Abstract
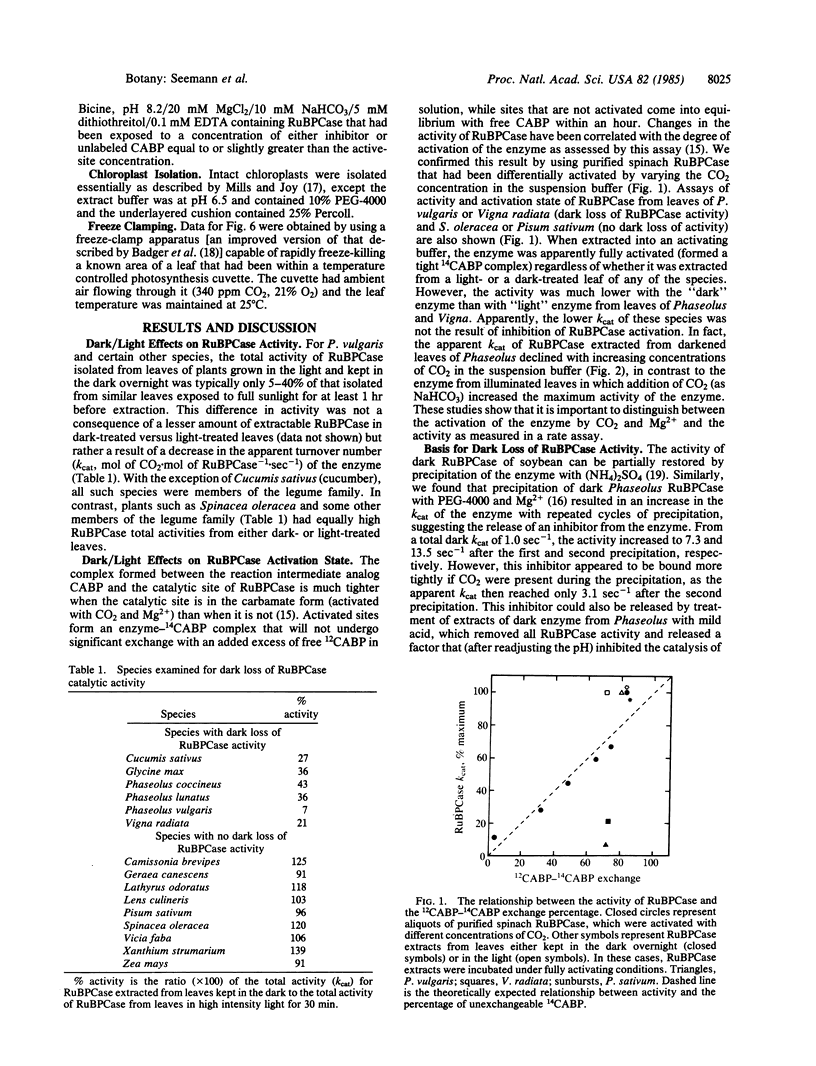
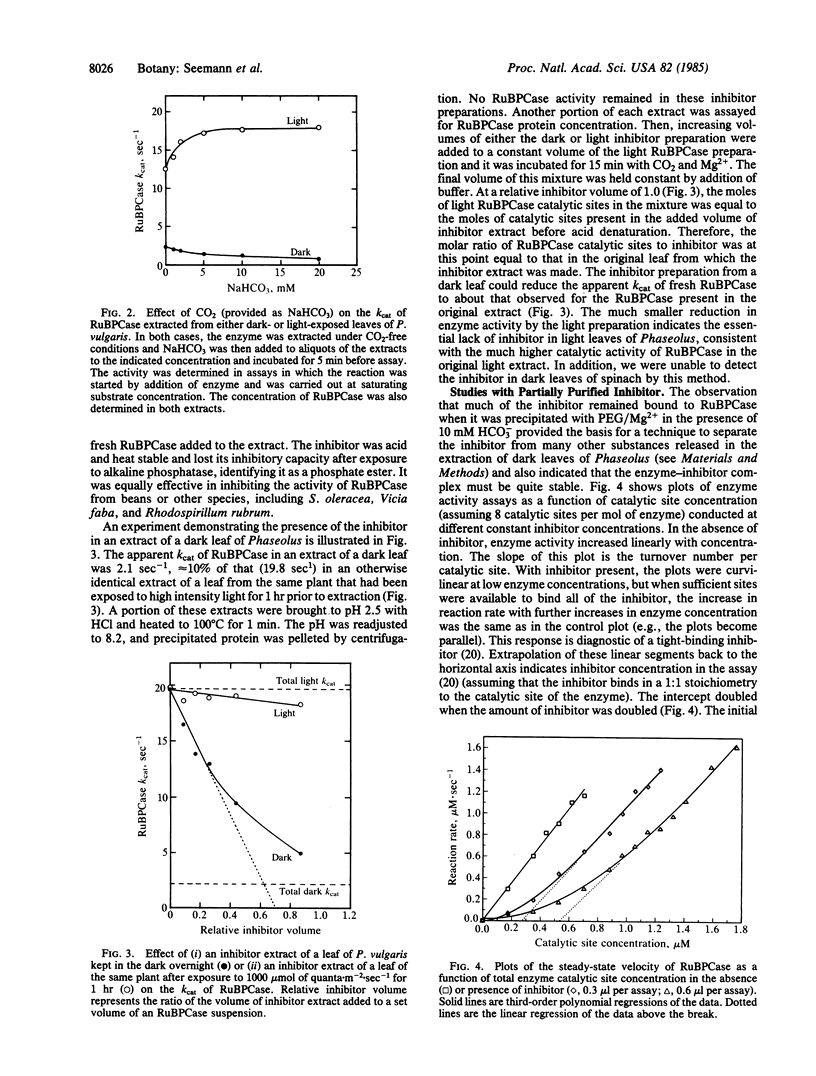
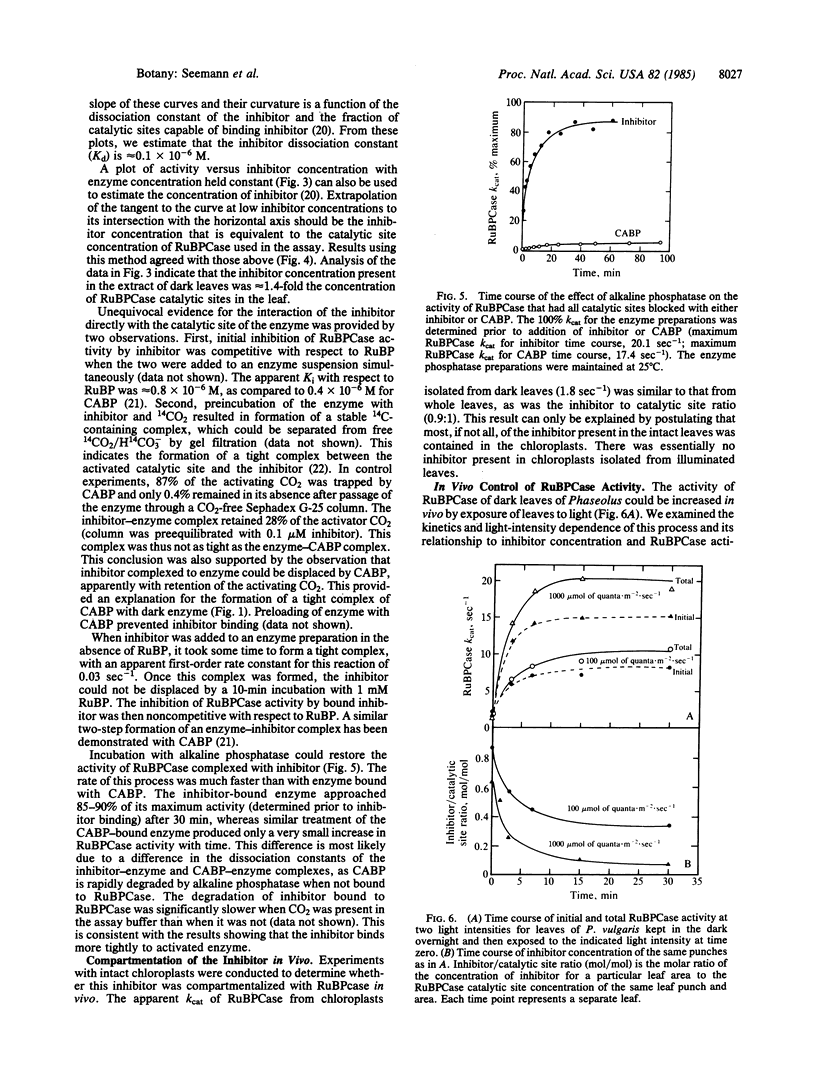
The activity of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase [RuBPCase; 3-phospho-D-glycerate carboxylyase (dimerizing), EC 4.1.1.39] in leaf extracts of a number of species kept in the dark overnight was found to be very low. This was not the result of a change in the activation state or in the amount of enzyme that could be extracted from “dark” leaves. Rather, in Phaseolus vulgaris it was due to an inhibitor of catalysis that occupied the catalytic site of the enzyme. This inhibitor was compartmentalized in the chloroplast and its maximum concentration in both dark leaves and in intact chloroplasts made from such leaves was slightly in excess of the RuBPCase catalytic site concentration. The inhibitor (a phosphate ester) was bound preferentially to the activated form of the enzyme, apparently functioning as a positive effector of activation. Treatment of the enzyme-inhibitor complex in vitro with alkaline phosphatase could restore RuBPCase activity. In vivo, both the initial rate of disappearance and the final concentration of inhibitor in intact leaves was found to vary with light intensity, and these changes could account for observed light-dependent changes in RuBPCase activity, indicating that light modulation of inhibitor concentration controlled RuBPCase activity. Recovery of activity in vivo could be inhibited by 3-(3′,4′,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea.
Keywords: photosynthesis, enzyme regulation, effector regulation
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badger M. R., Lorimer G. H. Interaction of sugar phosphates with the catalytic site of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2219–2225. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahr J. T., Jensen R. G. Activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in intact chloroplasts by CO2 and light. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 15;185(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by substrates and other metabolites: further evidence for several types of binding sites. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):720–726. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. R., Seemann J. R. Differences between Wheat Genotypes in Specific Activity of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase and the Relationship to Photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):759–765. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall N. P., Pierce J., Tolbert N. E. Formation of a carboxyarabinitol bisphosphate complex with ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and theoretical specific activity of the enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch A. L., Jensen R. G. Regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from tobacco: changes in pH response and affinity for CO2 and Mg2+ induced by chloroplast intermediates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):587–594. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurry S. D., Pierce J., Tolbert N. E., Orme-Johnson W. H. On the mechanism of effector-mediated activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6623–6628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Lorimer G. H. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:507–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J., Tolbert N. E., Barker R. Interaction of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase with transition-state analogues. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):934–942. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann J. R., Badger M. R., Berry J. A. Variations in the Specific Activity of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase between Species Utilizing Differing Photosynthetic Pathways. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):791–794. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servaites J. C. Binding of a Phosphorylated Inhibitor to Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase during the Night. Plant Physiol. 1985 Aug;78(4):839–843. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. E., Terry N. Limiting Factors in Photosynthesis: V. Photochemical Energy Supply Colimits Photosynthesis at Low Values of Intercellular CO(2) Concentration. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):82–86. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu C. V., Allen L. H., Bowes G. Effects of Light and Elevated Atmospheric CO(2) on the Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase Activity and Ribulose Bisphosphate Level of Soybean Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):729–734. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu J. C., Allen L. H., Bowes G. Dark/Light modulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in plants from different photosynthetic categories. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):843–845. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. W., Morrison J. F. The kinetics of reversible tight-binding inhibition. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:437–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


