Abstract
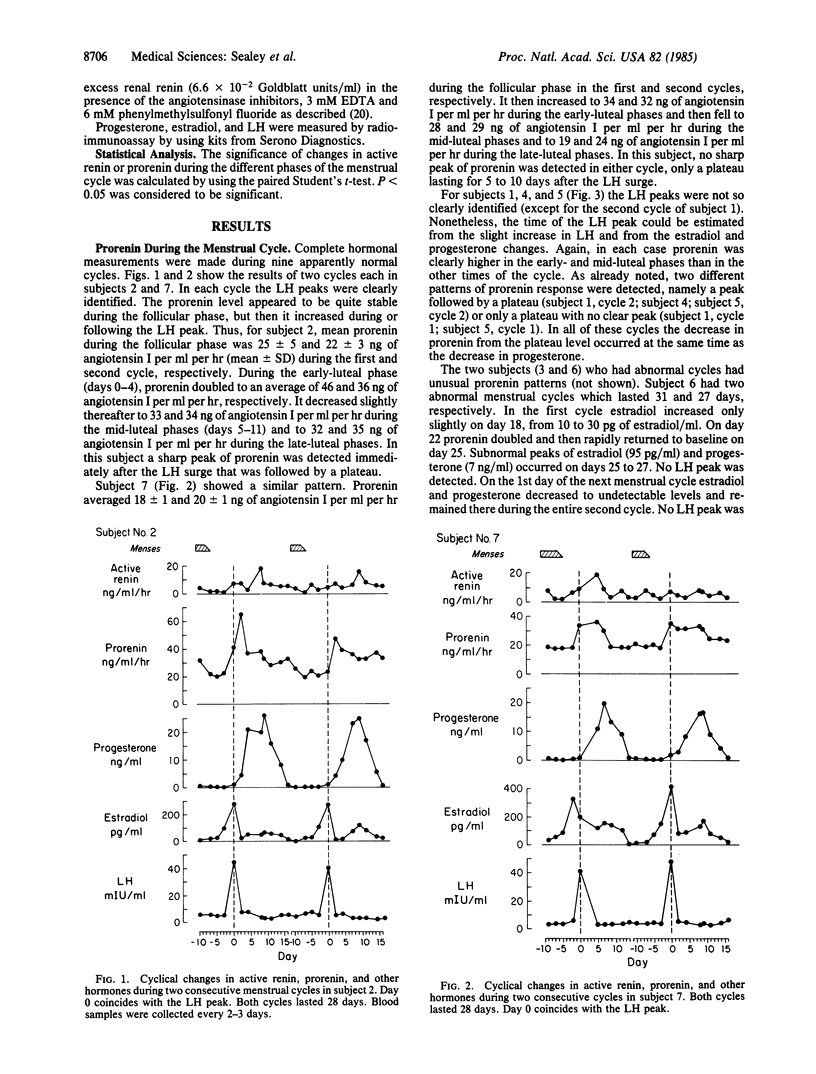
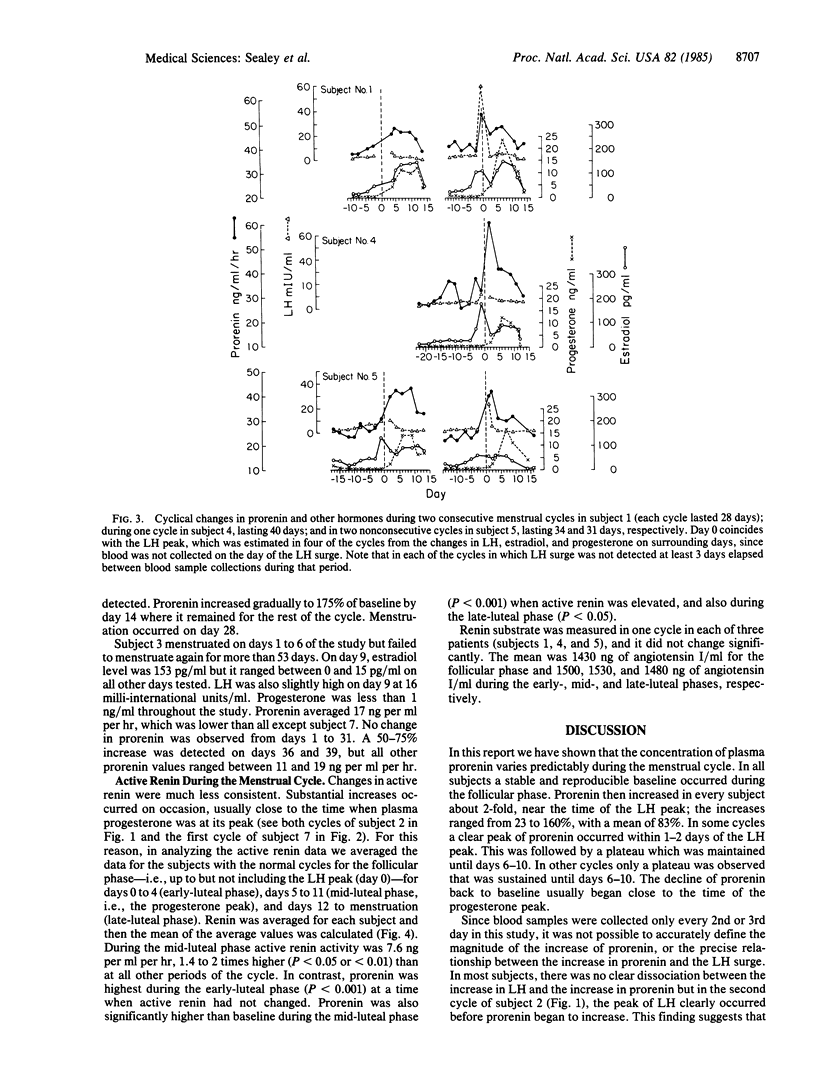
Plasma prorenin, a high molecular weight precursor form of renin, (renin, EC 3.4.23.15; old number, EC 3.4.99.19), was measured three times weekly in normal young women during the menstrual cycle and was related to changes in luteinizing hormone, estradiol, and progesterone. In all subjects a stable baseline level of prorenin occurred during the follicular phase. Then, simultaneously or soon after the luteinizing hormone peak, plasma prorenin consistently increased about 2-fold. Baseline prorenin ranged from 18 to 40 ng per ml per hr, and peak prorenin ranged from 35 to 65 ng per ml per hr. The maximum increase in prorenin averaged 80%. Prorenin remained elevated during the mid-luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and returned to baseline during the late-luteal phase in coordination with the decrease in progesterone. The changes in prorenin were not synchronized with changes in active renin which was significantly increased only during the mid-luteal phase. These findings suggest that prorenin may be involved in reproductive physiology.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas S. A., Christofalo P., Hesson T., Sealey J. E., Fritz L. C. Immunological evidence that inactive renin is prorenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):1038–1045. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91911-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas S. A., Hesson T. E., Sealey J. E., Dharmgrongartama B., Laragh J. H., Ruddy M. C., Aurell M. Characterization of inactive renin ("prorenin") from renin-secreting tumors of nonrenal origin. Similarity to inactive renin from kidney and normal plasma. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):437–447. doi: 10.1172/JCI111230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas S. A., Sealey J. E., Laragh J. H., Moon C. Plasma renin and "prorenin" in essential hypertension during sodium depletion, beta-blockade, and reduced arterial pressure. Lancet. 1977 Oct 15;2(8042):785–789. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90723-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN J. J., DAVIES D. L., LEVER A. F., ROBERTSON J. I. VARIATIONS IN PLASMA RENIN DURING THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE. Br Med J. 1964 Oct 31;2(5417):1114–1115. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5417.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouhnik J., Fehrentz J. A., Galen F. X., Seyer R., Evin G., Castro B., Menard J., Corvol P. Immunologic identification of both plasma and human renal inactive renin as prorenin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Feb;60(2):399–401. doi: 10.1210/jcem-60-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkx F. H., Tan-Tjiong L., Wenting G. J., Boomsma F., Man in 't Veld A. J., Schalekamp M. A. Asynchronous changes in prorenin and renin secretion after captopril in patients with renal artery stenosis. Hypertension. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):244–256. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.5.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez L. A., Tarlatzis B. C., Rzasa P. J., Caride V. J., Laufer N., Negro-Vilar A. F., DeCherney A. H., Naftolin F. Renin-like activity in ovarian follicular fluid. Fertil Steril. 1985 Aug;44(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)48740-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman M. C., Zimmerman E. A., Slater E. E. Renin and angiotensin: the complete system within the neuroblastoma x glioma cell. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.6272392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Saruta T., Nakamura R., Saito I., Kondo K., Kato E. Active and inactive renin in pregnancy and in women on estrogen-containing oral contraceptives. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1979;10(5):246–253. doi: 10.1159/000299969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W. A., Luetscher J. A., Carlson E. J., Grislis G., Fraze E., McHargue A. Changes in active and inactive renin throughout pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 May;54(5):1010–1016. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-5-1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. H., Romfh P. Plasma aldosterone and renin activity during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 May;34(5):819–821. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-5-819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARAGH J. H., ANGERS M., KELLY W. G., LIEBERMAN S. Hypotensive agents and pressor substances. The effect of epinephrine, norepinephrine, angiotensin II, and others on the secretory rate of aldosterone in man. JAMA. 1960 Sep 17;174:234–240. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03030030014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumbers E. R. Activation of renin in human amniotic fluid by low pH. Enzymologia. 1971 Jun 30;40(6):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller J. Aldosterone stimulation in vitro. 3. Site of action of different aldosterone-stimulating substances on steroid biosynthesis. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1966 Aug;52(4):515–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse K., Takii Y., Inagami T. Immunohistochemical localization of renin in luteinizing hormone-producing cells of rat pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7579–7583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura T., Clemens D. L., Inagami T. Renin, angiotensins, and angiotensin-converting enzyme in neuroblastoma cells: evidence for intracellular formation of angiotensins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier M., Inagami T., Pochet R., Desclin J. C. Pituitary-dependent renin-like immunoreactivity in the rat testis. Endocrinology. 1983 Apr;112(4):1318–1323. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-4-1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H. Prorenin and other large molecular weight forms of renin. Endocr Rev. 1980 Fall;1(4):365–391. doi: 10.1210/edrv-1-4-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Gerten-Banes J., Laragh J. H. The renin system: Variations in man measured by radioimmunoassay or bioassay. Kidney Int. 1972 Apr;1(4):240–253. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Glorioso N., Toth A., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H. Stimulation of plasma prorenin by gonadotropic hormones. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Nov 1;153(5):596–597. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(85)90495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., McCord D., Taufield P. A., Ales K. A., Druzin M. L., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H. Plasma prorenin in first-trimester pregnancy: relationship to changes in human chorionic gonadotropin. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Nov 1;153(5):514–519. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(85)90464-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Wilson M., Morganti A. A., Zervoudakis I., Laragh J. H. Changes in active and inactive renin throughout normal pregnancy. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1982;4(11-12):2373–2384. doi: 10.3109/10641968209062396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L., Cran E. J., Gibson R., Taylor R., Walters W. A., Catt K. J. Angiotensins I and II, active and inactive renin, renin substrate, renin activity, and angiotensinase in human liquor amnii and plasma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Mar 1;121(5):626–630. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L., Lumbers E. R., Symonds E. M. Alteration by oral contraceptives of normal menstrual changes in plasma renin activity, concentration and substrate. Clin Sci. 1969 Feb;36(1):67–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symonds E. M., Stanley M. A., Skinner S. L. Production of renin by in vitro cultures of human chorion and uterine muscle. Nature. 1968 Mar 23;217(5134):1152–1153. doi: 10.1038/2171152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


