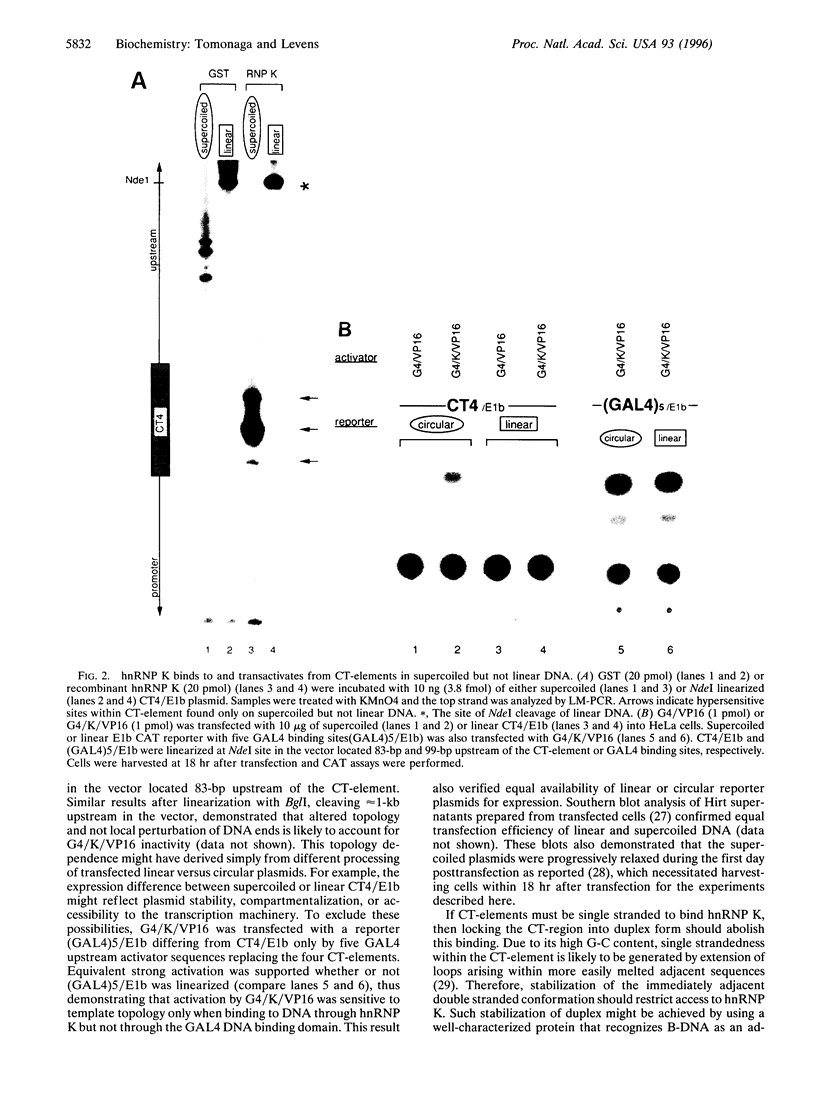
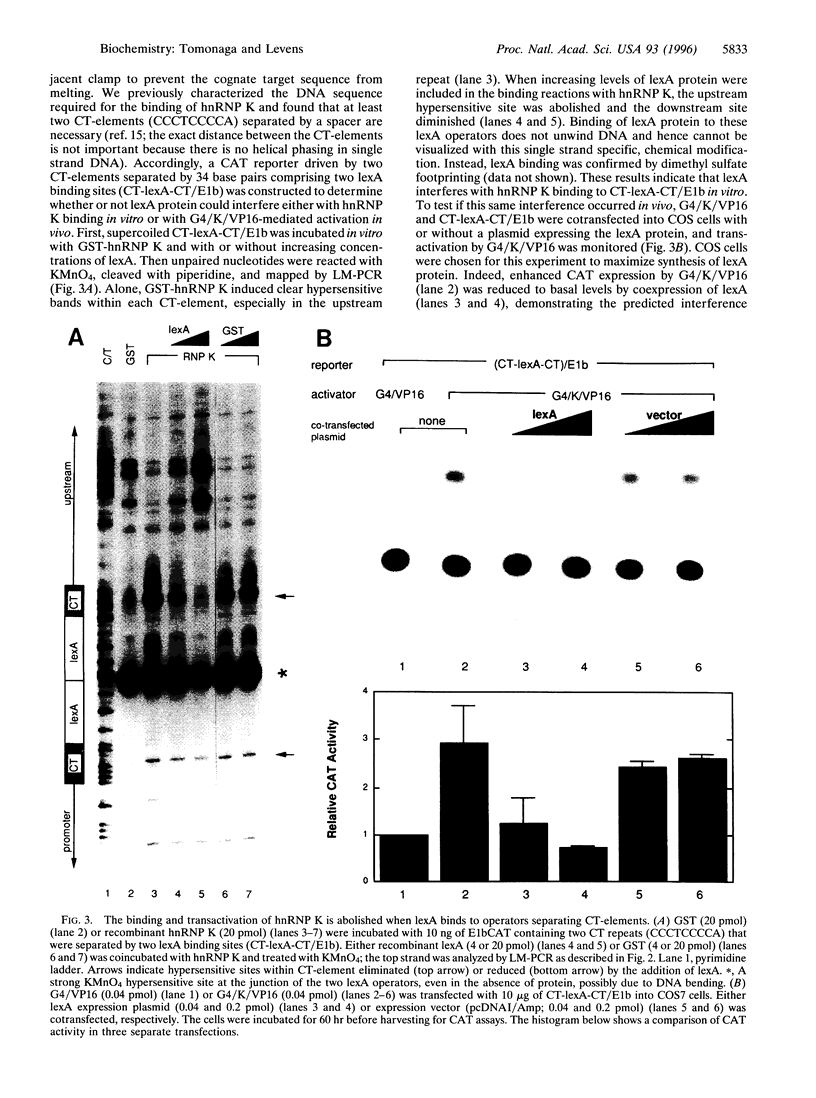
Abstract
Sequence specific regulators of eukaryotic gene expression, axiomatically, act through double stranded DNA targets. Proteins that recognize DNA cis-elements as single strands but for which compelling evidence has been lacking to indicate in vivo involvement in transcription are orphaned in this scheme. We sought to determine whether sequence specific single strand binding proteins can find their cognate elements and modify transcription in vivo by studying heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K), which binds the single stranded sequence (CCCTCCCCA; CT-element) of the human c-myc gene in vitro. To monitor its DNA binding in vivo, the ability of hnRNP K to activate a reporter gene was amplified by fusion with the VP16 transactivation domain. This chimeric protein was found to transactivate circular but not linear CT-element driven reporters, suggesting that hnRNP K recognizes a single strand region generated by negative supercoiling in circular plasmid. When CT-elements were engineered to overlap with lexA operators, addition of lexA protein, either in vivo or in vitro, abrogated hnRNP K binding most likely by preventing single strand formation. These results not only reveal hnRNP K to be a single strand DNA binding protein in vivo, but demonstrate how a segment of DNA may modify the transcriptional activity of an adjacent gene through the interconversion of duplex and single strands.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altiok S., Groner B. Interaction of two sequence-specific single-stranded DNA-binding proteins with an essential region of the beta-casein gene promoter is regulated by lactogenic hormones. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7303–7310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergemann A. D., Johnson E. M. The HeLa Pur factor binds single-stranded DNA at a specific element conserved in gene flanking regions and origins of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1257–1265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. General model for the chromosomes of higher organisms. Nature. 1971 Nov 5;234(5323):25–27. doi: 10.1038/234025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesJardins E., Hay N. Repeated CT elements bound by zinc finger proteins control the absolute and relative activities of the two principal human c-myc promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5710–5724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Bazar L., Michelotti G., Tomonaga T., Krutzsch H., Avigan M., Levens D. A sequence-specific, single-strand binding protein activates the far upstream element of c-myc and defines a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 15;8(4):465–480. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Collins I., Tomonaga T., Zhang T., Levens D. A unique transactivation sequence motif is found in the carboxyl-terminal domain of the single-strand-binding protein FBP. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 May;16(5):2274–2282. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.5.2274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard C., Cabannes E., Strauss F. Identity of the RNA-binding protein K of hnRNP particles with protein H16, a sequence-specific single strand DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 11;22(20):4183–4186. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.20.4183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrity P. A., Wold B. J. Effects of different DNA polymerases in ligation-mediated PCR: enhanced genomic sequencing and in vivo footprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1021–1025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilinger G., Alwine J. C. Transcriptional activation by simian virus 40 large T antigen: requirements for simple promoter structures containing either TATA or initiator elements with variable upstream factor binding sites. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6682–6688. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6682-6688.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann M. E., Tindall D. J. The androgen receptor is transcriptionally suppressed by proteins that bind single-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10968–10975. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosso L. E., Pitot H. C. Transcriptional regulation of c-myc during chemically induced differentiation of HL-60 cultures. Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):847–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Yun E., Crothers D. M. Detection of localized DNA flexibility. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):163–166. doi: 10.1038/368163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matunis M. J., Michael W. M., Dreyfuss G. Characterization and primary structure of the poly(C)-binding heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex K protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelotti E. F., Michelotti G. A., Aronsohn A. I., Levens D. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 May;16(5):2350–2360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.5.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelotti E. F., Tomonaga T., Krutzsch H., Levens D. Cellular nucleic acid binding protein regulates the CT element of the human c-myc protooncogene. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 21;270(16):9494–9499. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.16.9494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelotti G. A., Michelotti E. F., Pullner A., Duncan R. C., Eick D., Levens D. Multiple single-stranded cis elements are associated with activated chromatin of the human c-myc gene in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;16(6):2656–2669. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.6.2656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi Y., Nishita Y., Saëgusa Y., Kakizaki I., Galli I., Kihara F., Tamai K., Miyajima N., Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Ariga H. Identification and cDNA cloning of single-stranded DNA binding proteins that interact with the region upstream of the human c-myc gene. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1133–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Sharp P. A. DNA topology and a minimal set of basal factors for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):533–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90140-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Shykind B. M., Meyers R. E., Kim J., Sharp P. A. Multiple sets of basal factors initiate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18414–18421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Taylor A. K., Andalibi A., Svenson K. L., Lusis A. J. Identification of a zinc finger protein that binds to the sterol regulatory element. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):640–643. doi: 10.1126/science.2562787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. W., Cole C. N. Efficient transcriptional activation of many simple modular promoters by simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6689–6697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6689-6697.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Thurston S. J. SV40 stimulates expression of the transacting factor Sp1 at the mRNA level. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):659–666. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. Classification and purification of proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by RNA-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada H., Khalili K. A novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein, LCP-1, interacts with single-stranded DNA and differentially regulates early gene expression of the human neurotropic JC virus. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6885–6892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.6885-6892.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai T., Nishita Y., Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Ariga H. Molecular cloning of MSSP-2, a c-myc gene single-strand binding protein: characterization of binding specificity and DNA replication activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 25;22(25):5576–5581. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.25.5576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto M., Tomonaga T., Matunis M., Avigan M., Krutzsch H., Dreyfuss G., Levens D. Specific binding of heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particle protein K to the human c-myc promoter, in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18249–18258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Shalloway D. An RNA-binding protein associated with Src through its SH2 and SH3 domains in mitosis. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):867–871. doi: 10.1038/368867a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonaga T., Levens D. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a DNA-binding transactivator. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4875–4881. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Cheng P. F., Conrad K. Expression of transfected DNA depends on DNA topology. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90865-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]