Abstract
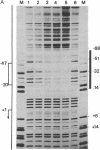
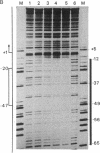
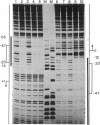
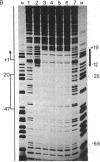
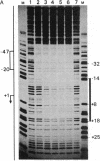
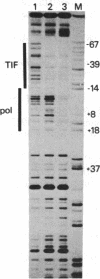
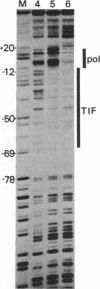
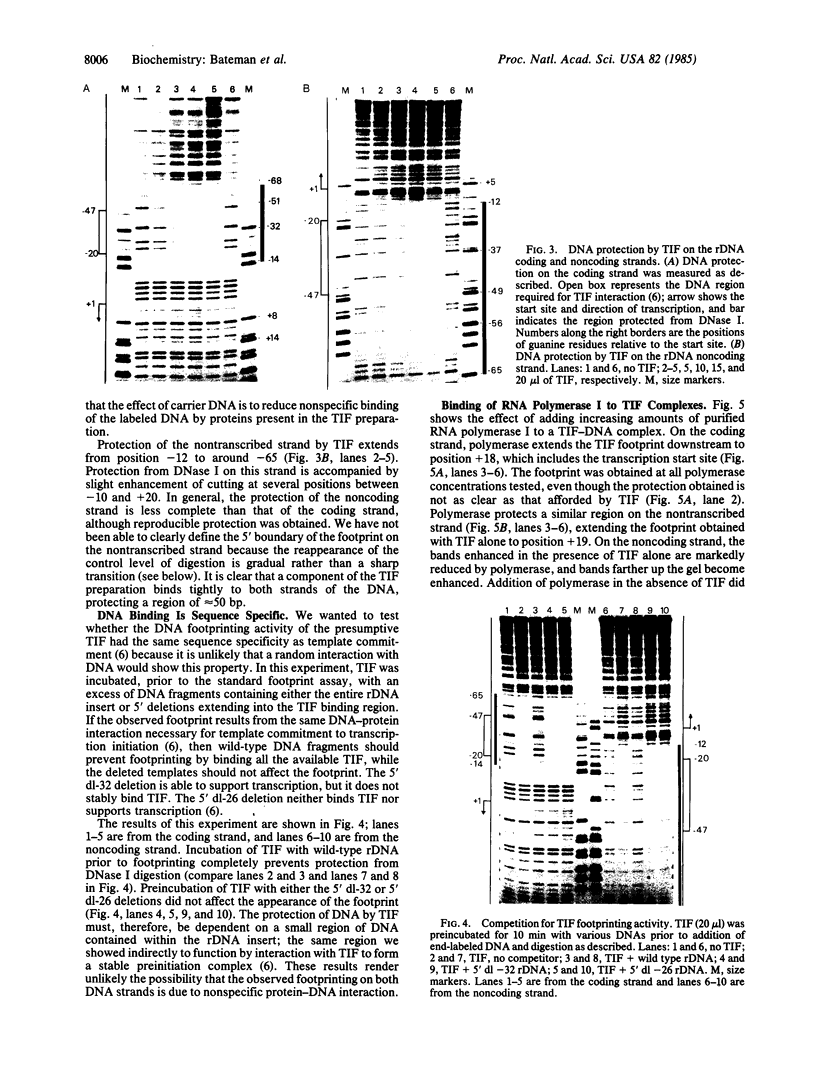
The binding of a species-specific transcription initiation factor (TIF) and purified RNA polymerase I to the promoter region of the 39S ribosomal RNA gene from Acanthamoeba were studied by using DNase I "footprinting." Conditions were chosen such that the footprints obtained could be correlated with the transcriptional activity of the TIF-containing fractions used and that the labeled DNA present would itself serve as a template for transcription. The transcription factor binds upstream from the transcription start site, protecting a region extending from around -14 to -67 on the coding strand, and -12 to -69 on the noncoding strand. The protein that binds to DNA within this region can be competed out by using wild-type promoters but not by using mutants which do not stably bind the factor. RNA polymerase I can form a stable complex in the presence of DNA and transcription factor, allowing footprinting of the complete transcription initiation complex. RNA polymerase I extends the protected region obtained with TIF alone to around +18 on the coding strand, and to +20 on the noncoding strand. This region is not protected by polymerase I in the absence of TIF. The close apposition of the regions protected by TIF and polymerase provides evidence that accurate transcription of the ribosomal gene may be achieved through protein-protein contacts as well as through DNA-protein interactions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieker J. J., Roeder R. G. Physical properties and DNA-binding stoichiometry of a 5 S gene-specific transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6158–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh A. H., Gokal P. K., Lawther R. P., Thompson E. A., Jr Glucocorticoid inhibition of initiation of transcription of the DNA encoding rRNA (rDNA) in lymphosarcoma P1798 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):718–721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA: glucocorticoid effects upon initiation and elongation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3357–3369. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cizewski V., Sollner-Webb B. A stable transcription complex directs mouse ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7043–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M., Reeder R. H. DNase I footprinting shows three protected regions in the promoter of the rRNA genes of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):313–319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. D., Clarkson S. G., Tocchini-Valentini G. Transcription initiation of eucaryotic transfer RNA genes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida C. T., Kownin P., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription: proteins and DNA sequences involved in preinitiation complex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1668–1672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J. Transcription of Xenopus 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):101–105. doi: 10.1038/295101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küntzel H., Piechulla B., Hahn U. Consensus structure and evolution of 5S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):893–900. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Species-specific rDNA transcription is due to promoter-specific binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paule M. R., Iida C. T., Perna P. J., Harris G. H., Brown Shimer S. L., Kownin P. Faithful initiation of ribosomal RNA transcription from cloned DNA by purified RNA polymerase I. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4167–4172. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., Brown D. D. Formation and stability of the 5 S RNA transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2483–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerville J. RNA polymerase I promoters and transcription factors. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):189–190. doi: 10.1038/310189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler S. R., Duester G. L., D'Alessio J. M., Paule M. R. A rapid and facile procedure for the preparation of RNA polymerase I from Acanthamoeba castellanii. Purification and subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4669–4675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. Protein contacts for promoter location in eukaryotes. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):755–755. doi: 10.1038/303755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandelt C., Grummt I. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes is a prerequisite for ribosomal DNA transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3795–3809. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]