Abstract
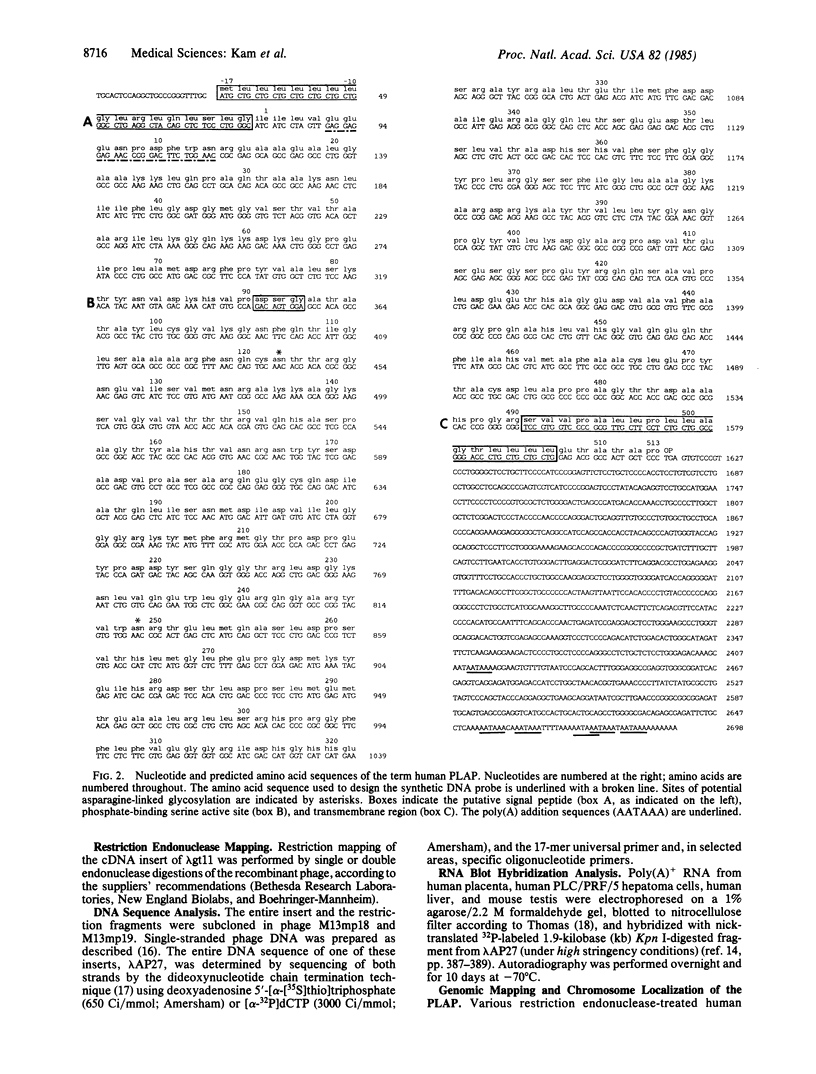
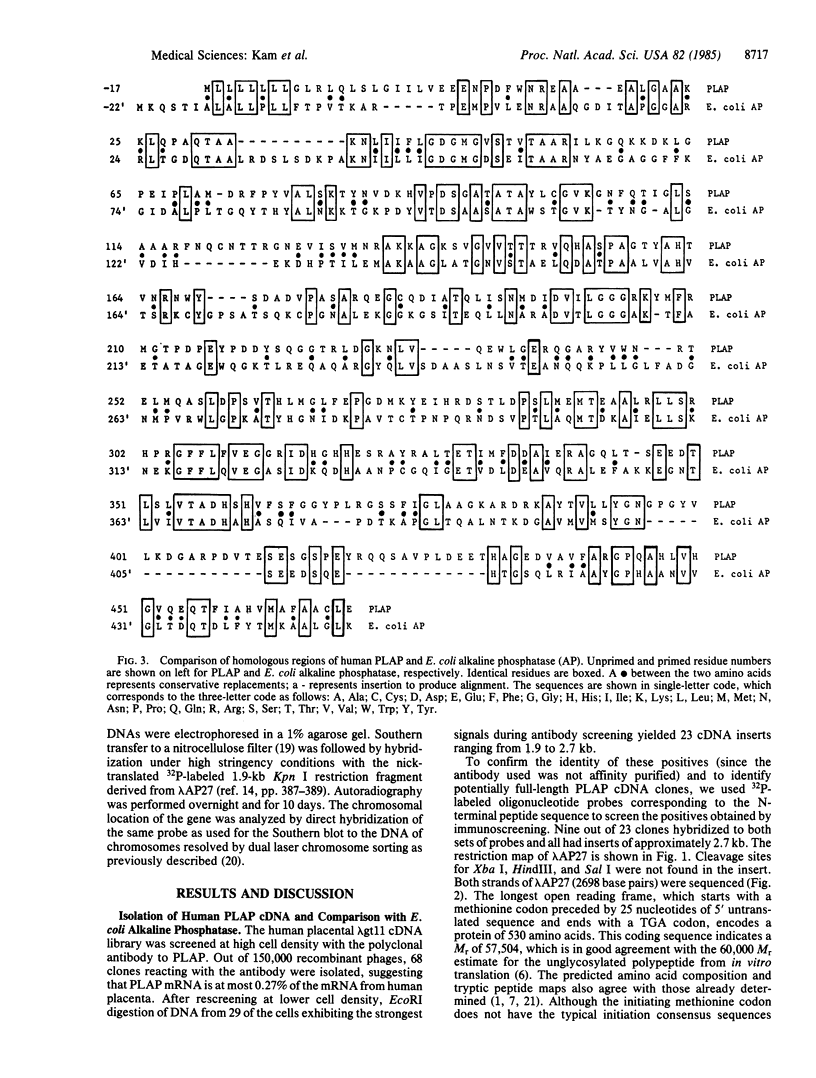
A human term (third trimester) placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP; EC 3.1.3.1) cDNA was isolated from a human placental lambda gt11 cDNA library. The expression library was screened by using rabbit antibodies against PLAP and oligonucleotide probes. DNA sequence analysis of a positive clone with an insert of 2.7 kilobase pairs allowed us to predict the complete amino acid sequence of PLAP (530 residues), which coincided with the reported 42 N-terminal amino acid sequence of PLAP except at position 3. Contrary to the previous supposition that there was no amino acid sequence homology between PLAP and Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase (471 residues), we found 30% overall homology, with regions of strong homology including the putative active site and the metal-binding sites. The 44-residue C-terminal extension of PLAP has a stretch of 17 hydrophobic amino acids, which presumably anchors the protein to the plasma membrane, a change perhaps necessary for the transition from a bacterial periplasmic enzyme to a mammalian membrane-associated enzyme. We have also localized PLAP-related DNA sequences mainly on chromosome 2 and to a lesser degree on chromosome 17. It seems likely therefore that the PLAP gene resides on chromosome 2 and other member(s) of the alkaline phosphatase family may exist (on this chromosome and) on chromosome 17.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Rose J. K. Structural requirements of a membrane-spanning domain for protein anchoring and cell surface transport. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias C. F., López S., Bell J. R., Strauss J. H. Primary structure of the neutralization antigen of simian rotavirus SA11 as deduced from cDNA sequence. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):657–661. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.657-661.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger K. S., Sussman H. H. Structural evidence that human liver and placental alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes are coded by different genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2201–2205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer S. H. Alkaline Phosphatase in Human Sera and Placentae: Starch gel electrophoresis reveals many phosphatase components including a polymorphism in placentae. Science. 1961 Oct 6;134(3484):1002–1004. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3484.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A., Cancedda F., Ericsson L. H., Neumann P. A., Piccoli S. P., Schlesinger M. J., Shriefer K., Walsh K. A. Amino acid sequence of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3473–3477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Barron L., Bedgood D., Van Heyningen V. Prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis using a monoclonal antibody specific for intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Prenat Diagn. 1984 Nov-Dec;4(6):421–426. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970040605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. E. Carbonic anhydrase: zinc and the mechanism of catalysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;429:26–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crea R., Horn T. Synthesis of oligonucleotides on cellulose by a phosphotriester method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2331–2348. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. G., Boeke J. D., Model P. Fine structure of a membrane anchor domain. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90329-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezra E., Blacher R., Udenfriend S. Purification and partial sequencing of human placental alkaline phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):1076–1083. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Inglis N. I., Stolbach L. L., Krant M. J. A serum alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme of human neoplastic cell origin. Cancer Res. 1968 Jan;28(1):150–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. Applications of monoclonal antibodies in enzyme genetics. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:279–314. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Nielsen E. A., Kavaler J., Cohen D. I., Davis M. M. Sequence relationships between putative T-cell receptor polypeptides and immunoglobulins. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):153–158. doi: 10.1038/308153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito F., Chou J. Y. Biosynthesis and processing of placental alkaline phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito F., Chou J. Y. Biosynthesis and processing of placental alkaline phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Yoda K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter and the amino-terminal region of alkaline phosphatase structural gene (phoA) of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5671–5678. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebo R. V., Gorin F., Fletterick R. J., Kao F. T., Cheung M. C., Bruce B. D., Kan Y. W. High-resolution chromosome sorting and DNA spot-blot analysis assign McArdle's syndrome to chromosome 11. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):57–59. doi: 10.1126/science.6587566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKusick V. A. The human gene map 1 December 1984. Clin Genet. 1985 Feb;27(2):207–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. W., Hansen H. F., Håkanson R., Sundler F., Tager H. S. Human pancreatic icosapeptide: isolation, sequence, and immunocytochemical localization of the COOH-terminal fragment of the pancreatic polypeptide precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):708–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Fong N., Selby M., Rutter W. J., Bell G. I. Structure of a mouse submaxillary messenger RNA encoding epidermal growth factor and seven related proteins. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):236–240. doi: 10.1126/science.6602382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. The hydrophobic effect and the organization of living matter. Science. 1978 Jun 2;200(4345):1012–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.653353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. Multiple polyadenylation sites in a mouse alpha-amylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2313–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Schold M., Johnson M. J., Dembek P., Itakura K. Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis of the human beta-globin gene: a general method for producing specific point mutations in cloned DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3647–3656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker K. B., Byfield P. G., Moss D. W. An active site peptide from human placental alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Sep 6;71(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff H. W., Handschumacher M., Murthy H. M., Sowadski J. M. The three dimensional structure of alkaline phosphatase from E. coli. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;55:453–480. doi: 10.1002/9780470123010.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi Y., Yoshikai Y., Leggett K., Clark S. P., Aleksander I., Mak T. W. A human T cell-specific cDNA clone encodes a protein having extensive homology to immunoglobulin chains. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):145–149. doi: 10.1038/308145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]