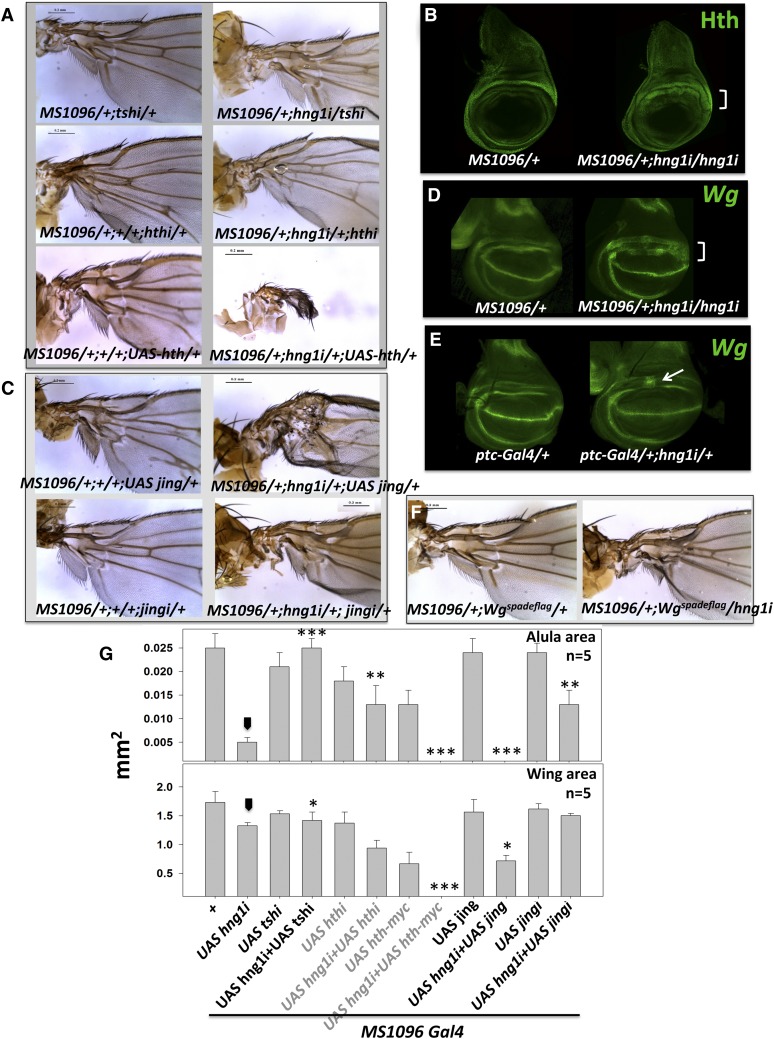
Figure 4.
hinge genes are part of the GRN that patterns the wing hinge. (A) A knockdown of tsh and hth in the MS1096/+; hng1i/+ animal rescues the hng1 phenotype, whereas overexpression of hth enhances the hng1 phenotype severely. The RNAi and the UAS lines used to alter transcript levels for hth and tsh, by themselves, have mild hypomorphic effects. (B) Hth is broadened/derepressed in and around the gap region when hng1 expression is reduced in the MS1096-Gal4 expression domain in the wing imaginal discs. (C) A knockdown of jing in the MS1096/+; hng1i/+ animal leads to a rescue of the hng1 phenotype while co-expression of UAS-jing leads to an enhancement of the proximal wing phenotype. (D) Wg is derepressed in and around the gap region between the IR and the OR in the MS1096/+; UAS-hng1i/UAS-hng1i wing imaginal disc. (E) Wg is derepressed in a small stripe in the gap region when hng1 expression is reduced in the ptc-Gal4 expression domain. (F) hng1 knockdown in heterozygous Wgspadeflag background in the MS1096-Gal4 domain mildly rescues the hinge defect. (G) Wing size (mm2) and alula size (mm2) are measured for genetics interactors of hng1 with known wing-hinge GRN genes. Arrowhead indicates the MS1096/+; UAS-hng1/+ line used as a control for statistical analyses. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.