Abstract
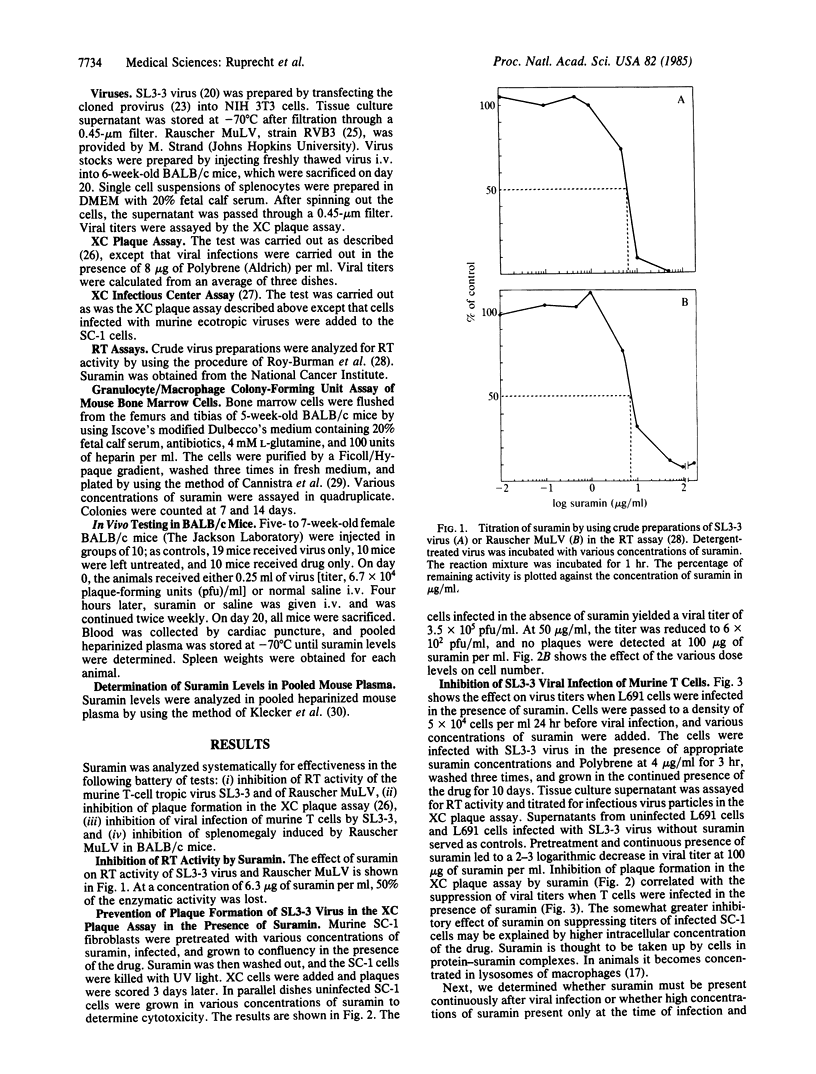
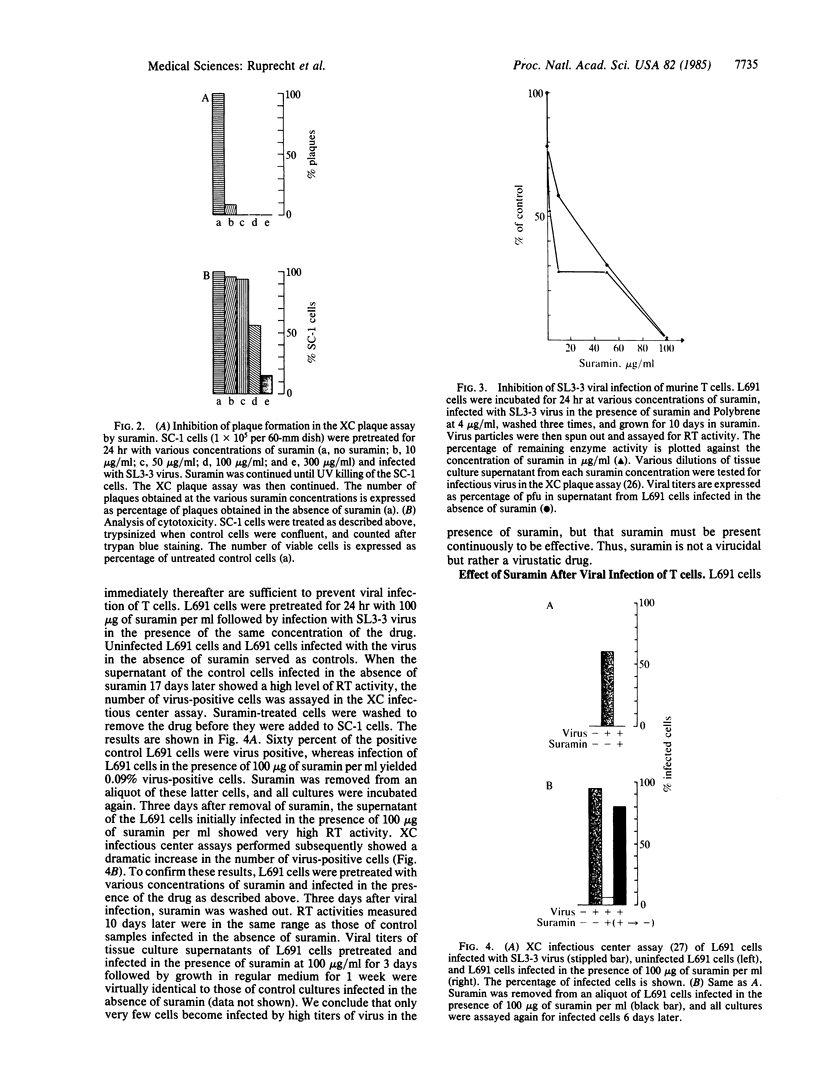
Retroviral propagation crucially depends on reverse transcriptase (RT). We have developed murine models to test the biological effectiveness of the RT inhibitor suramin. The drug was active in our assay system, which includes (i) inhibition of RT activity in the murine T-cell tropic virus SL3-3 and Rauscher murine leukemia virus (MuLV), (ii) inhibition of plaque formation in the XC plaque assay, (iii) inhibition of viral infection of cultured murine T cells, and (iv) inhibition of splenomegaly induced by Rauscher MuLV in BALB/c mice. Suramin decreases viral titers significantly, even if started 36 hr after infection. Viral titers and number of infected cells increased to control levels after removal of the drug. BALB/c mice treated i.v. with 40 mg of suramin per kg twice per week following infection with Rauscher MuLV showed a 35% decrease in splenomegaly. Suramin is an active antiretroviral agent whose effect on retroviral propagation is reversible. We conclude that it acts as a virustatic drug and that long-term administration of suramin will be necessary if it is used for experimental treatment of human retroviral illnesses such as the acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner W. A., Takatsuki K., Gallo R. C. Human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus and adult T-cell leukemia. JAMA. 1983 Aug 26;250(8):1074–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn P. A., Jr, Schechter G. P., Jaffe E., Blayney D., Young R. C., Matthews M. J., Blattner W., Broder S., Robert-Guroff M., Gallo R. C. Clinical course of retrovirus-associated adult T-cell lymphoma in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 4;309(5):257–264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308043090501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIRIGOS M. A. STUDIES WITH THE MURINE LEUKEMOGENIC RAUSCHER VIRUS. 3. AN IN VIVO ASSAY FOR ANTI-VIRAL AGENTS. Cancer Res. 1964 Jul;24:1035–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannistra S. A., Daley J. F., Larcom P., Griffin J. D. Expression of Ia antigens on myeloid progenitor cells in chronic myeloid leukemia: direct analysis using partially purified colony-forming cells. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):414–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catovsky D., Greaves M. F., Rose M., Galton D. A., Goolden A. W., McCluskey D. R., White J. M., Lampert I., Bourikas G., Ireland R. Adult T-cell lymphoma-leukaemia in Blacks from the West Indies. Lancet. 1982 Mar 20;1(8273):639–643. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E. Suramin: a potent inhibitor of the reverse transcriptase of RNA tumor viruses. Cancer Lett. 1979 Nov;8(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(79)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C. Human T-cell leukemia (lymphotropic) retroviruses and their causative role in T-cell malignancies and acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Cancer. 1985 May 15;55(10):2317–2323. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850515)55:10<2317::aid-cncr2820551003>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Schroff R., Schanker H. M., Weisman J. D., Fan P. T., Wolf R. A., Saxon A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and mucosal candidiasis in previously healthy homosexual men: evidence of a new acquired cellular immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1425–1431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawking F. Suramin: with special reference to onchocerciasis. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1978;15:289–322. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60486-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalyanaraman V. S., Sarngadharan M. G., Nakao Y., Ito Y., Aoki T., Gallo R. C. Natural antibodies to the structural core protein (p24) of the human T-cell leukemia (lymphoma) retrovirus found in sera of leukemia patients in Japan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1653–1657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Crowther R., Klimenko S., Haseltine W. Molecular cloning of a highly leukemogenic, ecotropic retrovirus from an AKR mouse. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):943–951. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.943-951.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Haseltine W. A. Localization of the leukemogenic determinants of SL3-3, an ecotropic, XC-positive murine leukemia virus of AKR mouse origin. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):317–328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.317-328.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Michelis M. A., Greene J. B., Onorato I., Stouwe R. A., Holzman R. S., Wormser G., Brettman L., Lange M., Murray H. W. An outbreak of community-acquired Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: initial manifestation of cellular immune dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1431–1438. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Popovic M., Yarchoan R., Matsushita S., Gallo R. C., Broder S. Suramin protection of T cells in vitro against infectivity and cytopathic effect of HTLV-III. Science. 1984 Oct 12;226(4671):172–174. doi: 10.1126/science.6091268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen F. S., Crowther R. L., Tenney D. Y., Reimold A. M., Haseltine W. A. Novel leukaemogenic retroviruses isolated from cell line derived from spontaneous AKR tumour. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):167–170. doi: 10.1038/292167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUSCHER F. J. A virus-induced disease of mice characterized by erythrocytopoiesis and lymphoid leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Sep;29:515–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivin B. E., Monroe J. M., Hubschman B. P., Thomas P. A. AIDS outcome: a first follow-up. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 27;311(13):857–857. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409273111314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Guroff M., Nakao Y., Notake K., Ito Y., Sliski A., Gallo R. C. Natural antibodies to human retrovirus HTLV in a cluster of Japanese patients with adult T cell leukemia. Science. 1982 Feb 19;215(4535):975–978. doi: 10.1126/science.6760397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy-Burman P., Dougherty M., Pal B. K., Charman H. P., Klement V., Gardner M. B. Assay for type C virus in mouse sera based on particulate reverse transcriptase activity. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):1107–1110. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.1107-1110.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Harper M. E., Hahn B. H., Epstein L. G., Gajdusek D. C., Price R. W., Navia B. A., Petito C. K., O'Hara C. J., Groopman J. E. HTLV-III infection in brains of children and adults with AIDS encephalopathy. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2981429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeves R. A., Strand M., August J. T. Structural proteins of mammalian oncogenic RNA viruses: murine leukemia virus neutralization by antisera prepared against purified envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):187–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.187-189.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainin Z., Wernicke D., Ungar-Waron H., Essex M. Suppression of the humoral antibody response in natural retrovirus infections. Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):858–859. doi: 10.1126/science.6302837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


