Abstract
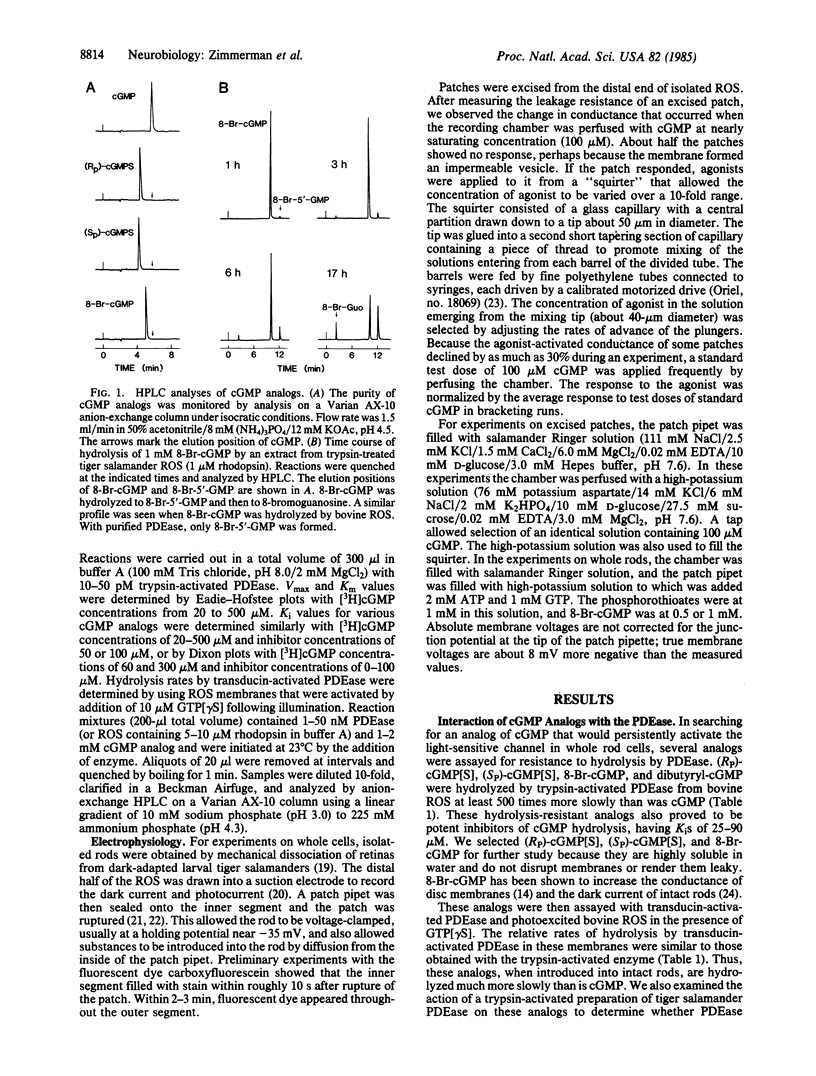
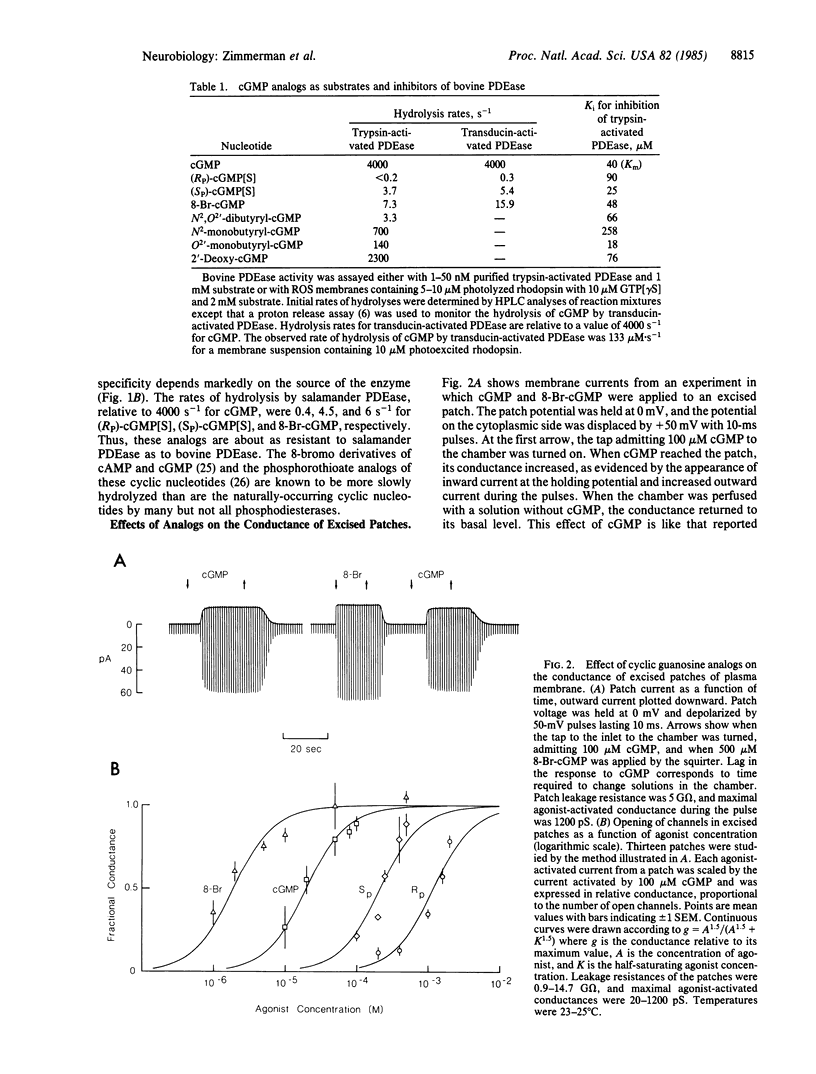
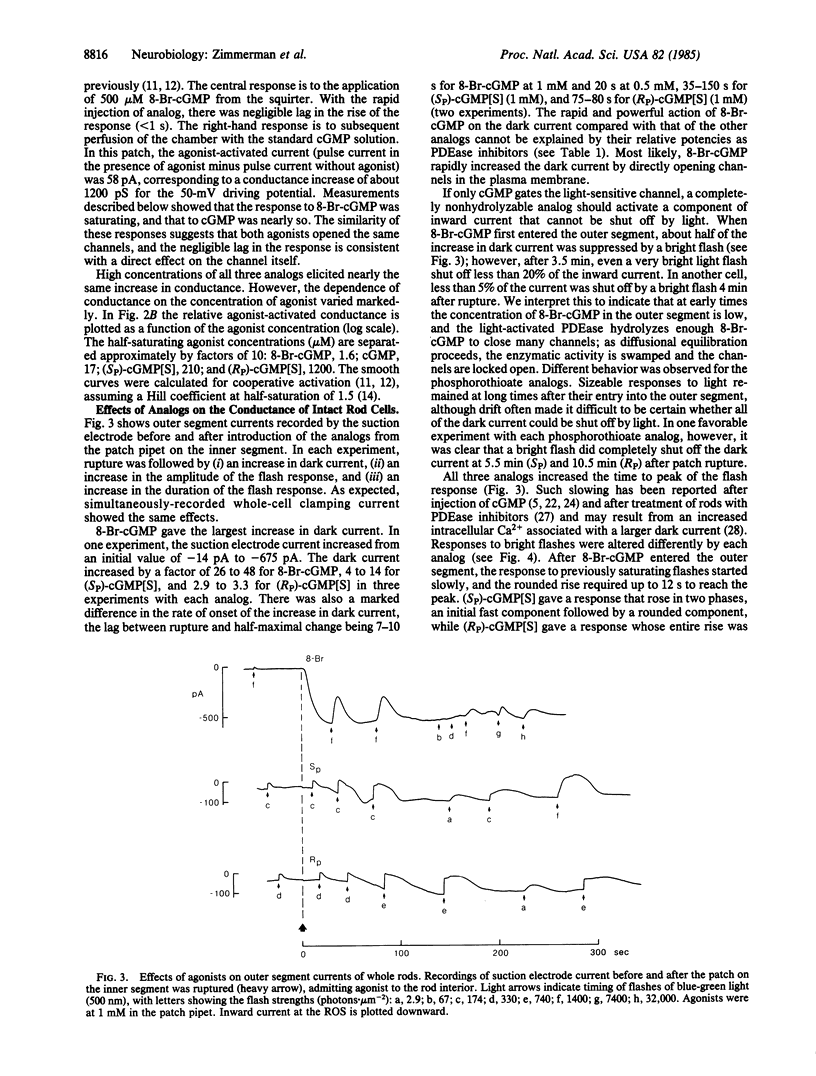
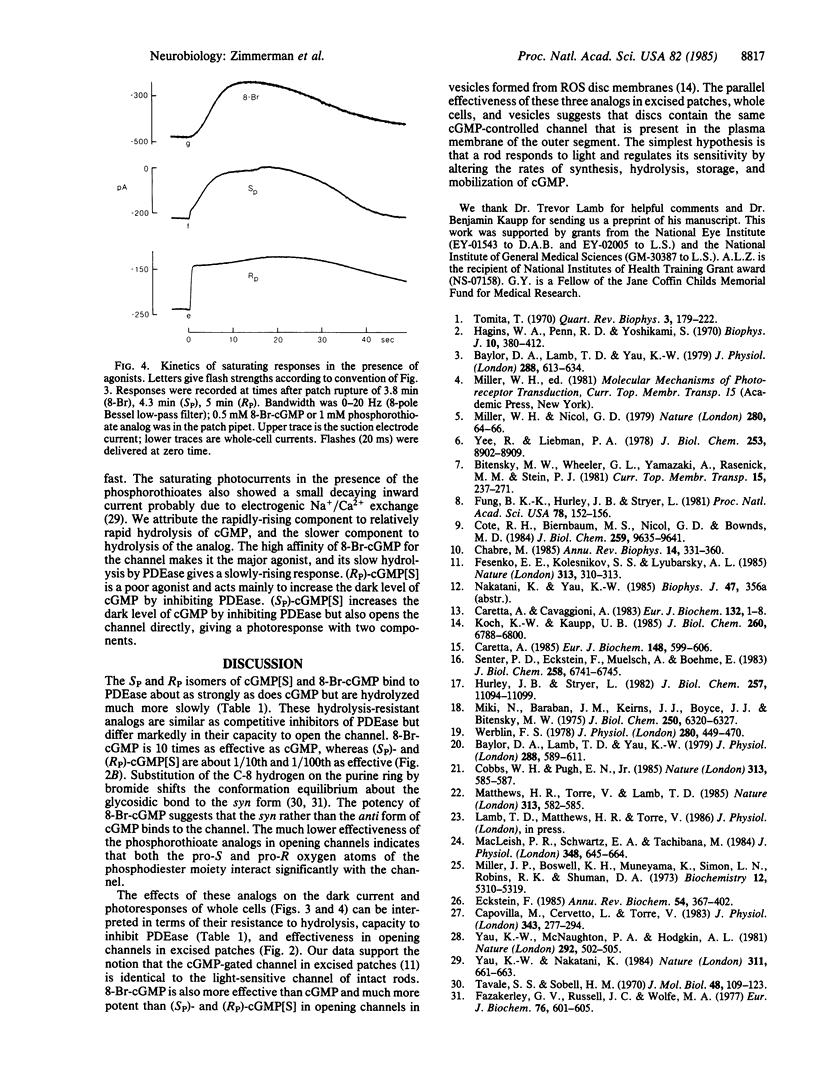
cGMP opens cation-selective channels when applied to the cytoplasmic side of excised patches of membrane from retinal rod outer segments (ROS). If the light-sensitive channel in intact rods is gated only by cGMP, it should be possible to find a hydrolysis-resistant analog of cGMP that blocks the normal response to light by holding the channel open independent of the degree of illumination. We have studied the interaction of 8-bromo-cGMP (8-Br-cGMP) and the SP and RP phosphorothioate derivatives of cGMP [(Sp)-cGMP[S] and (RP)-cGMP[S]) with the cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDEase) of ROS, the cGMP-sensitive channel of excised ROS patches, and the light-sensitive channel of intact rods. All three analogs were hydrolyzed by PDEase much more slowly than was cGMP. The maximal rates of hydrolysis of 8-Br-cGMP, (SP)-cGMP[S], and (RP)-cGMP[S] were 7.3, 3.7, and less than 0.2 s-1, respectively, compared with 4000 s-1 for cGMP. These analogs are effective competitive inhibitors of the PDEase, with Ki values of 48, 25, and 90 microM, respectively. The nucleotide-activated conductances of excised patches were half-maximal at concentrations of 1.6, 210, and 1200 microM, respectively, compared with 17 microM for cGMP. Thus, 8-Br-cGMP is a highly potent channel agonist. The effects of these analogs on the dark current and photoresponses of intact rod cells were also measured. A suction electrode monitored membrane current across the ROS, while a patch electrode sealed on the inner segment was used to introduce a cGMP analog and to control membrane potential. All three analogs increased the dark current and markedly slowed the response to light flashes. 8-Br-cGMP increased the dark current of the outer segment as much as 48-fold. After the concentration of this analog had risen sufficiently, little of the current could be shut off by light, as expected of a direct effect on the light-sensitive channel of the plasma membrane. These results are consistent with the notions that (i) the light-sensitive channel of rods is controlled solely by the instantaneous concentration of cGMP and (ii) the cGMP-sensitive channel of excised patches is identical to the light-sensitive channel of intact rods.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baylor D. A., Lamb T. D., Yau K. W. Responses of retinal rods to single photons. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:613–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Lamb T. D., Yau K. W. The membrane current of single rod outer segments. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:589–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capovilla M., Cervetto L., Torre V. The effect of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on the electrical activity of toad rods. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:277–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caretta A., Cavaggioni A. Fast ionic flux activated by cyclic GMP in the membrane of cattle rod outer segments. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;132(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caretta A. Effect of cGMP and cations on the permeability of cattle retinal disks. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):599–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabre M. Trigger and amplification mechanisms in visual phototransduction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:331–360. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbs W. H., Pugh E. N., Jr Cyclic GMP can increase rod outer-segment light-sensitive current 10-fold without delay of excitation. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):585–587. doi: 10.1038/313585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote R. H., Biernbaum M. S., Nicol G. D., Bownds M. D. Light-induced decreases in cGMP concentration precede changes in membrane permeability in frog rod photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9635–9641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley G. V., Russell J. C., Wolfe M. A. Determination of the syn-anti equilibrium of some purine 3':5'-nucleotides by nuclear-magnetic-relaxation perturbation in the presence of a lanthanide-ion probe. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 15;76(2):601–605. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko E. E., Kolesnikov S. S., Lyubarsky A. L. Induction by cyclic GMP of cationic conductance in plasma membrane of retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):310–313. doi: 10.1038/313310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Penn R. D., Yoshikami S. Dark current and photocurrent in retinal rods. Biophys J. 1970 May;10(5):380–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86308-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Purification and characterization of the gamma regulatory subunit of the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase from retinal rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11094–11099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. W., Kaupp U. B. Cyclic GMP directly regulates a cation conductance in membranes of bovine rods by a cooperative mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6788–6800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeish P. R., Schwartz E. A., Tachibana M. Control of the generator current in solitary rods of the Ambystoma tigrinum retina. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:645–664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews H. R., Torre V., Lamb T. D. Effects on the photoresponse of calcium buffers and cyclic GMP incorporated into the cytoplasm of retinal rods. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):582–585. doi: 10.1038/313582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki N., Baraban J. M., Keirns J. J., Boyce J. J., Bitensky M. W. Purification and properties of the light-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase of rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6320–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. P., Boswell K. H., Muneyama K., Simon L. N., Robins R. K., Shuman D. A. Synthesis and biochemical studies of various 8-substituted derivatives of guanosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate, inosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate, and xanthosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 18;12(26):5310–5319. doi: 10.1021/bi00750a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senter P. D., Eckstein F., Mülsch A., Böhme E. The stereochemical course of the reaction catalyzed by soluble bovine lung guanylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6741–6745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavale S. S., Sobell H. M. Crystal and molecular structure of 8-bromoguanosine and 8-bromoadenosine, two purine nucleosides in the syn conformation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):109–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S. Transmission along and between rods in the tiger salamander retina. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:449–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., McNaughton P. A., Hodgkin A. L. Effect of ions on the light-sensitive current in retinal rods. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):502–505. doi: 10.1038/292502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Electrogenic Na-Ca exchange in retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):661–663. doi: 10.1038/311661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee R., Liebman P. A. Light-activated phosphodiesterase of the rod outer segment. Kinetics and parameters of activation and deactivation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8902–8909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


