Abstract
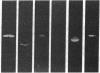
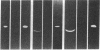
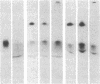
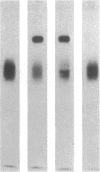
Monospecific antiserum to an unusually stable Mr 50,000 plasminogen-activator inhibitor (PAI) purified from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells was employed in conjunction with reverse fibrin autography to determine whether human platelets, serum, and plasma contain immunologically related inhibitors. Reverse fibrin autography revealed the presence of a Mr 50,000 inhibitor in the platelet and serum samples but not in normal plasma. However, a Mr 50,000 inhibitor was detected in plasma obtained from individuals with increased PAI activity. In each case, treatment of the sample with the anti-inhibitor serum removed the Mr 50,000 inhibitor. The inhibitor present in each sample neutralized exogenously added tissue-type plasminogen activator in a rapid manner. Inhibition was associated with the formation of a NaDodSO4-resistant enzyme-inhibitor complex of Mr 120,000. Again, treatment of the samples with the anti-inhibitor serum removed both the inhibitory activity and the component in these samples that binds to tissue-type plasminogen activator. Thus, the rapidly acting PAI present in human platelets, serum, and patient plasma is immunologically related to the PAI synthesized by cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. This molecule may be the physiologically relevant inhibitor of plasminogen activator in the vascular system and, as such, may serve an important role in regulating the initiation of vascular fibrinolysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann F., Kruithof I. E. Tissue plasminogen activator: chemical and physiological aspects. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Jan;10(1):6–17. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennet N. B. Further studies on an inhibitor of plasminogen activation in human serum. Release of the inhibitor during coagulation and thrombus formation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970 Jun 30;23(3):553–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett N. B. A method for the quantitative assay of inhibitor of plasminogen activation in human serum. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Feb 28;17(1-2):12–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Jr, Vavrin Z., Hibbs J. B., Jr Macrophage fibrinolytic activity: identification of two pathways of plasmin formation by intact cells and of a plasminogen activator inhibitor. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen U., Holmberg L., Bladh B., Astedt B. Kinetics of the reaction between urokinase and an inhibitor of fibrinolysis from placental tissue. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Aug 24;48(1):24–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmensen I., Thorsen S., Müllertz S. Purification of a plasminogen activator inhibitor indistinguishable from alpha1-antitrypsin and an urokinase inhibitor in pregnancy plasma. Haemostasis. 1976;5(4):218–230. doi: 10.1159/000214137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cwikel B. J., Barouski-Miller P. A., Coleman P. L., Gelehrter T. D. Dexamethasone induction of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator in HTC hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6847–6851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., van Hinsbergh V. W., Verheijen J. H., Wijngaards G. Inhibition of tissue-type plasminogen activator by conditioned medium from cultured human and porcine vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. A., Ginsberg M. H., Loskutoff D. J. Detection and partial characterization of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1465–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI111559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Reverse fibrin autography: a method to detect and partially characterize protease inhibitors after sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1984 Mar;137(2):454–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore M. J., Nulkar M. V., Shaw J. T. A comparative study of the inhibitors of fibrinolysis in human, dog and rabbit blood. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Sep 1;14(1-2):145–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurewich V., Hyde E., Lipinski B. The resistance of fibrinogen and soluble fibrin monomer in blood to degradation by a potent plasminogen activator derived from cadaver limbs. Blood. 1975 Oct;46(4):555–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedner U. Studies on an inhibitor of plasminogen activation in human serum. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973 Nov;30(2):414–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hender U., Collen D. Immunochemical distinction between the inhibitors of plasminogen activation and antiplasmin in human plasma. Thromb Res. 1976 Jun;8(6):875–879. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierowski M. T., Schally A. V. An inhibitor of urokinase and tissue plasminogen activators in Dunning R3327H prostate tumors of rats treated with D-Trp6-LH-RH. Horm Res. 1985;21(2):124–135. doi: 10.1159/000180036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggroth L., Mattsson C., Friberg J. Inhibition of the human tissue plasminogen activator in plasma from different species. Thromb Res. 1984 Mar 15;33(6):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Collen D. Neutralization of human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in human plasma: no evidence for a specific inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Oct;46(3):662–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Ransijn A., Bachmann F. Demonstration of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activators in human plasma. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G. Latent tissue plasminogen activator produced by human endothelial cells in culture: evidence for an enzyme-inhibitor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6804–6808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., van Mourik J. A., Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. Detection of an unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins D. E., Bazer F. W., Roberts R. M. Secretion of a progesterone-induced inhibitor of plasminogen activator by the porcine uterus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):865–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J., Crawford G. P., Ogston D., Douglas A. S. Studies on an inhibitor of plasminogen activators in human platelets. Br J Haematol. 1974 Apr;26(4):661–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Bjersing L., Hsueh A. J., Loskutoff D. J. Cultured granulosa cells produce two plasminogen activators and an antiactivator, each regulated differently by gonadotropins. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1666–1668. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Wijngaards G., Welbergen J. Relationship between tissue plasminogen activator and the activators in blood and vascular wall. Thromb Res. 1980 Jun 15;18(6):815–830. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleef R. R., Sinha M., Loskutoff D. J. Characterization of two monoclonal antibodies against human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Apr 22;53(2):170–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. W., Baker J. B. Purification of human protease nexin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10439–10444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen S., Philips M. Isolation of tissue-type plasminogen activator-inhibitor complexes from human plasma. Evidence for a rapid plasminogen activator inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 6;802(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissot J. D., Schneider P., Hauert J., Ruegg M., Kruithof E. K., Bachmann F. Isolation from human plasma of a plasminogen activator identical to urinary high molecular weight urokinase. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1320–1323. doi: 10.1172/JCI110733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen J. H., Chang G. T., Kluft C. Evidence for the occurrence of a fast-acting inhibitor for tissue-type plasminogen activator in human plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Jul 29;51(3):392–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijngaards G., Kluft C., Groeneveld E. Demonstration of urokinase-related fibrinolytic activity in human plasma. Br J Haematol. 1982 May;51(1):165–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb07300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Chmielewska J., Rånby M. Inactivation of tissue plasminogen activator in plasma. Demonstration of a complex with a new rapid inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3644–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Schleuning W. D., Reich E. Isolation and characterization of urokinase from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3276–3283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator (antiactivator) synthesized by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14914–14921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]