Abstract
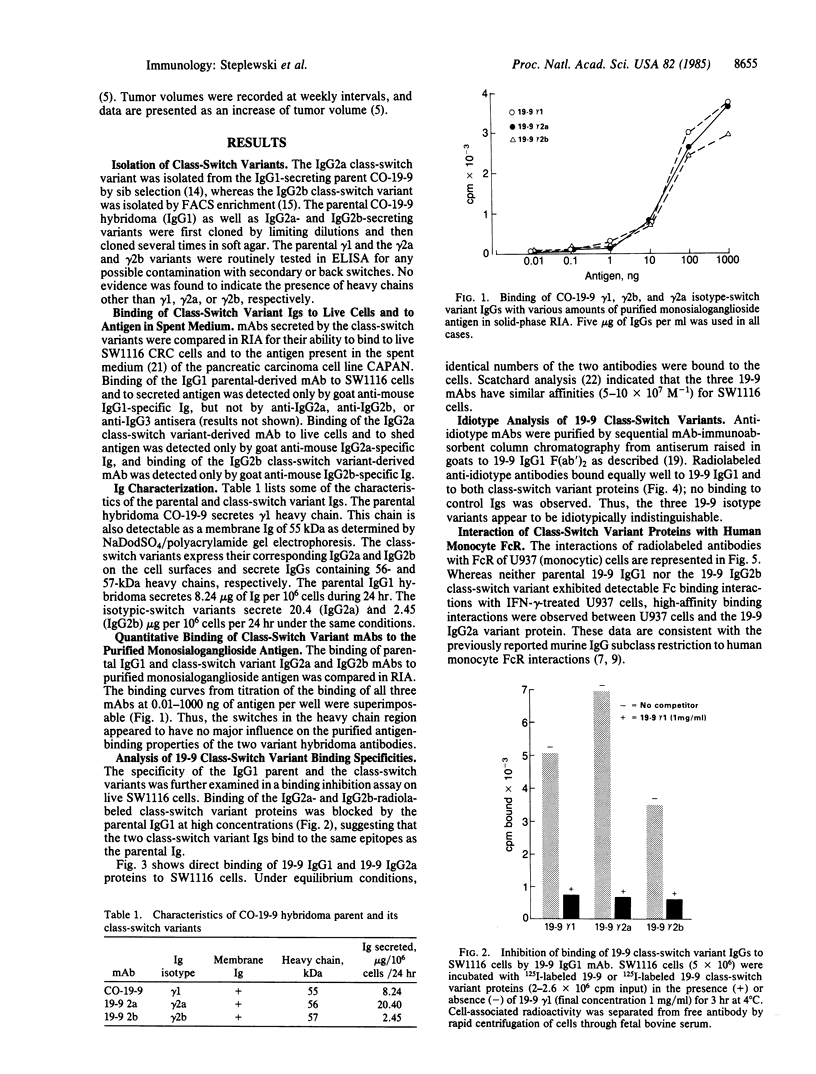
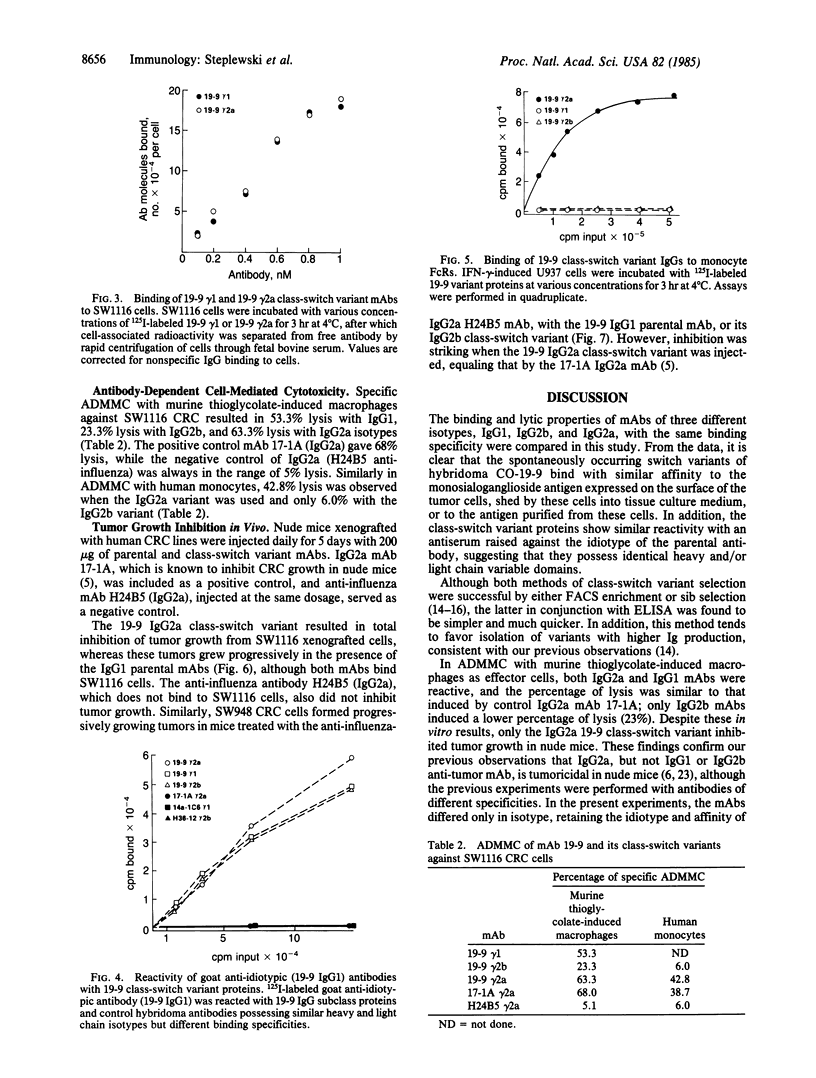
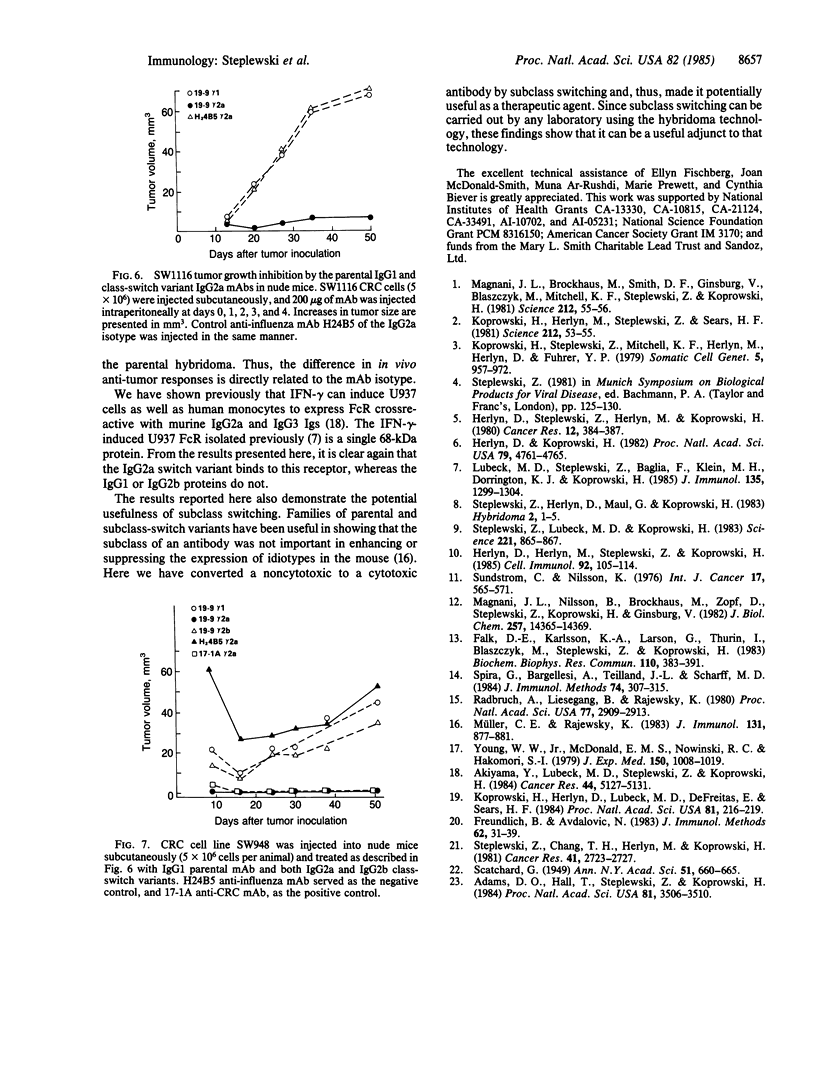
Three different monoclonal antibody isotypes, IgG1, IgG2b, and IgG2a, were derived by selection of isotype-switch variants from the CO-19-9 hybridoma. All three antibodies retained their binding specificities and affinities and bound to the same epitope--as defined by the anti-idiotype analysis. Availability of gamma 1, gamma 2b, and gamma 2a Ig heavy chain variants directed against the same epitope on the monosialoganglioside antigen permitted detailed analysis of their Fc fragment receptor (FcR) binding affinities, their cytolytic activities (antibody-dependent, macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity) in vitro, and their tumoricidal activities in vivo. Analysis of the binding of three isotypes to the human FcR expressed by U937 cells induced by gamma interferon has shown that only IgG2a proteins bound to high-affinity FcR, but not IgG1 or IgG2b variants. Although all three isotypes were active in the antibody-dependent, macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity assay with murine thioglycolate-elicited macrophages, the IgG2a gave the highest percentage of lysis; similar results were obtained in the same assay with human monocytes as effector cells. In the nude mice experiment, only the IgG2a variant inhibited growth of human colorectal carcinoma, while IgG1 and IgG2b were ineffective. Thus, selection of isotype-switch variants resulted in the conversion of monoclonal antibody from noncytolytic to cytolytic with possible immunotherapeutic application.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hall T., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Tumors undergoing rejection induced by monoclonal antibodies of the IgG2a isotype contain increased numbers of macrophages activated for a distinctive form of antibody-dependent cytolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3506–3510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama Y., Lubeck M. D., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Induction of mouse IgG2a- and IgG3-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in human monocytic cells (U937) by immune interferon. Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):5127–5131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K. E., Karlsson K. A., Larson G., Thurin J., Blaszczyk M., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Mass spectrometry of a human tumor glycolipid antigen being defined by mouse monoclonal antibody NS-19-9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich B., Avdalovic N. Use of gelatin/plasma coated flasks for isolating human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Aug 12;62(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn D., Herlyn M., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Monoclonal anti-human tumor antibodies of six isotypes in cytotoxic reactions with human and murine effector cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Apr 15;92(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn D., Koprowski H. IgG2a monoclonal antibodies inhibit human tumor growth through interaction with effector cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4761–4765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Herlyn D., Lubeck M., DeFreitas E., Sears H. F. Human anti-idiotype antibodies in cancer patients: Is the modulation of the immune response beneficial for the patient? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):216–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Herlyn M., Steplewski Z., Sears H. F. Specific antigen in serum of patients with colon carcinoma. Science. 1981 Apr 3;212(4490):53–55. doi: 10.1126/science.6163212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Steplewski Z., Mitchell K., Herlyn M., Herlyn D., Fuhrer P. Colorectal carcinoma antigens detected by hybridoma antibodies. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Nov;5(6):957–971. doi: 10.1007/BF01542654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubeck M. D., Steplewski Z., Baglia F., Klein M. H., Dorrington K. J., Koprowski H. The interaction of murine IgG subclass proteins with human monocyte Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1299–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani J. L., Brockhaus M., Smith D. F., Ginsburg V., Blaszczyk M., Mitchell K. F., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. A monosialoganglioside is a monoclonal antibody-defined antigen of colon carcinoma. Science. 1981 Apr 3;212(4490):55–56. doi: 10.1126/science.7209516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani J. L., Nilsson B., Brockhaus M., Zopf D., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H., Ginsburg V. A monoclonal antibody-defined antigen associated with gastrointestinal cancer is a ganglioside containing sialylated lacto-N-fucopentaose II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14365–14369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C. E., Rajewsky K. Isolation of immunoglobulin class switch variants from hybridoma lines secreting anti-idiotope antibodies by sequential sublining. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):877–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. Isolation of variants of mouse myeloma X63 that express changed immunoglobulin class. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2909–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira G., Bargellesi A., Teillaud J. L., Scharff M. D. The identification of monoclonal class switch variants by sib selection and an ELISA assay. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 30;74(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steplewski Z., Chang T. H., Herlyn M., Koprowski H. Release of monoclonal antibody-defined antigens by human colorectal carcinoma and melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Jul;41(7):2723–2727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steplewski Z., Herlyn D., Maul G., Koprowski H. Hypothesis: macrophages as effector cells for human tumor destruction mediated by monoclonal antibody. Hybridoma. 1983;2(1):1–5. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1983.2.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steplewski Z., Lubeck M. D., Koprowski H. Human macrophages armed with murine immunoglobulin G2a antibodies to tumors destroy human cancer cells. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):865–867. doi: 10.1126/science.6879183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. W., Jr, MacDonald E. M., Nowinski R. C., Hakomori S. I. Production of monoclonal antibodies specific for two distinct steric portions of the glycolipid ganglio-N-triosylceramide (asialo GM2). J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):1008–1019. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


