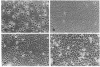
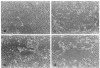
Abstract
We have examined the interaction of freshly isolated human blood monocytes with cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. Purified monocytes incubated with confluent primary or passaged endothelial cells (EC) for 90 min at 37 degrees C bound at maximal densities of 6.5-7.0 X 10(3)/mm2 (8 or 9 per EC) without causing disruption of the monolayer. Monocyte-EC binding proceeded in the presence of plasma proteins or optimal phagocytic doses of opsonized zymosan particles. The avidity of attachment was not diminished by alternative monocyte isolation techniques. Monocyte attachment to EC was dependent upon the presence of divalent cations (magnesium greater than calcium) and was inhibited at 4 degrees C. Monocytes selectively bound to EC when incubated with monolayers composed of smooth muscle cells and EC. Neither EC monolayer confluence nor a variety of EC culture conditions affected the high levels of monocyte binding. In contrast, human neutrophils (less than 1 per EC) and lymphocytes (less than 2-3.5 per EC) bound at lower maximal densities under the same conditions, while platelet reactivity remained minimal. The distinctively higher affinity of human blood monocytes relative to other circulating white cells for binding to cultured human EC may have relevance to their function in vivo.
Full text
PDF

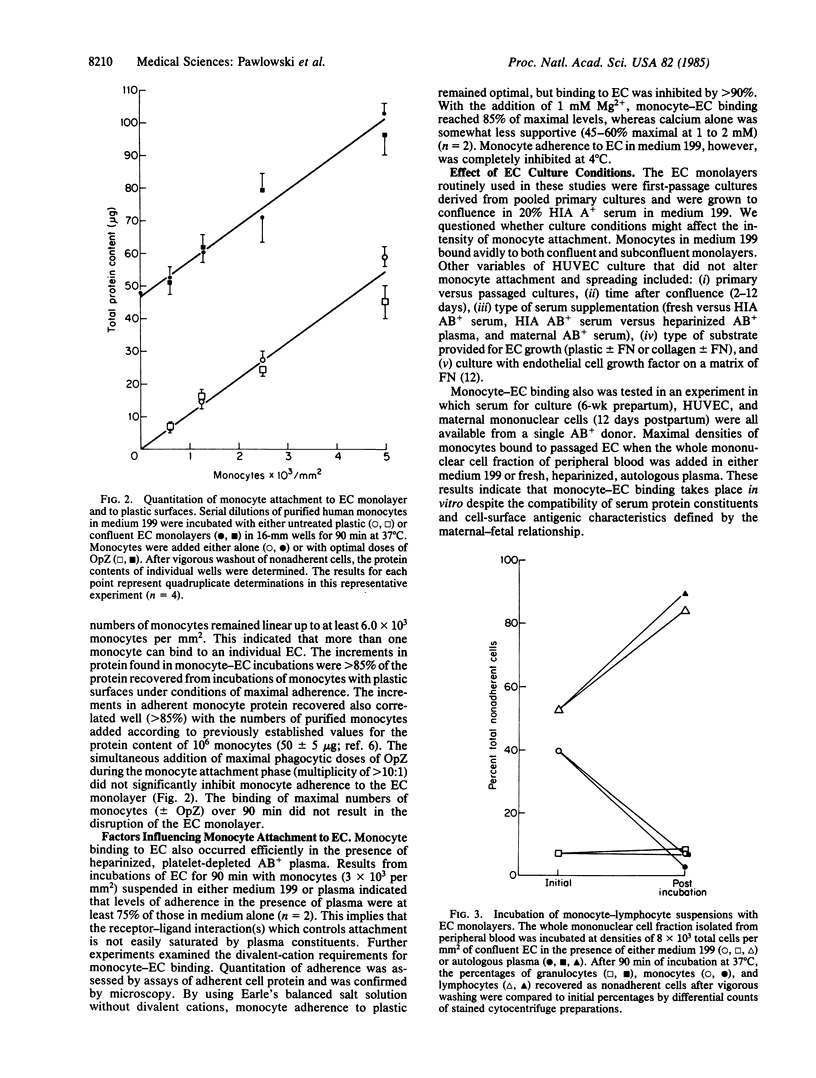
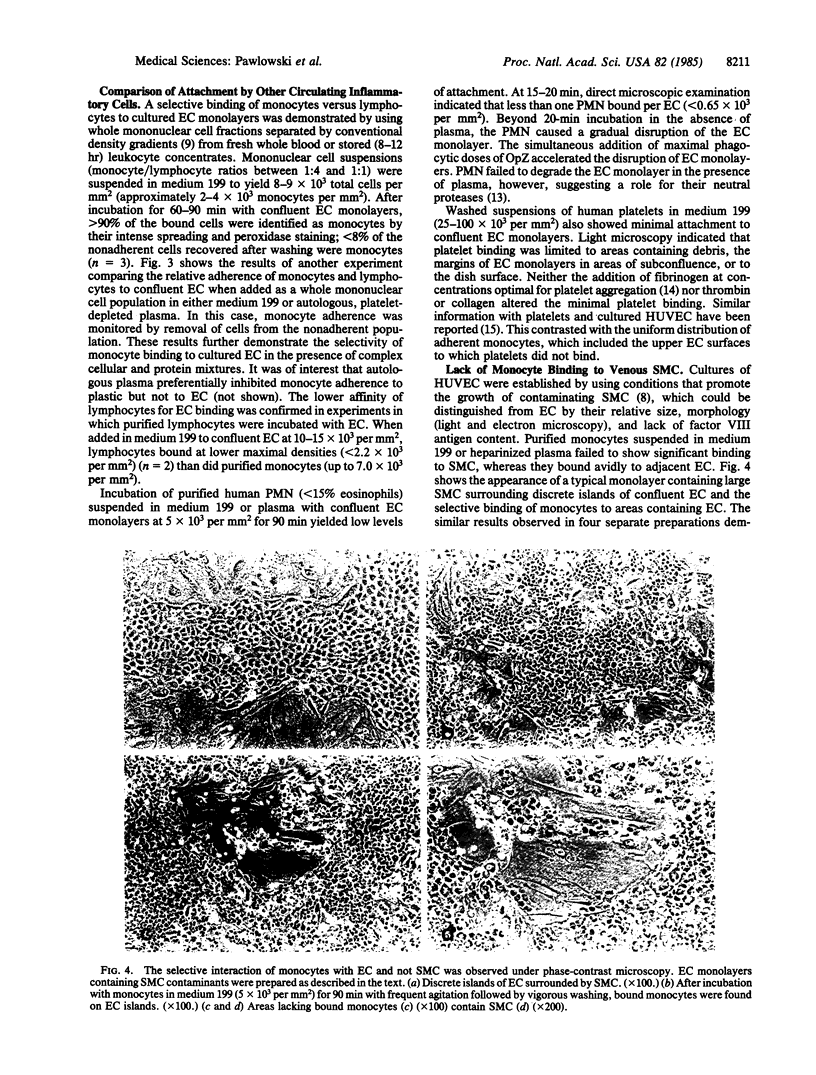

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTER R. H., JANDL J. H. PLATELET SEQUESTRATION IN MAN. I. METHODS. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:843–855. doi: 10.1172/JCI104970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley J. E., Pearson J. D., Carleton J. S., Hutchings A., Gordon J. L. Interaction of leukocytes with vascular cells in culture. J Cell Sci. 1978 Oct;33:85–101. doi: 10.1242/jcs.33.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley J. E., Pearson J. D., Hutchings A., Carleton J. S., Gordon J. L. Granulocyte migration through endothelium in culture. J Cell Sci. 1979 Aug;38:237–248. doi: 10.1242/jcs.38.1.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charo I. F., Yuen C., Goldstein I. M. Adherence of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes to endothelial monolayers: effects of temperature, divalent cations, and chemotactic factors on the strength of adherence measured with a new centrifugation assay. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):473–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer E. B., Pologe L., Pawlowski N. A., Cohn Z. A., Scott W. A. Leukotriene C promotes prostacyclin synthesis by human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4109–4113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Bailey P. J., Goldenberg M. M., Ford-Hutchinson A. W. The role of arachidonic acid oxygenation products in pain and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:335–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggiotto A., Ross R., Harker L. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. I. Changes that lead to fatty streak formation. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):323–340. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Brock A. F., Schafer A. I. Leukotriene B4 stimulates polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesion to cultured vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1552–1555. doi: 10.1172/JCI111570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Vlodavsky I., Savion N. The extracellular matrix and the control of proliferation of vascular endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(3):339–372. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Killen P. D., Harker L. A., Striker G. E., Wright D. G. Neutrophil-mediated endothelial injury in vitro mechanisms of cell detachment. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1394–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI110390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M. Leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):513–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill H. C., Jr George Lyman Duff memorial lecture. Persistent problems in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Sep-Oct;4(5):443–451. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.5.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. The macrophage as an effector cell. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski N. A., Kaplan G., Hamill A. L., Cohn Z. A., Scott W. A. Arachidonic acid metabolism by human monocytes. Studies with platelet-depleted cultures. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):393–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski N. A., Scott W. A., Andreach M., Cohn Z. A. Uptake and metabolism of monohydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acids by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1653–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polley M. J., Nachman R. L. Human platelet activation by C3a and C3a des-arg. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):603–615. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedmore C. V., Williams T. J. Control of vascular permeability by polymorphonuclear leukocytes in inflammation. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):646–650. doi: 10.1038/289646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetter B. R., Johnson L. K., Shuman M. A., Gospodarowicz D. The isolation of vascular endothelial cell lines with altered cell surface and platelet-binding properties. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman G. A., Wiseman G. A., Hill H. R. Human endothelial cells modulate granulocyte adherence and chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1866–1874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bono D. P., Green C. The adhesion of different cell types to cultured vascular endothelium: effects of culture density and age. Br J Exp Pathol. 1984 Feb;65(1):145–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]