Abstract
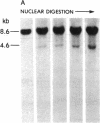
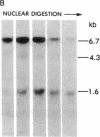
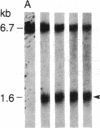
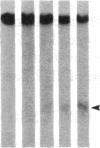
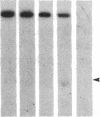
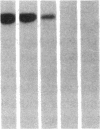
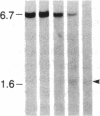
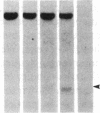
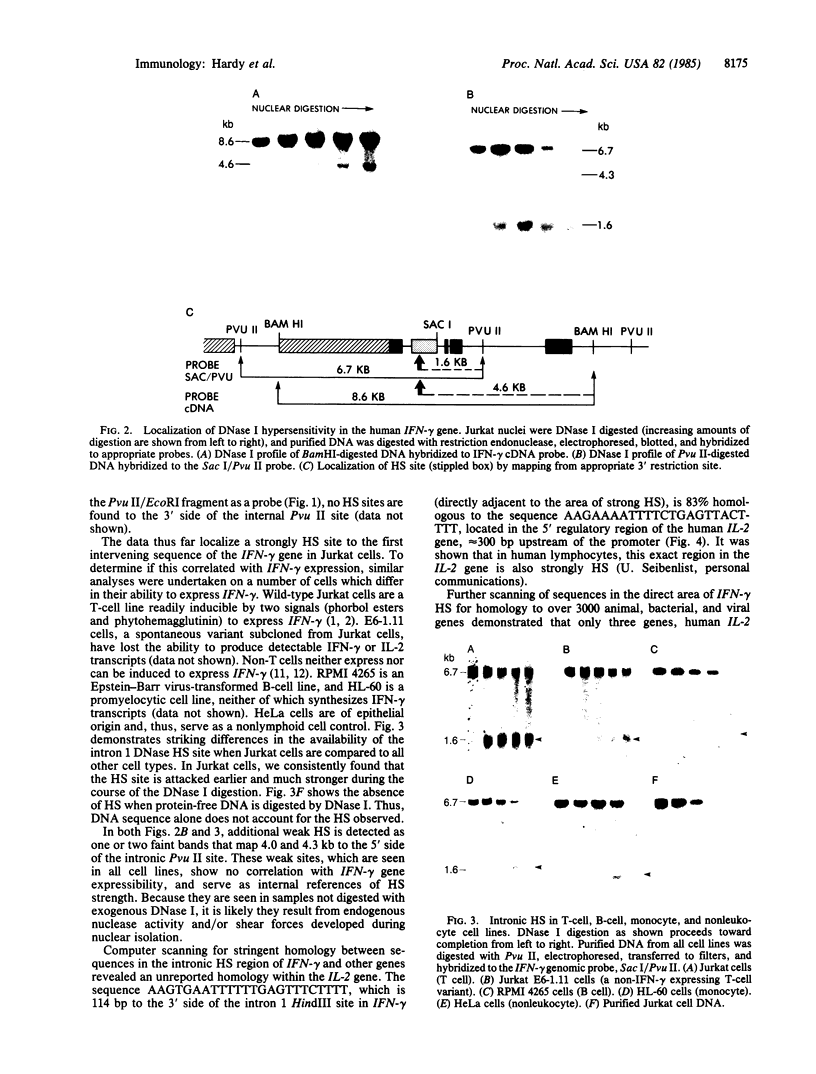
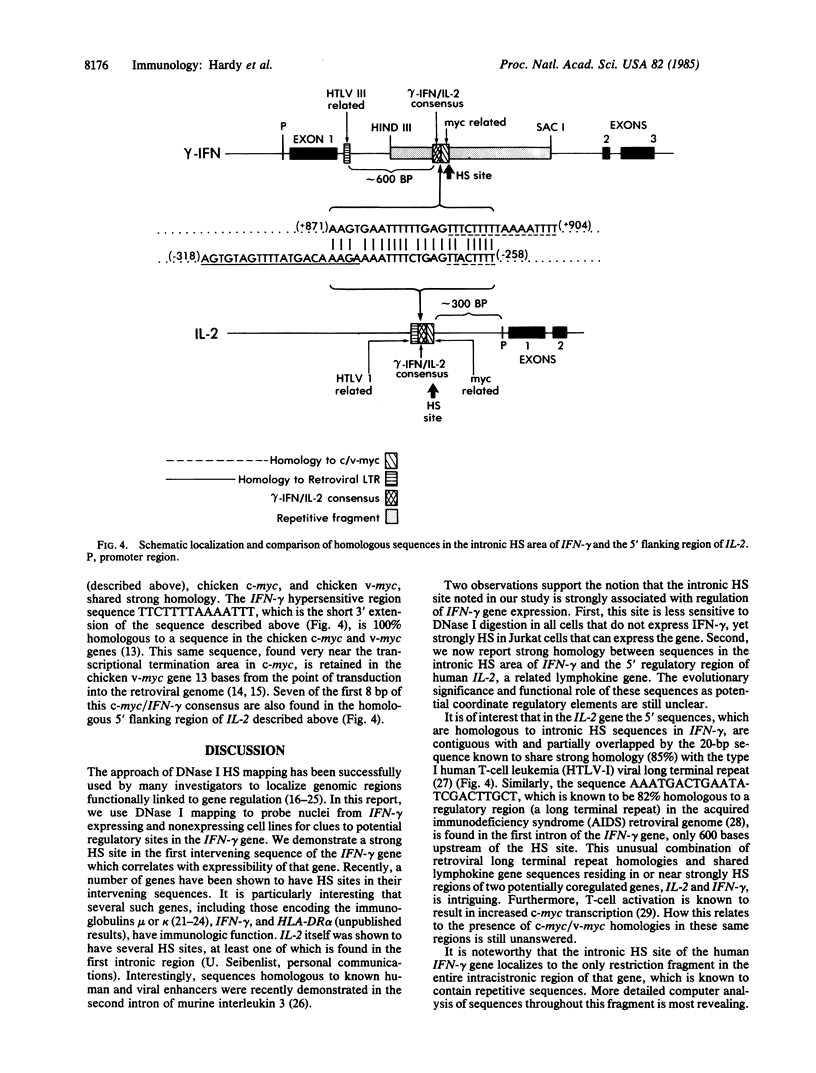
DNA fragments isolated from a genomic clone of human gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) as well as IFN-gamma cDNA were used to map potential regulatory regions of the IFN-gamma gene by DNase I-hypersensitivity analyses. In nuclei from the human T-cell line Jurkat, which can be induced to express the IFN-gamma gene, we observed a strongly hypersensitive site in the first intervening sequence that localized to the only intracistronic repeat element in the gene. DNase I mapping of Jurkat cells was compared to that of several other cell types, including B cells, macrophages, and epithelial cells. The presence of strong intronic hypersensitivity was found only in cells capable of expressing the IFN-gamma gene. No hypersensitivity was found in the 3' regions of the gene. Further, no hypersensitivity was observed when purified genomic DNA from Jurkat was analyzed, suggesting that DNA-protein interactions, and not simply DNA sequence alone, were responsible for DNase I hypersensitivity. The sequence AAGTGTAATTTTTTGAGTTTCTTTT, which is directly in the intronic hypersensitive area of IFN-gamma, is 83% homologous to a nearly identical sequence in the 5' flanking region of the interleukin 2 gene. In interleukin 2, the homologous sequence is about 300 base pairs upstream of that gene's promoter in an area of potential regulatory importance.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Bishop J. M., Smith D. H., Chen E. Y., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Nucleotide sequence to the v-myc oncogene of avian retrovirus MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P., Renkawitz R., Schütz G. Tissue-specific DNaseI hypersensitive sites in the 5'-flanking sequences of the tryptophan oxygenase and the tyrosine aminotransferase genes. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2015–2020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02084.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheley S., Anderson R. A reproducible microanalytical method for the detection of specific RNA sequences by dot-blot hybridization. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T., Nowock J., Strech-Jurk U., Theisen M., Sippel A. E. Alternative sets of DNase I-hypersensitive sites characterize the various functional states of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):163–165. doi: 10.1038/311163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginder G. D., Whitters M. J., Pohlman J. K. Activation of a chicken embryonic globin gene in adult erythroid cells by 5-azacytidine and sodium butyrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3954–3958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Structure of the human immune interferon gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):859–863. doi: 10.1038/298859a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Gelinas R., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Papayannopoulou T. Human fetal to adult hemoglobin switching: changes in chromatin structure of the beta-globin gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. J., Lieber M., Crabtree G. R. DNA sequence of the 5' flanking region of the human interleukin 2 gene: homologies with adult T-cell leukemia virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5005–5013. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Wang X. F., Olsen J., Calame K. Transcriptional enhancer elements in the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.6306772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Fisher L. M., Kuroda R., Ford A. M., Gould H. J. DNase I hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of human mu immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):809–812. doi: 10.1038/306809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for murine interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):316–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Pardue M. L., Lafer E. M., Möller A., Stollar B. D., Rich A. Antibodies to left-handed Z-DNA bind to interband regions of Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):417–422. doi: 10.1038/294417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Granner D. K. Chromatin changes accompany immunoglobulin kappa gene activation: a potential control region within the gene. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):449–451. doi: 10.1038/299449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Reynolds R. K., Watson D. K., Schultz R. A., Lautenberger J., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the proviral genome of avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2500–2504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcich B., Ratner L., Josephs S. F., Okamoto T., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Characterization of long terminal repeat sequences of HTLV-III. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):538–540. doi: 10.1126/science.2981438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Shoback D., Stobo J. Role of T3 surface molecules in human T-cell activation: T3-dependent activation results in an increase in cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Wiskocil R., Stobo J. The role of T3 in the activation of human T cells. J Clin Immunol. 1984 May;4(3):165–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00914963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Wiskocil R. L., Stobo J. D. The role of T3 surface molecules in the activation of human T cells: a two-stimulus requirement for IL 2 production reflects events occurring at a pre-translational level. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]