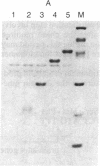
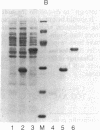
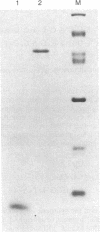
Abstract
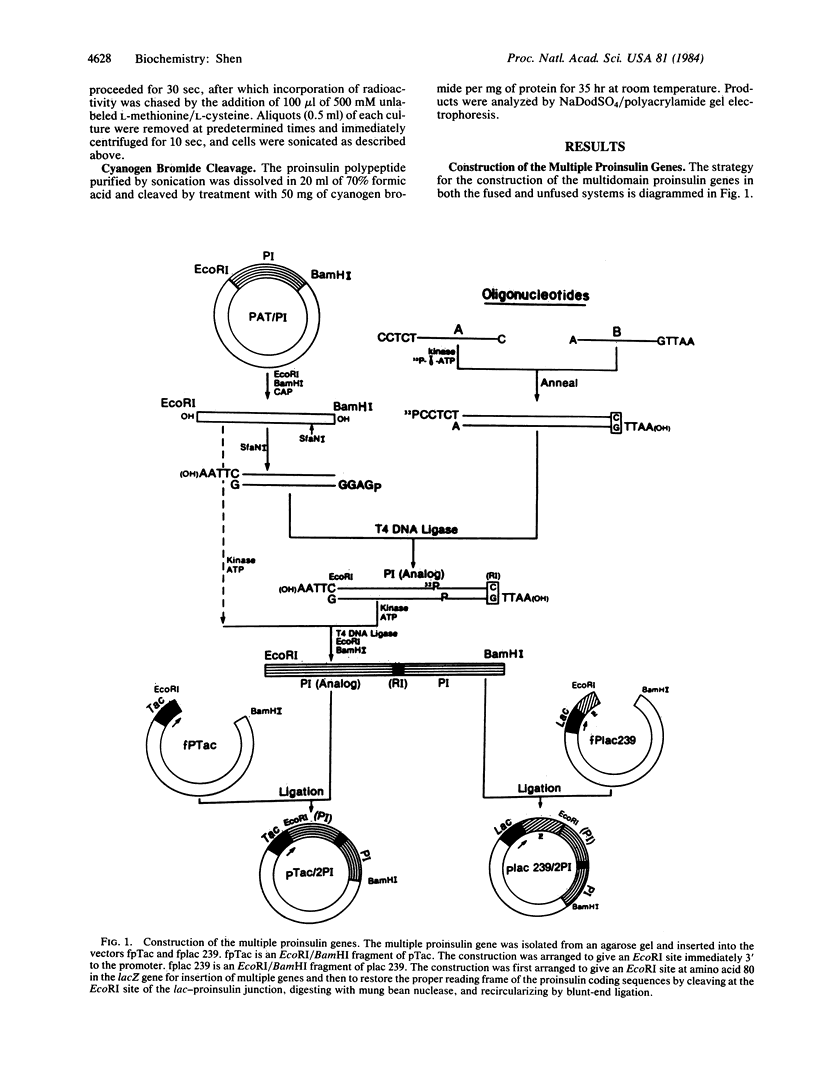
A method is described that allows the expression of a stable human proinsulin product in Escherichia coli as encoded by either a fused or an unfused gene construction. In the fused system, the human proinsulin coding sequence is joined to the 3' side of a fragment containing the lac promoter and the coding sequence for a small part of the NH2 terminus of beta-galactosidase. In the unfused system, the proinsulin coding sequence is linked directly to a fragment containing the Tac promoter followed by a bacterial Shine-Dalgarno sequence. In both systems, the human proinsulin product is too unstable to be detected by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or even pulse-chase analysis. However, when multiple copies of the proinsulin coding sequence are tandemly linked such that the resultant protein product contains multiple copies of the proinsulin domain, the stability of the product is markedly increased in both the fused and the unfused expression systems. In the unfused system, three tandemly linked proinsulin polypeptide domains are required for stabilization, whereas two proinsulin domains plus the bacterial leader protein enhance stability in the fused system. The polypeptide product of a multiple copy proinsulin gene can be cleaved into single proinsulin units by cyanogen bromide treatment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bikel I., Roberts T. M., Bladon M. T., Green R., Amann E., Livingston D. M. Purification of biologically active simian virus 40 small tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):906–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brousseau R., Scarpulla R., Sung W., Hsiung H. M., Narang S. A., Wu R. Synthesis of a human insulin gene. V. Enzymatic assembly, cloning and characterization of the human proinsulin DNA. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I., Zipser D. Mutants of Escherichia coli with a defect in the degradation of nonsense fragments. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):238–241. doi: 10.1038/newbio243238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Weiss J., Konrad M., White T., Bahl C., Yu S. D., Marks D., Steiner D. F. Biosynthesis and periplasmic segregation of human proinsulin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5401–5405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charette M. F., Henderson G. W., Markovitz A. ATP hydrolysis-dependent protease activity of the lon (capR) protein of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4728–4732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Kwoh D. Y., Kwoh T. J., Soltvedt B. C., Zipser D. Stabilization of a degradable protein by its overexpression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1981 Jun-Jul;14(1-2):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. R., Bos T., Ueda M., Nayak D. P., Dowbenko D., Compans R. W. Immune response to human influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Mar;21(3):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L., Hozumi T., Arentzen R., Itakura K., Yansura D. G., Ross M. J., Miozzari G., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. Direct expression in Escherichia coli of a DNA sequence coding for human growth hormone. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):544–548. doi: 10.1038/281544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Kleid D. G., Bolivar F., Heyneker H. L., Yansura D. G., Crea R., Hirose T., Kraszewski A., Itakura K., Riggs A. D. Expression in Escherichia coli of chemically synthesized genes for human insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):106–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt R. In vivo degradation of nonsense fragments in E. coli. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1151–1154. doi: 10.1038/2281151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Zipser D. Deg phenotype of Escherichia coli lon mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):844–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.844-851.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Hirose T., Crea R., Riggs A. D., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Boyer H. W. Expression in Escherichia coli of a chemically synthesized gene for the hormone somatostatin. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1056–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.412251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Hirose T., Crea R., Riggs A. D., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Boyer H. W. Expression in Escherichia coli of a chemically synthesized gene for the hormone somatostatin. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1056–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.412251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Zabin I. Beta-galactosidase. Rates of synthesis and degradation of incomplete chains. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2205–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt S., Zalkin H. Role of primary structure and disulfide bond formation in beta-lactamase secretion. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.27-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. Preparation of product-specific antisera by gene fusion: antibodies specific for the product of the yeast cell-division-cycle gene CDC28. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Fettes I., Lan N. C., Roberts J. L., Baxter J. D. Expression of cloned beta-endorphin gene sequences by Escherichia coli. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):456–463. doi: 10.1038/285456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K., Gilbert W. Cellular location affects protein stability in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1830–1833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Guarente L., Roberts T. M., Kimelman D., Douhan J., 3rd, Ptashne M. Expression of the human fibroblast interferon gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5230–5233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. C., Van Frank R. M., Muth W. L., Burnett J. P. Cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli producing biosynthetic human insulin proteins. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):687–689. doi: 10.1126/science.7036343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelverton E., Norton S., Obijeski J. F., Goeddel D. V. Rabies virus glycoprotein analogs: biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):614–620. doi: 10.1126/science.6297004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]