Abstract
A 36-year-old woman was diagnosed with anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) by excisional biopsy of a left frontal skin lesion. During the first cycle of chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone), the patient complained of right ocular pain and inflammation. Cytologic examination using aqueous humor revealed atypical lymphocytes, suggesting intraocular ALCL involvement. Acute angle closure developed in the anterior chamber due to rapid progression of ALCL, causing pupillary block. Laser and surgical interventions were attempted but failed to relieve the pupillary block. Finally, radiation therapy resolved the pupillary block to restore the anterior chamber and normalize intraocular pressure. This is the first case in the English literature of ALCL involving the iris to cause acute secondary angle closure.
Keywords: Acute angle closure, Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, Eye, Radiotherapy
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a newly introduced T-cell lymphoma that is responsible for approximately 3% of all non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) in adults and between 10% to 30% of NHL in children [1-3]. It is a mature T-cell lymphoma with expression of 1 or more T-cell antigens in addition to the characteristic CD30 staining. ALCL presents clinically as a systemic or localized cutaneous growth.
Both primary and metastatic lymphomas may involve intraocular structures [4]. The most common intraocular lymphoma is B-cell primary intraocular lymphoma (PIOL), which is a subset of the primary central nervous system lymphomas (PCNSL) [5,6]. Approximately 10% to 25% of PCNSL presents as PIOL. Approximately 60% to 80% of patients with PIOL develop central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma [7]. The T-cell type of PIOL is very rare, and only three published cases of primary T-cell PIOL were identified at the time this report was written [6,7]. Most cases of intraocular T-cell lymphoma are an extension of primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma or systemic T-cell lymphoma [6,8,9]. In this article, we report a case of anterior eye involvement with a rare variant of T-cell lymphoma, ALCL.
Case Report
This case report followed the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the institutional review board of Dongguk University, Ilsan Hospital.
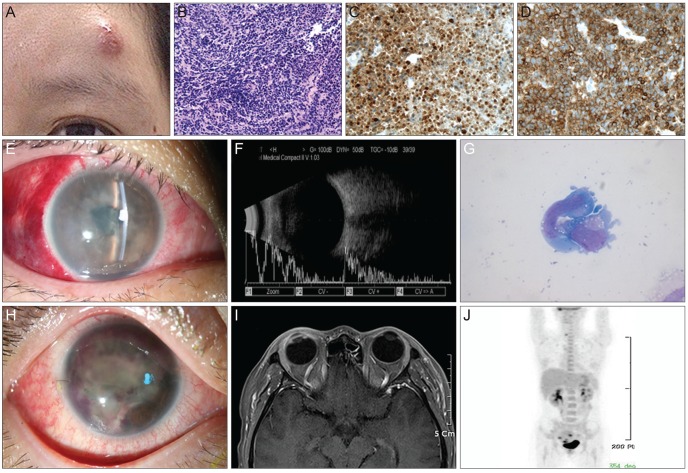
A 36-year-old woman presented with multiple facial masses in the left submandibular and forehead area (Fig. 1A). Incisional biopsy of the forehead lesion revealed ALCL with positivity for CD30, CD3, and ALK (Fig. 1B-1D). No evidence of other body part involvement was found on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), or cerebrospinal fluid analysis. With a diagnosis of ALCL involving skin only, the patient received 1 cycle of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone) chemotherapy. On day 5 after chemotherapy, the patient complained of conjunctival injection, ocular pain, and blurred vision in the right eye. Ophthalmic examination detected a mild inflammatory reaction in the anterior chamber with normal visual acuity, intraocular pressure (11 mmHg), and fundus findings in the right eye. Topical fluorometholone (0.1%) was prescribed to control inflammation. However, the symptoms rapidly aggravated. On the second visit after 2 days, the patient's right eye demonstrated severe inflammatory reaction with dense fibrin clots around the pupillary margin in the anterior chamber with significant corneal edema (Fig. 1E). No fundus details were observed and ocular ultrasonography revealed a relatively clear posterior segment (Fig. 1F). Because the complete blood count showed reduced white blood cell count of 1.61 × 103/µL (normal range, 4.0 to 10 × 103/µL) with an absolute neutrophil count of 580 (normal range, 1,500 to 7,700), the presumed diagnosis was endogenous endophthalmitis or neoplastic masquerade syndrome. Cytologic examination and aqueous humor culture were simultaneously conducted with vancomycin (1 mg/0.1 mL), ceftazidime (2 mg/0.1 mL), and dexamethasone (250 µg/0.1 mL) intravitreal injections. A 0.5% moxifloxacin ophthalmic solution was applied every two hours. Vancomycin was administered in travenously. A cytospin smear of aqueous humor aspiration revealed atypical lymphocytes (Fig. 1G). On the next day of aqueous humor culture, acute angle closure developed (intraocular pressure rose to 40 mmHg) due to pupillary block by dense fibrin (Fig. 1H). Tissue plasminogen activator (25 µg/0.05 mL) was injected into the anterior chamber to reduce fibrin and open the aqueous passage, but this therapy failed. The increased intraocular pressure (IOP) (over 40 mmHg) was uncontrollable despite maximum tolerated drug therapy including intravenous mannitol, anti-glaucoma ophthalmic solutions, and oral acetazolamide. Blood and aqueous humor cultures showed no bacterial growth. Laser iridotomy was attempted to relieve the pupillary block, but fibrin materials closed the opening within one day. Surgical removal of dense fibrotic membrane was attempted but failed due to recurrent bleeding and fibrotic membranes. MRI showed focal enhancement of the iris, ciliary body, and anterior chamber without posterior segment involvement (Fig. 1I). A PET scan revealed increased fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) metabolism in the right eye, right thyroid, and uterine wall (Fig. 1J). Oncologists recommended localized radiation therapy to the right orbit. After 2 consecutive radiation therapy sessions with 3 Gy each, intraocular pressure normalized to 19 mmHg, the anterior chamber deepened, and fibrin material gradually disappeared. After 30 Gy of radiation therapy in total, the patient's best-corrected visual acuity was restored to 20 / 25 with an IOP of 11 mmHg without glaucoma medication (Fig. 2). No evidence of tumor recurrence was detected at 18 months after radiation therapy.
Fig. 1.
(A) Skin mass is visible in left frontal area. On microscopic examination, excisional biopsy reveals tissue heavily infiltrated by small lymphocytic cells (B) (H&E, ×40). Immunohistochemistry reveals infiltrating cells that strongly express CD3 (C) (×200) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (D) (×200). (E) Slit lamp photograph of right eye on second visit. Significant inflammation with fibrin reaction is visible in anterior chamber. Subconjunctival hemorrhage is present. (F) Ocular ultrasonography demonstrates relatively clear posterior segment, suggesting that inflammation is localized in the anterior eye. (G) Cytospin smear shows atypical cells harboring a moderate amount of cytoplasm and eccentric kidney-shaped nuclei (Wright stain, ×1,000). (H) During treatment course, acute angle closure due to pupillary block by dense fibrin clots is noted. (I) Magnetic resonance imaging shows focal enhancement of the iris and ciliary body without posterior segment involvement. (J) Positron emission tomography scan shows increased fluorodeoxyglucose metabolism in the right eye surface, right thyroid, and uterine wall.
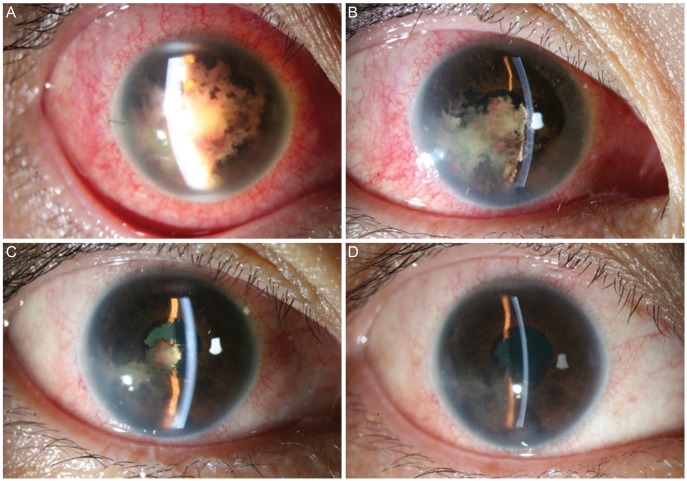
Fig. 2.
Changes in silt lamp findings on days 6 (A), 9 (B), 11 (C), and 14 (D) after radiotherapy. Gradual regression of tumor material and fibrin reaction is noted.
Discussion
The most common manifestation of intraocular lymphoma involvement is uveitis that is refractory to corticosteroid treatment. However, lymphoma involving ocular or periocular structures can occasionally manifest as secondary glaucoma [4,5,10]. Various types of glaucoma can occur, including open angle, closed angle, or neovascular [5,11-14]. In a recent review by Mashayekhi et al. [10], four out of 14 cases of lymphoma with iris involvement manifested with elevated intraocular pressure. The current case manifested as acute angle closure related lymphoma infiltrating the iris and anterior chamber.
Intraocular lymphoma is one of the most challenging masquerade syndromes [4]. Usually, diseases mimicking intraocular lymphoma respond poorly to routine corticosteroid treatment. Many infectious and non-infectious conditions should be considered in the differential diagnosis. Endogenous endophthalmitis should be ruled out first in severely immune compromised states due to systemic chemotherapy [15-17]. Viral retinitis, such as acute retinal necrosis syndrome, retinal toxoplasmosis, retinal tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, and cytomegalovirus retinitis may all mimic intraocular lymphoma [18]. Syphilitic retinitis and Whipple disease (caused by Tropheryma whipplei) can rarely manifest as intraocular inflammation mimicking intraocular lymphoma [19]. Therefore, the correct and early diagnosis of intraocular lymphoma is challenging. For a definite diagnosis of lymphoma, the malignant cells must be verified. In cases with anterior segment involvement, aqueous fluid analysis using cytospin is an effective and minimally invasive technique alternative to tissue biopsy [20].
Imaging methods such as computed tomography and MRI are necessary to rule out CNS lesions. PET using FDG is a useful method for the diagnosis and staging of lymphoma involving eye or brain [21]. Lesions generally show hot uptake of FDG in PET. This imaging modality is also useful for detecting any residual or recurrent lymphoma lesions within the eye.
Due to the high sensitivity of lymphoma cells to radiation, eye and CNS radiotherapy are the principal forms of treatment for intraocular lymphoma. However, initial remission rates are high, and most patients suffer from recurrences and die. The median survival duration for this condition is 12 to 24 months [22]. Cataract formation, corneal epitheliopathy, maculopathy, vitreous hemorrhage, optic atrophy, neovascular glaucoma, and sterile endophthalmitis are all complications experienced by these patients [4]. Systemic chemotherapy to control intraocular lymphoma is principally limited by poor drug penetration due to blood-ocular barriers. Intraocular lymphoma can be treated using systemic agents such as methotrexate, cytarabine, ifosfamide, and trofosfamide, all of which can penetrate the blood-ocular barrier in cytostatic concentrations. These drugs have been investigated and showed effectiveness [23-26]. A combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is also applicable [27].
In summary, we presented a rare case of ALCL involving the anterior segment. The anterior chamber rapidly progressed to develop pupillary block and acute angle closure. Although lymphoma infiltration localized to the anterior segment is relatively rare, it should be considered in lymphoma patients presenting with anterior segment inflammation of unknown origin.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (NRF 2010-0002532).
Footnotes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
- 1.Fornari A, Piva R, Chiarle R, et al. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: one or more entities among T-cell lymphoma? Hematol Oncol. 2009;27:161–170. doi: 10.1002/hon.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Inghirami G, Pileri SA European T-Cell Lymphoma Study Group. Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2011;28:190–201. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2011.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Medeiros LJ, Elenitoba-Johnson KS. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;127:707–722. doi: 10.1309/r2q9ccuvtlrycf3h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Coupland SE, Damato B. Understanding intraocular lymphomas. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2008;36:564–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9071.2008.01843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Coupland SE, Heimann H, Bechrakis NE. Primary intraocular lymphoma: a review of the clinical, histopathological and molecular biological features. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2004;242:901–913. doi: 10.1007/s00417-004-0973-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Coupland SE, Anastassiou G, Bornfeld N, et al. Primary intraocular lymphoma of T-cell type: report of a case and review of the literature. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005;243:189–197. doi: 10.1007/s00417-004-0890-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Levy-Clarke GA, Greenman D, Sieving PC, et al. Ophthalmic manifestations, cytology, immunohistochemistry, and molecular analysis of intraocular metastatic T-cell lymphoma: report of a case and review of the literature. Surv Ophthalmol. 2008;53:285–295. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2008.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kohno T, Uchida H, Inomata H, et al. Ocular manifestations of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. A clinicopathologic study. Ophthalmology. 1993;100:1794–1799. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(13)31398-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shibata K, Shimamoto Y, Nishimura T, et al. Ocular manifestations in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 1997;74:163–168. doi: 10.1007/s002770050276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mashayekhi A, Shields CL, Shields JA. Iris involvement by lymphoma: a review of 13 cases. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2013;41:19–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9071.2012.02811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shields CL, Shields JA, Shields MB, Augsburger JJ. Prevalence and mechanisms of secondary intraocular pressure elevation in eyes with intraocular tumors. Ophthalmology. 1987;94:839–846. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(87)33537-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kim WI, Larar JG, Cheson BD, et al. Resolution of lymphoma-associated open-angle glaucoma by rituximab. J Glaucoma. 2011;20:398–400. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e3181efb334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Matsui N, Kamao T, Azumi A. Case of metastatic intraocular malignant lymphoma with neovascular glaucoma. Nihon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2005;109:434–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Berthold S, Kottler UB, Frisch L, et al. Secondary glaucoma in hyphema, hypopyon, iris prominence and iris hyperemia. Ophthalmologe. 2005;102:290–292. doi: 10.1007/s00347-003-0988-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Patel AS, Hemady RK, Rodrigues M, et al. Endogenous Fusarium endophthalmitis in a patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994;117:363–368. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)73147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gupta SR, Agnani S, Tehrani S, et al. Endogenous Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Streptococcus) endophthalmitis as a presenting sign of precursor T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128:384–385. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2009.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dave VP, Majji AB, Suma N, Pappuru RR. A rare case of Aspergillus terreus endogenous endophthalmitis in a patient of acute lymphoid leukemia with good clinical outcome. Eye (Lond) 2011;25:1094–1096. doi: 10.1038/eye.2011.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sen HN, Bodaghi B, Hoang PL, Nussenblatt R. Primary intraocular lymphoma: diagnosis and differential diagnosis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2009;17:133–141. doi: 10.1080/09273940903108544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Drancourt M, Raoult D, Lepidi H, et al. Culture of Tropheryma whippelii from the vitreous fluid of a patient presenting with unilateral uveitis. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:1046–1047. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-139-12-200312160-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Finger PT, Papp C, Latkany P, et al. Anterior chamber paracentesis cytology (cytospin technique) for the diagnosis of intraocular lymphoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006;90:690–692. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.087346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Matsuo T, Ichimura K, Ichikawa T, et al. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography after immunocytochemical and clonal diagnosis of intraocular lymphoma with vitrectomy cell blocks. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2009;49:77–87. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.49.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Margolis L, Fraser R, Lichter A, Char DH. The role of radiation therapy in the management of ocular reticulum cell sarcoma. Cancer. 1980;45:688–692. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800215)45:4<688::aid-cncr2820450412>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jahnke K, Thiel E, Bechrakis NE, et al. Ifosfamide or trofosfamide in patients with intraocular lymphoma. J Neurooncol. 2009;93:213–217. doi: 10.1007/s11060-008-9761-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.De Smet MD, Stark-Vancs V, Kohler DR, et al. Intraocular levels of methotrexate after intravenous administration. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996;121:442–444. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70444-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Batchelor TT, Kolak G, Ciordia R, et al. High-dose methotrexate for intraocular lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:711–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.De Smet MD, Vancs VS, Kohler D, et al. Intravitreal chemotherapy for the treatment of recurrent intraocular lymphoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1999;83:448–451. doi: 10.1136/bjo.83.4.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tempescul A, Pradier O, Marianowski-Cochard C, et al. Combined therapy associating systemic platinum-based chemotherapy and local radiotherapy into the treatment of primary intraocular lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2011;90:1117–1118. doi: 10.1007/s00277-010-1139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]