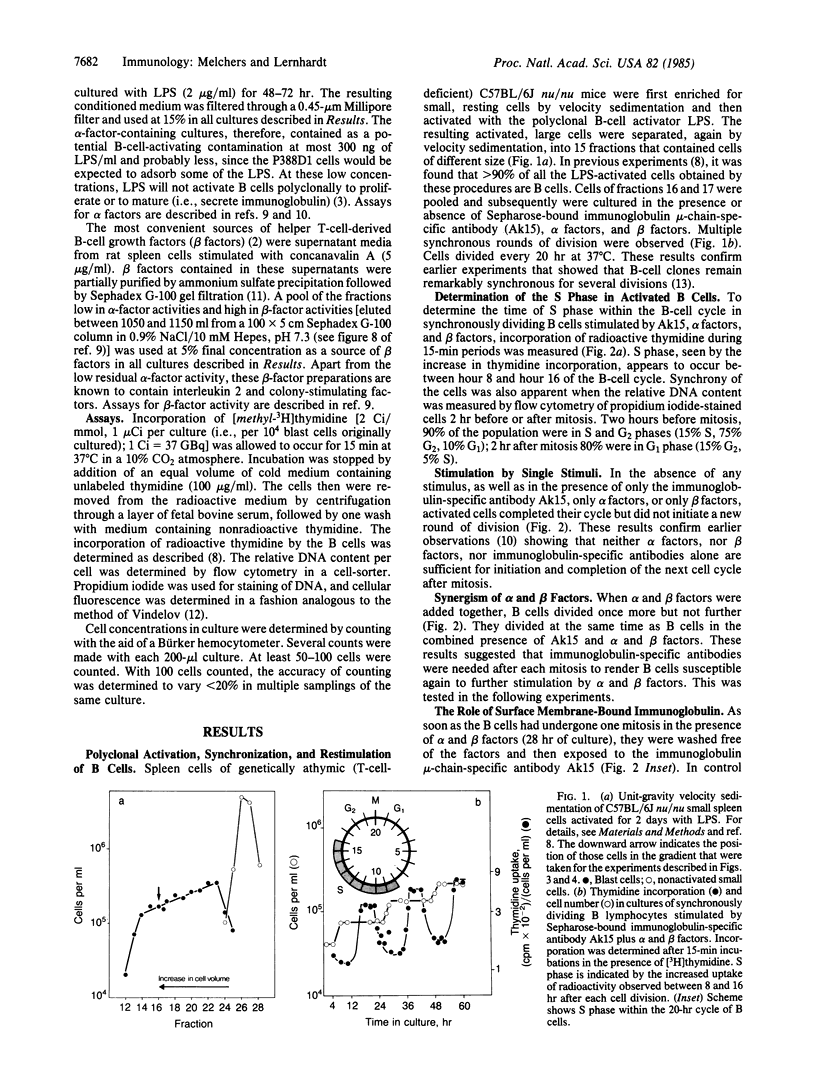
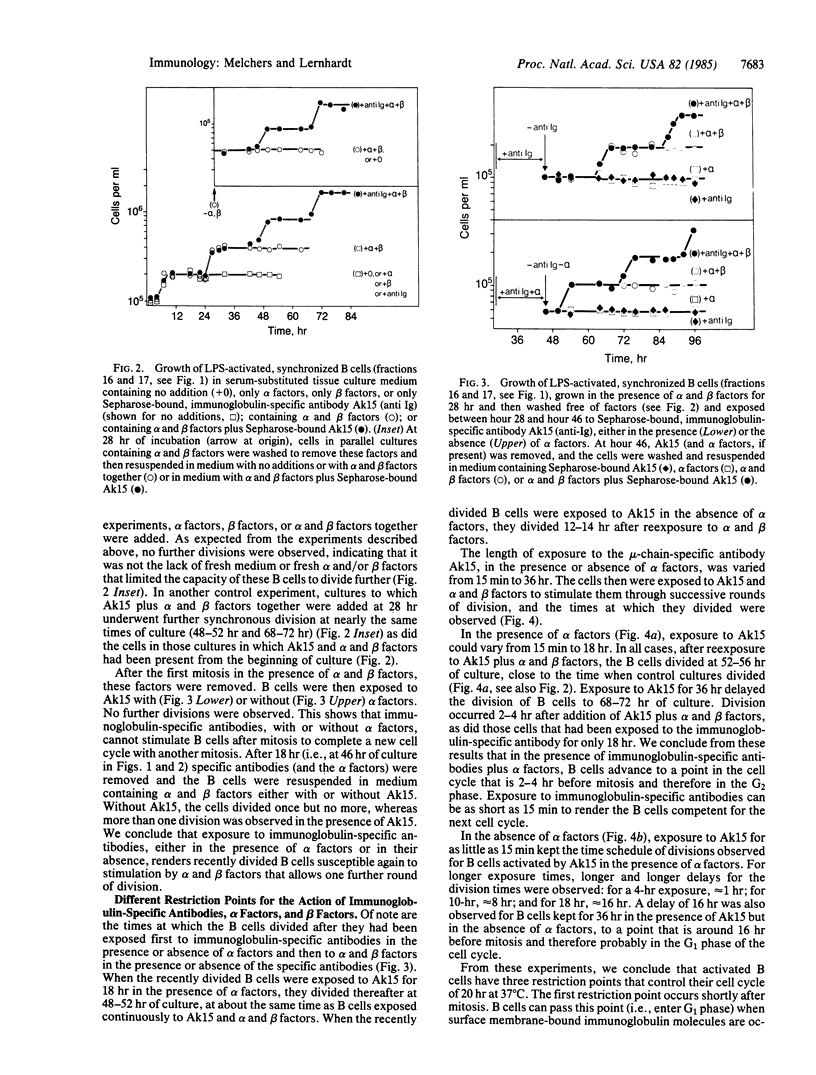
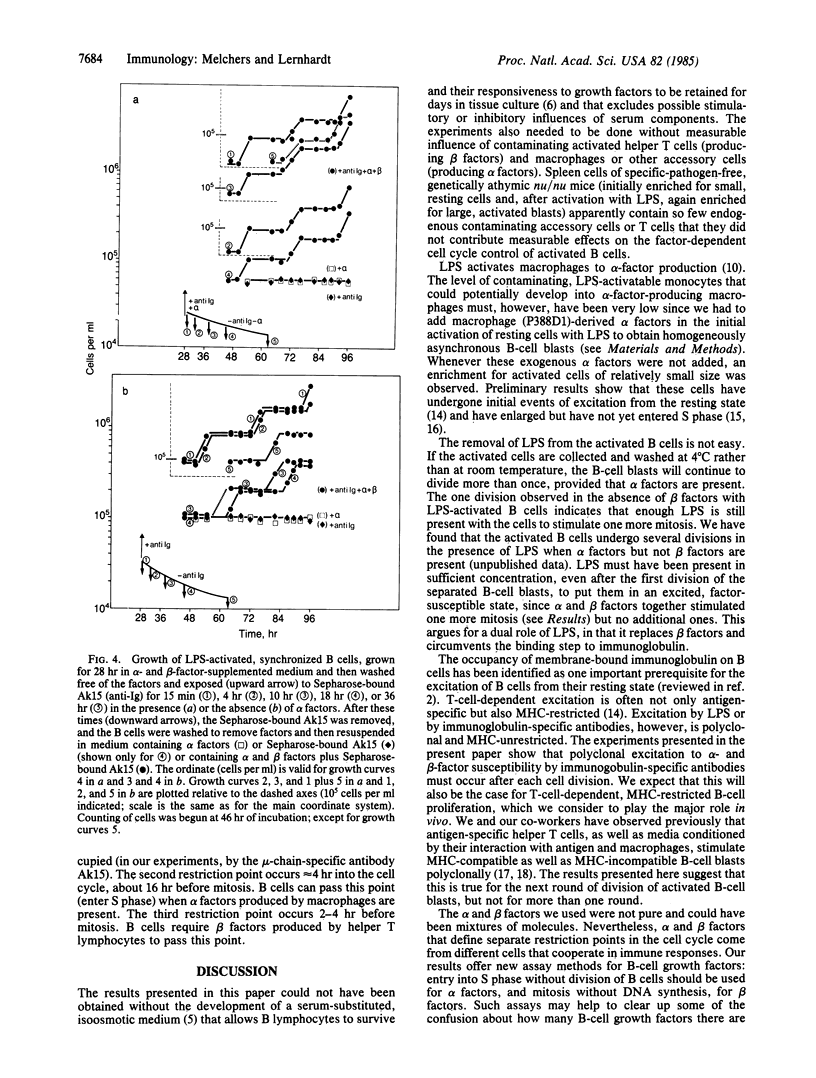
The cell cycle of activated B lymphocytes was found to be controlled by three restriction points. The first occurs immediately after mitosis and was found to be controlled by the binding of Sepharose-bound, immunoglobulin-specific antibodies to surface membrane-bound immunoglobulin. Exposure to this stimulus as short as 15 min or as long as 36 hr allowed B cells to move into the G1 phase up to the next restriction point. The second restriction point was observed to be approximately equal to 4 hr after mitosis, in the G1 phase of the cycle and 3-4 hr before the B cells entered S phase, and was found to be controlled by alpha-type B-cell growth factors produced by the P388D1 macrophage line. A third restriction point occurs in the G2 phase, 2-4 hr before mitosis, and is apparently controlled by beta-type B-cell growth factors that are likely to be produced by helper T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Lernhardt W., Melchers F. Clonal growth and maturation to immunoglobulin secretion in vitro of every growth-inducible B lymphocyte. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Coutinho A., Melchers F. Mitogen-activated B-cell blasts reactive to more than one mitogen. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):553–564. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Schreier M. H., Melchers F. T-cell-dependent B-cell stimulation is H-2 restricted and antigen dependent only at the resting B-cell level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1612–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Sjöberg O., Möller G. Induction of immunoglobulin and antibody synthesis in vitro by lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Aug;2(4):349–353. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Smith G. L. Effects of withdrawal of a mitogenic stimulus on progression of fibroblasts into S phase: differences between serum and purified multiplication-stimulating activity. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):441–448. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel C., Melchers F. Requirement for macrophages or for macrophage- or T cell-derived factors in the mitogenic stimulation of murine B lymphocytes by lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jul;13(7):528–533. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel C., Melchers F. The synergism of accessory cells and of soluble alpha-factors derived from them in the activation of B cells to proliferation. Immunol Rev. 1984 Apr;78:51–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Kung J. T., Paul W. E. Regulation of growth and proliferation in B cell subpopulations. Immunol Rev. 1982;64:161–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Hess B. Cyclic-AMP-controlled oscillations in suspended Dictyostelium cells: their relation to morphogenetic cell interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2118–2122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönvik K. O., Andersson J. The role of T cell growth stimulating factors in T cell triggering. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:35–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert L. J., Iscove N. N. Partial replacement of serum by selenite, transferrin, albumin and lecithin in haemopoietic cell cultures. Nature. 1976 Oct 14;263(5578):594–595. doi: 10.1038/263594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Baldwin J. H., Kiernan J. A. Control of growth of a tumor cell by linoleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3976–3978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Kiernan J. A. Control of the initiation of DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells: low-molecular weight nutrients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2942–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Paul W. E. Regulation of B-cell growth and differentiation by soluble factors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:307–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Melchers F. Complete replacement of serum by albumin, transferrin, and soybean lipid in cultures of lipopolysaccharide-reactive B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):923–933. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Wharton W., van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and somatomedin C regulate G1 progression in competent BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leptin M., Potash M. J., Grützmann R., Heusser C., Shulman M., Köhler G., Melchers F. Monoclonal antibodies specific for murine IgM I. Characterization of antigenic determinants on the four constant domains of the mu heavy chain. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jun;14(6):534–542. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren A., Westermark B., Pontén J. Serum stimulation of stationary human glia and glioma cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 15;95(2):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90556-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren A., Westermark B. Subdivision of the G1 phase of human glia cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Andersson J. B cell activation: three steps and their variations. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):713–720. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90407-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Andersson J., Corbel C., Leptin M., Lernhardt W., Gerhard W., Zeuthen J. Regulation of B lymphocyte replication and maturation. J Cell Biochem. 1982;19(4):315–332. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240190403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Phillips R. A. Separation of cells by velocity sedimentation. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Jun;73(3):191–201. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H., Steiner R. Reversible alterations in the mitotic cycle of chick embryo cells in various states of growth regulation. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Apr;85(2 Pt 1):261–270. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Andersson J., Lernhardt W., Melchers F. Antigen-specific T-helper cells stimulate H-2-compatible and H-2-incompatible B-cell blasts polyclonally. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):194–203. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stambrook P. J., Velez C. Reversible arrest of Chinese hamster V79 cells in G2 by dibutytyl AMP. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Apr;99(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90679-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Stimulation by serum of multiplication of stationary chicken cells. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Oct;78(2):161–170. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobey R. A. Production and characterization of mammalian cells reversibly arrested in G1 by growth in isoleucine-deficient medium. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;6:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vindelov L. L. Flow microfluorometric analysis of nuclear DNA in cells from solid tumors and cell suspensions. A new method for rapid isolation and straining of nuclei. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1977 Aug 10;24(3):227–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton W., Van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Inhibition of BALB/c-3T3 cells in late G1: commitment to DNA synthesis controlled by somatomedin C. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Apr;107(1):31–39. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041070105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



