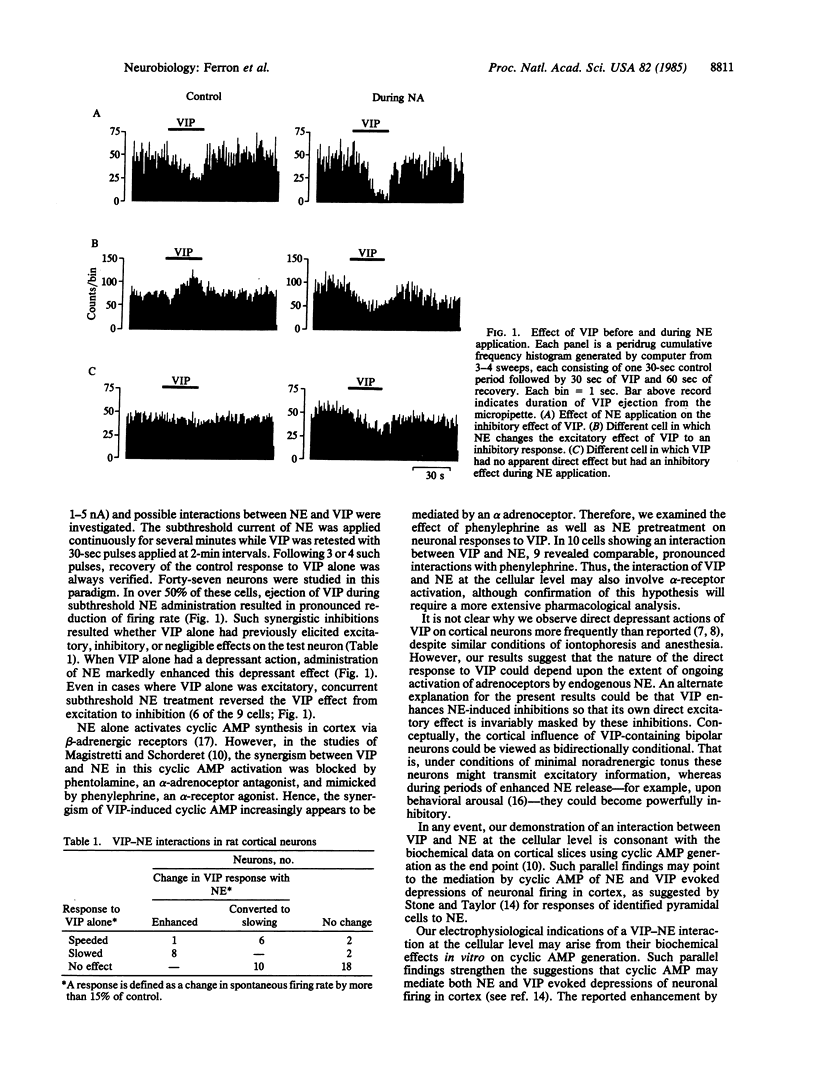
Abstract
Cortical neurons are densely innervated by noradrenergic fibers and by intrinsic cortical interneurons containing vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). Biochemically, VIP and norepinephrine (NE) synergistically interact to stimulate the synthesis of cyclic AMP in cortical slices. Therefore, we sought physiological indices of this peptide-monoamine interaction by applying VIP and NE to single cortical neurons of the rat while recording their spontaneous discharge. VIP applied alone inhibited discharge of 24% and accelerated discharge in 20% of cortical neurons. NE alone had a predominantly depressant effect on the same neurons. However, when VIP was retested during the continuous application of subthreshold currents of NE, VIP exerted predominantly depressant effects. These synergistic inhibitions resulted even in cells previously showing excitations to VIP alone. If VIP alone was depressant, subthreshold NE further enhanced the VIP depression. Subthreshold amounts of phenylephrine, an alpha-adrenoceptor agonist, also produced comparable interactions, suggesting involvement of an alpha receptor, as in the biochemical studies. These results support a peptide-monoamine interaction in cortex that could have important ramifications for neuronal integration.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dutar P., Lamour Y., Jobert A. Effets excitateurs de deux peptides sur les neurones corticaux du rat: distribution laminaire et corrélation avec les effets de l'acétylcholine. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1982 Sep 27;295(3):247–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emson P. C., Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. B., Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP): vesicular localization and potassium evoked release from rat hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1978 Mar 17;143(1):174–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90762-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. B. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in the porcine central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1445–1451. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferron A., Descarries L., Reader T. A. Altered neuronal responsiveness to biogenic amines in rat cerebral cortex after serotonin denervation or depletion. Brain Res. 1982 Jan 7;231(1):93–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. L., Bloom F. E., Aston-Jones G. Nucleus locus ceruleus: new evidence of anatomical and physiological specificity. Physiol Rev. 1983 Jul;63(3):844–914. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.3.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachetti A., Said S. I., Reynolds R. C., Koniges F. C. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in brain: localization in and release from isolated nerve terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3424–3428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Ljungdahl A., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M. Peptidergic neurones. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):515–521. doi: 10.1038/284515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein D. C., Sugden D., Weller J. L. Postsynaptic alpha-adrenergic receptors potentiate the beta-adrenergic stimulation of pineal serotonin N-acetyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorén I., Emson P. C., Fahrenkrug J., Björklund A., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat and mouse brain. Neuroscience. 1979;4(12):1953–1976. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magistretti P. J., Morrison J. H., Shoemaker W. J., Sapin V., Bloom F. E. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide induces glycogenolysis in mouse cortical slices: a possible regulatory mechanism for the local control of energy metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6535–6539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magistretti P. J., Schorderet M. VIP and noradrenaline act synergistically to increase cyclic AMP in cerebral cortex. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):280–282. doi: 10.1038/308280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Potentiation of alpha 1-adrenergic responses in rat liver by a cAMP-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4208–4212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. H., Magistretti P. J., Benoit R., Bloom F. E. The distribution and morphological characteristics of the intracortical VIP-positive cell: an immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 6;292(2):269–282. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90763-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. H., Magistretti P. J., Benoit R., Bloom F. E. The distribution and morphological characteristics of the intracortical VIP-positive cell: an immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 6;292(2):269–282. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90763-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson J. A. Cyclic nucleotides and nervous system function. Physiol Rev. 1977 Apr;57(2):157–256. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer M. R., Hoffer B. J. Catecholamine modulation of enkephalin-induced electrophysiological responses in cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 May;213(2):205–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Kirkpatrick J. R., Said S. I. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide excitation of central neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Apr;56(2):337–340. doi: 10.1139/y78-052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quik M., Iversen L. L., Bloom S. R. Effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and other peptides on cAMP accumulation in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(18):2209–2213. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Taylor D. A. Microiontophoretic studies of the effects of cylic nucleotides on excitability of neurones in the rat cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):523–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. P., Pert C. B. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: specific binding to rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):660–664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


